Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article outlines how to use the copy activity in a pipeline to copy data from and to the Fabric Lakehouse. By default, data is written to Lakehouse Table in V-Order, and you can go to Delta Lake table optimization and V-Order for more information.
This connector supports Lakehouse in the workspace with a private link enabled. For more information on configuration, see Set up and use private links.
To support workspace-level private link in the on-premises data gateway (version 3000.286.12 or above), you need to add *.dfs.fabric.microsoft.com to the allowlist to ensure Lakehouse connector can access Onelake APIs through the network.
Supported format
Lakehouse supports the following file formats. Refer to each article for format-based settings.
- Avro format
- Binary format
- Delimited text format
- Excel format
- JSON format
- ORC format
- Parquet format
- XML format
Supported configuration
For the configuration of each tab under copy activity, go to the following sections respectively.
General
For the General tab configuration, go to General.
Source
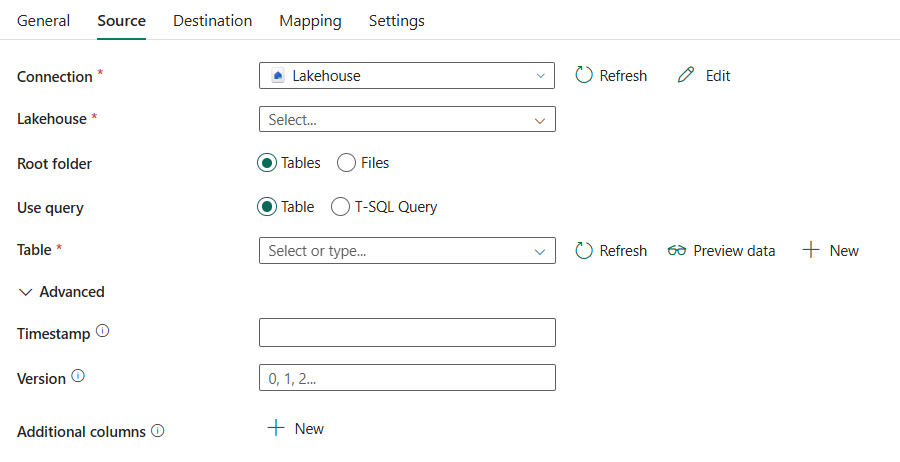
The following properties are supported for Lakehouse under the Source tab of a copy activity.
The following properties are required:
Connection: Select a Lakehouse connection from the connection list. If no connection exists, then create a new Lakehouse connection. If you apply Use dynamic content to specify your Lakehouse, add a parameter and specify the Lakehouse object ID as the parameter value. To get your Lakehouse object ID, open your Lakehouse in your workspace, and the ID is after
/lakehouses/in your URL.
Lakehouse: Select an existing Lakehouse that you want to use.
Root folder: Select Tables or Files, which indicates the virtual view of the managed or unmanaged area in your lake. For more information, refer to Lakehouse introduction.
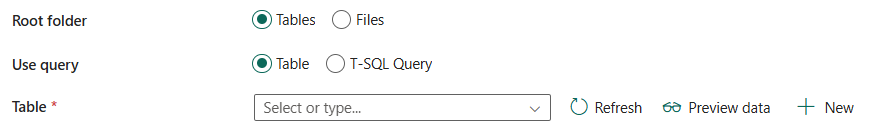
If you select Tables:
- Use query: Select from Table or T-SQL Query.
If you select Table:
Table: Choose an existing table from the table list or specify a table name as the source. Or you can select New to create a new table.
When you apply Lakehouse with schemas in the connection, choose an existing table with a schema from the table list or specify a table with a schema as the source. Or you can select New to create a new table with a schema. If you don't specify a schema name, the service will use dbo as the default schema.
