重要
此功能目前为预览版。
Azure AI 语言 是一项 Azure AI 服务 ,可用于使用自然语言处理(NLP)功能执行文本挖掘和文本分析。
本文介绍如何直接在 Microsoft Fabric 中使用 Azure AI 语言服务来分析文本。 本文结束时,可以:
- 在句子或文档级别检测情感标签
- 标识给定文本输入的语言
- 从文本中提取关键短语
- 识别文本中的不同实体并将其分类为预定义类或类型
先决条件
获取 Microsoft Fabric 订阅。 或者注册免费的 Microsoft Fabric 试用版。
登录到 Microsoft Fabric。
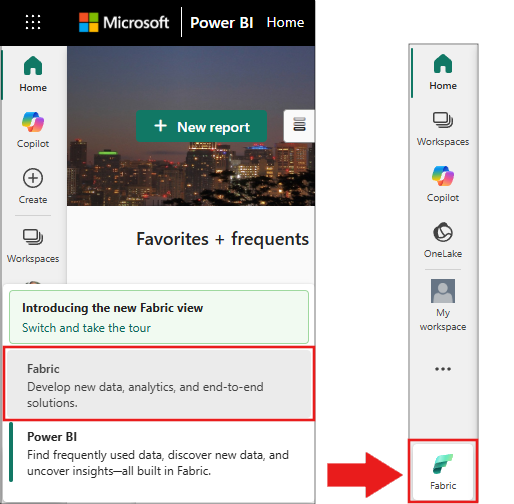
使用主页左下侧的体验切换器切换到 Fabric。
- 创建新的笔记本。
- 将笔记本附加到湖屋。 在笔记本的左侧,选择 添加 来添加已有的湖仓或创建一个新的湖仓。
注释
本文使用 Microsoft Fabric 的内置预生成 AI 服务,这些服务会自动处理身份验证。 无需获取单独的 Azure AI 服务密钥 - 身份验证是通过 Fabric 工作区管理的。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Fabric 中的预生成 AI 模型(预览版)。
本文中的代码示例使用预安装在 Microsoft Fabric 笔记本中的库:
- SynapseML:预安装在 Fabric 笔记本中,用于机器学习功能
- PySpark:默认情况下在 Fabric Spark 计算中可用
-
标准 Python 库:
json是uuidPython 标准库的一部分
注释
Microsoft Fabric 笔记本中预安装了许多常用库。 SynapseML 库在 Spark 环境中自动提供 MLflow 集成和文本分析功能。
选择你的方法
本文提供了在 Fabric 中使用 Azure AI 语言服务的两种方法:
- REST API 方法:对服务的直接 HTTP 调用(建议初学者使用)
- SynapseML 方法:使用 Spark 数据帧进行大规模处理
小窍门
新用户应从 REST API 方法开始 ,因为它更易于理解和调试。 SynapseML 方法更适用于使用 Spark 处理大型数据集。
设置身份验证和终结点
将此代码复制并粘贴到 Fabric 笔记本的第一个单元中,以设置与 Azure AI 语言服务的连接:
注释
此代码使用 Fabric 的内置身份验证。 该 get_fabric_env_config 函数会自动检索工作区凭据并连接到预生成的 AI 服务。 不需要 API 密钥。
# Get workload endpoints and access token
from synapse.ml.fabric.service_discovery import get_fabric_env_config
from synapse.ml.fabric.token_utils import TokenUtils
import json
import requests
fabric_env_config = get_fabric_env_config().fabric_env_config
auth_header = TokenUtils().get_openai_auth_header()
# Make a RESful request to AI service
prebuilt_AI_base_host = fabric_env_config.ml_workload_endpoint + "cognitive/textanalytics/"
print("Workload endpoint for AI service: \n" + prebuilt_AI_base_host)
service_url = prebuilt_AI_base_host + "language/:analyze-text?api-version=2022-05-01"
print("Service URL: \n" + service_url)
auth_headers = {
"Authorization" : auth_header
}
def print_response(response):
if response.status_code == 200:
print(json.dumps(response.json(), indent=2))
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}, {response.content}")
情绪分析
情绪分析功能提供了一种检测情绪标签(如“负”、“中性”和“积极”)和句子和文档级别的置信度分数的方法。 此功能还会为每个文档及其中的句子返回介于0和1之间的置信度分数,用于评估积极、中立和负面情绪。 请参阅 情绪分析和观点挖掘语言支持,以获取启用的语言列表。
分析文本情绪
将此代码复制到笔记本中的新单元格中,以分析示例文本的情绪:
payload = {
"kind": "SentimentAnalysis",
"parameters": {
"modelVersion": "latest",
"opinionMining": "True"
},
"analysisInput":{
"documents":[
{
"id":"1",
"language":"en",
"text": "The food and service were unacceptable. The concierge was nice, however."