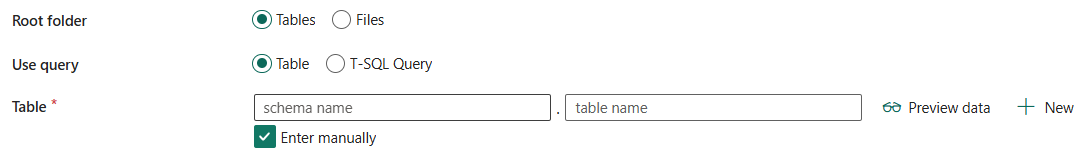
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
- Timestamp: Specify to query an older snapshot by timestamp.
- Version: Specify to query an older snapshot by version.
- Additional columns: Add additional data columns to the store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter.
If you select T-SQL Query:
T-SQL Query: Specify the custom SQL query to read data through the Lakehouse SQL analytics endpoint. For example:
SELECT * FROM MyTable. Note that Lakehouse table query mode does not support workspace-level private links.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
Query timeout (minutes): Specify the timeout for query command execution, default is 120 minutes.
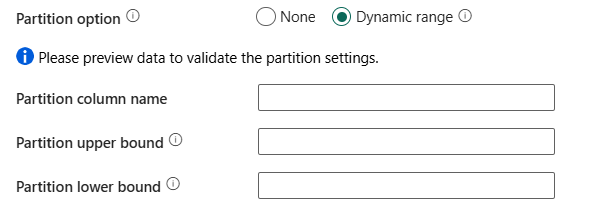
Partition option: Specifies the data partitioning options used to load data from Lakehouse table query mode. You can select None (default) or Dynamic range.
If you select None, you choose not to use partition.
If you select Dynamic range, when using query with parallel enabled, range partition parameter(
?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) is needed. Sample query:SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition.Partition column name: Specify the name of the source column in integer type that's used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the index or the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?DfDynamicRangePartitionConditionin the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query section.Partition upper bound: Specify the maximum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query section.
Partition lower bound: Specify the minimum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query section.
Additional columns: Add additional data columns to the store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter.
- Use query: Select from Table or T-SQL Query.
If you select Files:
File path type: You can choose File path, Wildcard file path, or List of files as your file path type. The following list describes the configuration of each setting:
File path: Select Browse to choose the file that you want to copy, or fill in the path manually.
Wildcard file path: Specify the folder or file path with wildcard characters under your given Lakehouse unmanaged area (under Files) to filter your source folders or files. Allowed wildcards are:
*(matches zero or more characters) and?(matches zero or single character). Use^to escape if your folder or file name has wildcard or this escape character inside.Wildcard folder path: The path to the folder under the given container. If you want to use a wildcard to filter the folder, skip this setting and specify that information in the activity source settings.
Wildcard file name: The file name under the given Lakehouse unmanaged area (under Files) and folder path.
List of files: Indicates to copy a given file set.
- Folder path: Points to a folder that includes files you want to copy.
- Path to file list: Points to a text file that includes a list of files you want to copy, one file per line, which is the relative path to the file path configured.
Recursively: Indicates whether the data is read recursively from the subfolders or only from the specified folder. If enabled, all files in the input folder and its subfolders are processed recursively. This property doesn't apply when you configure your file path type as List of files.
File format: Select your file format from the drop-down list. Select the Settings button to configure the file format. For settings of different file formats, refer to articles in Supported format for detailed information.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
- Filter by last modified: Files are filtered based on the last modified dates. This property doesn't apply when you configure your file path type as List of files.
- Start time: The files are selected if their last modified time is greater than or equal to the configured time.
- End time: The files are selected if their last modified time is less than the configured time.
- Enable partition discovery: For files that are partitioned, specify whether to parse the partitions from the file path and add them as extra source columns.
- Partition root path: When partition discovery is enabled, specify the absolute root path in order to read partitioned folders as data columns.
- Max concurrent connections: Indicates the upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections.
- Filter by last modified: Files are filtered based on the last modified dates. This property doesn't apply when you configure your file path type as List of files.
Destination
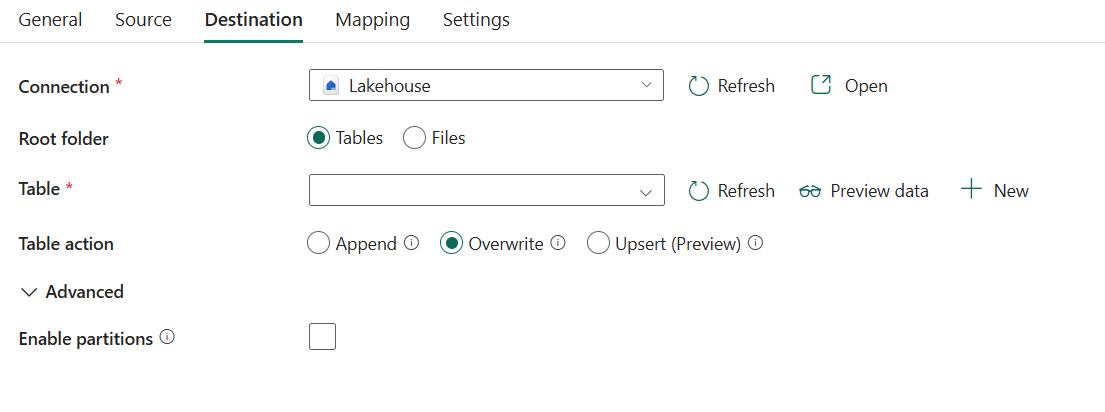
The following properties are supported for Lakehouse under the Destination tab of a copy activity.
The following properties are required:
Connection: Select a Lakehouse connection from the connection list. If no connection exists, then create a new Lakehouse connection. If you apply Use dynamic content to specify your Lakehouse, add a parameter and specify the Lakehouse object ID as the parameter value. To get your Lakehouse object ID, open your Lakehouse in your workspace, and the ID is after
/lakehouses/in your URL.
Root folder: Select Tables or Files, which indicates the virtual view of the managed or unmanaged area in your lake. For more information, refer to Lakehouse introduction.
If you select Tables:
Table: Choose an existing table from the table list or specify a table name as the destination. Or you can select New to create a new table.

When you apply Lakehouse with schemas in the connection, choose an existing table with a schema from the table list or specify a table with a schema as the destination. Or you can select New to create a new table with a schema. If you don't specify a schema name, the service will use dbo as the default schema.
Note
The table name must be at least one character long, without '/' or '\', no trailing dot, and no leading or trailing spaces.
Table actions: Specify the operation against the selected table.
Append: Append new values to existing table. Under Advanced, you can enable partition on your target table:
- Enable Partition: This selection allows you to create partitions in a folder structure based on one or multiple columns. Each distinct column value (pair) is a new partition. For example, "year=2000/month=01/file".
- Partition column name: Select from the destination columns in schemas mapping when you append data to a new table. When you append data to an existing table that already has partitions, the partition columns are derived from the existing table automatically. Supported data types are string, integer, boolean, and datetime. Format respects type conversion settings under the Mapping tab.
- Enable Partition: This selection allows you to create partitions in a folder structure based on one or multiple columns. Each distinct column value (pair) is a new partition. For example, "year=2000/month=01/file".
Overwrite: Overwrite the existing data and schema in the table using the new values. Under Advanced, you can enable partition on your target table:
- Enable Partition: This selection allows you to create partitions in a folder structure based on one or multiple columns. Each distinct column value (pair) is a new partition. For example, "year=2000/month=01/file".
- Partition column name: Select from the destination columns in schemas mapping. Supported data types are string, integer, boolean, and datetime. Format respects type conversion settings under the Mapping tab.
It supports Delta Lake time travel. The overwritten table has delta logs for the previous versions, which you can access in your Lakehouse. You can also copy the previous version table from Lakehouse, by specifying Version in the copy activity source.