}
]
}
}
response = requests.post(service_url, json=payload, headers=auth_headers)
# Output all information of the request process
print_response(response)
小窍门
可以将“text”字段中的文本替换为要分析的内容。 服务返回情绪分数,并标识文本的哪些部分为正、负或中性。
预期输出
成功运行以下代码时,应会看到如下所示的输出:
{
"kind": "SentimentAnalysisResults",
"results": {
"documents": [
{
"id": "1",
"sentiment": "negative",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.0,
"neutral": 0.0,
"negative": 1.0
},
"sentences": [
{
"sentiment": "negative",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.0,
"neutral": 0.0,
"negative": 1.0
},
"offset": 0,
"length": 40,
"text": "The food and service were unacceptable. ",
"targets": [
{
"sentiment": "negative",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.01,
"negative": 0.99
},
"offset": 4,
"length": 4,
"text": "food",
"relations": [
{
"relationType": "assessment",
"ref": "#/documents/0/sentences/0/assessments/0"
}
]
},
{
"sentiment": "negative",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.01,
"negative": 0.99
},
"offset": 13,
"length": 7,
"text": "service",
"relations": [
{
"relationType": "assessment",
"ref": "#/documents/0/sentences/0/assessments/0"
}
]
}
],
"assessments": [
{
"sentiment": "negative",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.01,
"negative": 0.99
},
"offset": 26,
"length": 12,
"text": "unacceptable",
"isNegated": false
}
]
},
{
"sentiment": "neutral",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 0.22,
"neutral": 0.75,
"negative": 0.04
},
"offset": 40,
"length": 32,
"text": "The concierge was nice, however.",
"targets": [
{
"sentiment": "positive",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 1.0,
"negative": 0.0
},
"offset": 44,
"length": 9,
"text": "concierge",
"relations": [
{
"relationType": "assessment",
"ref": "#/documents/0/sentences/1/assessments/0"
}
]
}
],
"assessments": [
{
"sentiment": "positive",
"confidenceScores": {
"positive": 1.0,
"negative": 0.0
},
"offset": 58,
"length": 4,
"text": "nice",
"isNegated": false
}
]
}
],
"warnings": []
}
],
"errors": [],
"modelVersion": "2025-01-01"
}
}
语言检测器
语言检测器评估每个文档的文本输入,并返回具有指示分析强度的分数的语言标识符。 此功能对于收集任意文本的内容存储非常有用,其中语言未知。 请参阅语言检测支持的语言以获取支持的语言列表。
payload = {
"kind": "LanguageDetection",
"parameters": {
"modelVersion": "latest"
},
"analysisInput":{
"documents":[
{
"id":"1",
"text": "This is a document written in English."
}
]
}
}
response = requests.post(service_url, json=payload, headers=auth_headers)
# Output all information of the request process
print_response(response)
输出
{
"kind": "LanguageDetectionResults",
"results": {
"documents": [
{
"id": "1",
"warnings": [],
"detectedLanguage": {
"name": "English",
"iso6391Name": "en",
"confidenceScore": 0.95
}
}
],
"errors": [],
"modelVersion": "2024-11-01"
}
}
关键短语提取程序
关键短语提取计算非结构化文本并返回关键短语的列表。 如果需要快速识别文档集合中的要点,此功能非常有用。 请参阅关键短语提取支持的语言以获取支持的语言列表。
payload = {
"kind": "KeyPhraseExtraction",
"parameters": {
"modelVersion": "latest"
},
"analysisInput":{
"documents":[
{
"id":"1",
"language":"en",
"text": "Dr. Smith has a very modern medical office, and she has great staff."
}
]
}
}
response = requests.post(service_url, json=payload, headers=auth_headers)
# Output all information of the request process
print_response(response)
输出
{
"kind": "KeyPhraseExtractionResults",
"results": {
"documents": [
{
"id": "1",
"keyPhrases": [
"modern medical office",
"Dr. Smith",
"great staff"
],
"warnings": []
}
],
"errors": [],
"modelVersion": "2022-10-01"
}
}
命名实体识别 (NER)
命名实体识别(NER)能够识别文本中的不同实体,并将其分类为预定义类或类型,例如:人员、位置、事件、产品和组织。 有关已启用的语言列表,请参阅 NER 语言支持。
payload = {
"kind": "EntityRecognition",
"parameters": {
"modelVersion": "latest"
},
"analysisInput":{
"documents":[
{
"id":"1",
"language": "en",
"text": "I had a wonderful trip to Seattle last week."
}
]
}
}
response = requests.post(service_url, json=payload, headers=auth_headers)
# Output all information of the request process
print_response(response)
输出
{
"kind": "EntityRecognitionResults",
"results": {
"documents": [
{
"id": "1",
"entities": [
{
"text": "trip",
"category": "Event",
"offset": 18,
"length": 4,
"confidenceScore": 0.66
},
{
"text": "Seattle",
"category": "Location",
"subcategory": "City",
"offset": 26,
"length": 7,
"confidenceScore": 1.0
},
{
"text": "last week",
"category": "DateTime",
"subcategory": "DateRange",
"offset": 34,
"length": 9,
"confidenceScore": 1.0
}
],
"warnings": []
}
],
"errors": [],
"modelVersion": "2025-02-01"
}
}
实体链接
相关内容
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的文本分析与 SynapseML 结合使用
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的 Azure AI 翻译与 REST API 结合使用
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的 Azure AI 翻译与 SynapseML 结合使用
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的 Azure OpenAI 与 REST API 结合使用
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的 Azure OpenAI 与 Python SDK 结合使用
- 将 Fabric 中预生成的 Azure OpenAI 与 SynapseML 结合使用
- SynapseML GitHub 存储库 - SynapseML 的源代码和文档
- Azure AI 语言文档 - Azure AI 语言服务的完整参考