- Enable Partition: This selection allows you to create partitions in a folder structure based on one or multiple columns. Each distinct column value (pair) is a new partition. For example, "year=2000/month=01/file".
Upsert (Preview): Insert new values to existing table and update existing values. Upsert is not supported when using partitioned Lakehouse tables. Partition cannot be enabled while this action is selected.
- Key columns: Choose which column is used to determine if a row from the source matches a row from the destination. A drop-down listing all destination columns. You can select one or more columns to be treated as key columns while writing into Lakehouse Table.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
- Apply V-Order: Specify to apply V-Order via copy. Disabling it preserves the original parquet files without applying additional V-Order optimization. For more information, see Delta Lake table optimization and V-Order.
If you select Files:
File path: Select Browse to choose the file that you want to copy, or fill in the path manually.
File format: Select your file format from the drop-down list. Select Settings to configure the file format. For settings of different file formats, refer to articles in Supported format for detailed information.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
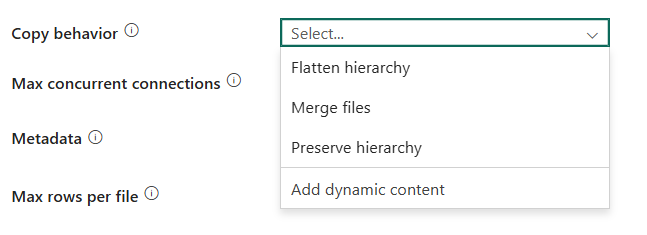
Copy behavior: Defines the copy behavior when the source is files from a file-based data store. You can choose Flatten hierarchy, Merge files, Preserve hierarchy, or Add Dynamic content as your copy behavior. The configuration of each setting is:
Flatten hierarchy: All files from the source folder are in the first level of the destination folder. The destination files have autogenerated names.
Merge files: Merges all files from the source folder to one file. If the file name is specified, the merged file name is the specified name. Otherwise, it's an auto-generated file name.
Preserve hierarchy: Preserves the file hierarchy in the target folder. The relative path of a source file to the source folder is identical to the relative path of a target file to the target folder.
Add dynamic content: To specify an expression for a property value, select Add dynamic content. This field opens the expression builder where you can build expressions from supported system variables, activity output, functions, and user-specified variables or parameters. For more information about the expression language, go to Expressions and functions.
Max concurrent connections: The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections.
Block size (MB): Specify the block size in MB when writing data to Lakehouse. Allowed value is between 4 MB and 100 MB.
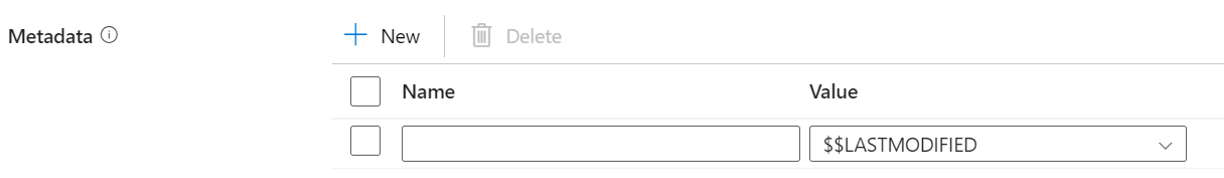
Metadata: Set custom metadata when copying to the destination data store. Each object under the
metadataarray represents an extra column. Thenamedefines the metadata key name, and thevalueindicates the data value of that key. If preserve attributes feature is used, the specified metadata will union/overwrite with the source file metadata. The allowed data values are:
Mapping
For the Mapping tab configuration, if you don't apply Lakehouse table as your destination data store, go to Mapping.
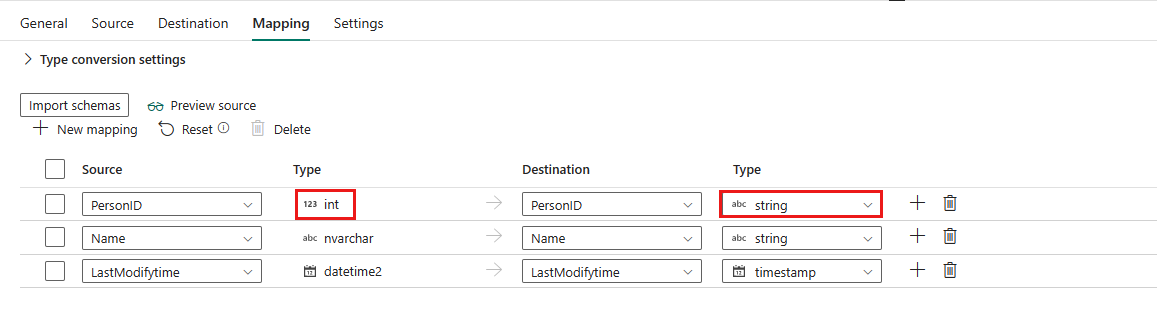
If you apply Lakehouse table as your destination data store, except the configuration in Mapping, you can edit the type for your destination columns. After selecting Import schemas, you can specify the column type in your destination.
For example, the type for PersonID column in source is int, and you can change it to string type when mapping to destination column.
Note
Editing the destination type currently is not supported when your source is decimal type.
If you choose Binary as your file format, mapping isn't supported.
Settings
For the Settings tab configuration, go to Settings.
Lakehouse tables data type mapping
The following sections describe data type mappings when copying data from Lakehouse tables. Refer to the subsection corresponding to your source mode for details.
Table
When copying data from Lakehouse tables in Table mode, the following mappings are used from Lakehouse table data types to interim data types used by the service internally.
| Lakehouse table data type | Interim service data type |
|---|---|
| string | String |
| long | Int64 |
| integer | Int32 |
| short | Int16 |
| byte | SByte |
| float | Single |
| double | Double |
| decimal | Decimal |
| boolean | Boolean |
| binary | Byte array |
| date | Date |
| timestamp | DateTime |
When copying data to Lakehouse tables in Table mode, the following mappings are used from interim data types used by the service internally to supported delta destination data types.
| Interim service data type | Supported delta destination type |
|---|---|
| Boolean | boolean |
| SByte | byte |
| Byte | short |
| Int16 | short |
| UInt16 | integer |
| Int32 | integer |
| UInt32 | long |
| Int64 | long |
| UInt64 | decimal (20,0) |
| Single | float |
| Double | double |
| GUID | string |
| Date | date |
| TimeSpan | Not supported |
| DateTime | timestamp |
| DateTimeOffset | timestamp |
| String | string |
| Byte array | binary |
| Decimal | decimal |
T-SQL Query
When copying data from Lakehouse tables in T-SQL Query mode, the following mappings are used from Lakehouse table data types to interim data types used by the service internally.
| Lakehouse table data type in T-SQL Query mode | Interim service data type |
|---|---|
| int | Int32 |
| varchar | String |
| bigint | Int64 |
| smallint | Int16 |
| real | Single |
| float | Double |
| decimal | Decimal |
| bit | Boolean |
| varbinary | Byte[] |
| date | Date |
| datetime2 | DateTime |
Parallel copy from Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query
The Lakehouse tables connector using T-SQL Query in copy activity provides built-in data partitioning to copy data in parallel. You can find data partitioning options on the Source tab of the copy activity.
When you enable partitioned copy, copy activity runs parallel queries against your Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query source to load data by partitions. The parallel degree is controlled by the Degree of copy parallelism in the copy activity settings tab. For example, if you set Degree of copy parallelism to four, the service concurrently generates and runs four queries based on your specified partition option and settings, and each query retrieves a portion of data from your Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query.
You are suggested to enable parallel copy with data partitioning especially when you load large amount of data from your Lakehouse tables using T-SQL Query. The following are suggested configurations for different scenarios. When copying data into file-based data store, it's recommended to write to a folder as multiple files (only specify folder name), in which case the performance is better than writing to a single file.
| Scenario | Suggested settings |
|---|---|
| Full load from large table, without physical partitions, while with an integer or datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Partition column (optional): Specify the column used to partition data. If not specified, the index or primary key column is used. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the table will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detects the values and it can take long time depending on MIN and MAX values. It is recommended to provide upper bound and lower bound. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions - IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, without physical partitions, while with an integer or date/datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Query: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions- IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. Here are more sample queries for different scenarios: • Query the whole table: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition• Query from a table with column selection and additional where-clause filters: SELECT <column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Query with subqueries: SELECT <column_list> FROM (<your_sub_query>) AS T WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Query with partition in subquery: SELECT <column_list> FROM (SELECT <your_sub_query_column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) AS T |
Delta Lake table support
In the sections below, you will find detailed information on Delta Lake table support for both the source and destination.
Source
Delta column mapping is supported when you apply reader version 2 or reader version 3 with columnMapping in readerFeatures in your Lakehouse table.
Delta table's column mapping capability allows for more flexible schema evolution, ensuring that changes in table structure do not disrupt data workflows. With column mapping, you can read data from an existing delta Lake table with delta.columnMapping.mode set to name or id.
Deletion vectors is supported
when you apply reader version 3 with deletionVectors in readerFeatures in your Lakehouse table. Rows that are soft deleted are marked in deletion vector files and skipped when reading the delta lake table.
Change Data Feed is supported.
Destination
Delta column mapping is supported. This capability allows for more flexible schema evolution, ensuring that changes in table structure do not disrupt data workflows. With column mapping, you can:
- Write data to an existing delta lake table with
delta.columnMapping.modeset toname. - Auto-create a table with
delta.columnMapping.modeset tonamewhen the destination table does not exist and the source columns include special characters and whitespaces. - Auto-create a table with
delta.columnMapping.modeset tonamewhen the table action is overwrite and the source dataset columns include special characters and whitespaces.
Deletion vectors is supported.
Change Data Feed is supported.
Table summary
The following tables contain more information about a copy activity in Lakehouse.
Source information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | The section to select your connection. | < your Lakehouse connection> | Yes | workspaceId itemId |
| Root folder | The type of the root folder. | • Tables • Files |
No | rootFolder: Tables or Files |
| Use query | The way to read data from Lakehouse. Apply Table to read data from the specified table or apply T-SQL Query to read data using query. | • Table • T-SQL Query |
Yes | / |
| Table | The name of the table that you want to read data, or the name of the table with a schema that you want to read data when you apply Lakehouse with schemas as the connection. | <your table name> | Yes when you select Tables in Root folder | table |
| schema name | Name of the schema. | < your schema name > | No | schema |
| table name | Name of the table. | < your table name > | No | table |
| T-SQL Query | Use the custom query to read data. An example is SELECT * FROM MyTable. |
< query > | No | sqlReaderQuery |
| Timestamp | The timestamp to query an older snapshot. | <timestamp> | No | timestampAsOf |
| Version | The version to query an older snapshot. | <version> | No | versionAsOf |
| Query timeout (minutes) | The timeout for query command execution, default is 120 minutes. | timespan | No | queryTimeout |
| Partition option | The data partitioning options used to load data from Lakehouse table query mode. | • None • Dynamic range |
No | partitionOption |
| Partition column name | The name of the source column in integer type that will be used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column. | <partition column name> | No | partitionColumnName |
| Partition upper bound | The maximum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. | <partition upper bound> | No | partitionUpperBound |
| Partition lower bound | The minimum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. | <partition lower bound> | No | partitionLowerBound |
| Additional columns | Additional data columns to store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter. | • Name • Value |
No | additionalColumns: • name • value |
| File path type | The type of the file path that you use. | • File path • Wildcard file path • List of files |
Yes when you select Files in Root folder | / |
| File path | Copy from the path to a folder/file under source data store. | <file path> | Yes when choosing File path | • folderPath • fileName |
| Wildcard paths | The folder path with wildcard characters under the source data store configured to filter source folders. | <wildcard paths> | Yes when choosing Wildcard file path | • wildcardFolderPath • wildcardFileName |
| Folder path | Points to a folder that includes files you want to copy. | <folder path> | No | folderPath |
| Path to file list | Indicates to copy a given file set. Point to a text file that includes a list of files you want to copy, one file per line, which is the relative path to the path configured. | <path to file list> | No | fileListPath |
| Recursively | Process all files in the input folder and its subfolders recursively or just the ones in the selected folder. This setting is disabled when a single file is selected. | select or unselect | No | recursive: true or false |
| File format | The file format for your source data. For the information of different file formats, refer to articles in Supported format for detailed information. | / | Yes when you select Files in Root folder | / |
| Filter by last modified | The files with last modified time in the range [Start time, End time) will be filtered for further processing. The time is applied to UTC time zone in the format of yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss.fffZ.This property can be skipped which means no file attribute filter is applied. This property doesn't apply when you configure your file path type as List of files. |
• Start time • End time |
No | modifiedDatetimeStart modifiedDatetimeEnd |
| Enable partition discovery | Whether to parse the partitions from the file path and add them as extra source columns. | Selected or unselected | No | enablePartitionDiscovery: true or false (default) |
| Partition root path | The absolute partition root path to read partitioned folders as data columns. | <your partition root path> | No | partitionRootPath |
| Max concurrent connections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. A value is needed only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | <max concurrent connections> | No | maxConcurrentConnections |
Destination information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | The section to select your connection. | < your Lakehouse connection> | Yes | workspaceId itemId |
| Root folder | The type of the root folder. | • Tables • Files |
Yes | rootFolder: Table or Files |
| Table | The name of the table that you want to write data to. Or the name of the table with a schema that you want to write data to when you apply Lakehouse with schemas as the connection. | <your table name> | Yes when you select Tables in Root folder | table |
| schema name | The name of the schema. | <your schema name> (the default is dbo) |
No | schema |
| table name | The name of the table. | <your table name> | Yes | table |
| Table action | Append new values to an existing table, overwrite the existing data and schema in the table using the new values or insert new values to existing table and update existing values. | • Append • Overwrite • Upsert |
No | tableActionOption: • Append • OverwriteSchema • Upsert |
| Apply V-Order | Apply V-Order via copy. Disabling it preserves the original parquet files without applying additional V-Order optimization. For more information, see Delta Lake table optimization and V-Order. | Selected (default) or unselected | No | applyVOrder |
| Enable partitions | This selection allows you to create partitions in a folder structure based on one or multiple columns. Each distinct column value (pair) is a new partition. For example, "year=2000/month=01/file". | Selected or unselected | No | partitionOption: PartitionByKey or None |
| Partition columns | The destination columns in schemas mapping. | <your partition columns> | No | partitionNameList |
| Key columns | Choose which column is used to determine if a row from the source matches a row from the destination. | <your key columns> | Yes | keyColumns |
| File path | Write data to the path to a folder/file under destination data store. | <file path> | No | • folderPath • fileName |
| File format | The file format for your destination data. For the information of different file formats, refer to articles in Supported format for detailed information. | / | Yes when you select Files in Root folder | / |
| Copy behavior | The copy behavior defined when the source is files from a file-based data store. | • Flatten hierarchy • Merge files • Preserve hierarchy • Add dynamic content |
No | copyBehavior: • FlattenHierarchy • MergeFiles • PreserveHierarchy |
| Max concurrent connections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | <max concurrent connections> | No | maxConcurrentConnections |
| Block size (MB) | The block size in MB used to write data to Lakehouse. Allowed value is between 4 MB and 100 MB. | <block size> | No | blockSizeInMB |
| Metadata | The custom metadata set when copying to a destination. | • $$LASTMODIFIED• Expression • Static value |
No | metadata |