Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this quickstart, you deploy a basic Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB application using Python. Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB is a schemaless data store allowing applications to store unstructured documents in the cloud with MongoDB libraries. You learn how to create documents and perform basic tasks within your Azure Cosmos DB resource using Python.
Library source code | Package (PyPI) | Azure Developer CLI
Prerequisites
- Azure Developer CLI
- Docker Desktop
- Python 3.12
If you don't have an Azure account, create a free account before you begin.
Initialize the project
Use the Azure Developer CLI (azd) to create an Azure Cosmos DB for Table account and deploy a containerized sample application. The sample application uses the client library to manage, create, read, and query sample data.
Open a terminal in an empty directory.
If you're not already authenticated, authenticate to the Azure Developer CLI using
azd auth login. Follow the steps specified by the tool to authenticate to the CLI using your preferred Azure credentials.azd auth loginUse
azd initto initialize the project.azd init --template cosmos-db-mongodb-python-quickstartDuring initialization, configure a unique environment name.
Deploy the Azure Cosmos DB account using
azd up. The Bicep templates also deploy a sample web application.azd upDuring the provisioning process, select your subscription, desired location, and target resource group. Wait for the provisioning process to complete. The process can take approximately five minutes.
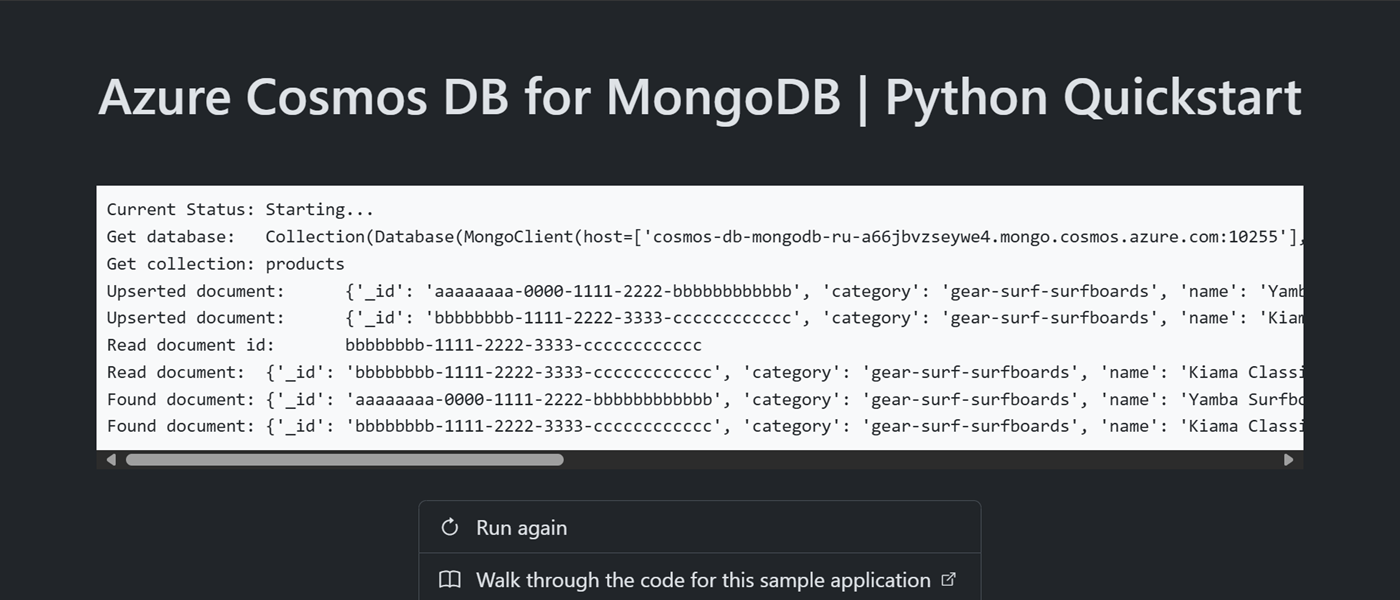
Once the provisioning of your Azure resources is done, a URL to the running web application is included in the output.
Deploying services (azd deploy) (✓) Done: Deploying service web - Endpoint: <https://[container-app-sub-domain].azurecontainerapps.io> SUCCESS: Your application was provisioned and deployed to Azure in 5 minutes 0 seconds.Use the URL in the console to navigate to your web application in the browser. Observe the output of the running app.
Install the client library
The client library is available through PyPi, as the pymongo package.
Open a terminal and navigate to the
/srcfolder.cd ./srcIf not already installed, install the
pymongopackage usingpip install.pip install pymongoOpen and review the src/requirements.txt file to validate that the
pymongoentry exists.
Import libraries
Import the MongoClient type into your application code.
from pymongo import MongoClient
Object model
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
MongoClient |
Type used to connect to MongoDB. |
Database |
Represents a database in the account. |
Collection |
Represents a collection within a database in the account. |
Code examples
- Authenticate the client
- Get a database
- Get a collection
- Create a document
- Get a document
- Query documents
The sample code in the template uses a database named cosmicworks and collection named products. The products collection contains details such as name, category, quantity, and a unique identifier for each product. The collection uses the /category property as a shard key.
Authenticate the client
This sample creates a new instance of the MongoClient type.
connection_string = "<azure-cosmos-db-for-mongodb-connection-string>"
client = MongoClient(connection_string)
Get a database
This sample creates an instance of the Database type using the get_database function of the MongoClient type.
database = client.get_database("<database-name>")
Get a collection
This sample creates an instance of the Collection type using the get_collection function of the Database type.
collection = database.get_collection("<collection-name>")
Create a document
Create a document in the collection using collection.update_one. This method "upserts" the item effectively replacing the item if it already exists.
new_document = {
"_id": "aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb",
"category": "gear-surf-surfboards",
"name": "Yamba Surfboard",
"quantity": 12,
"sale": False,
}
filter = {
"_id": "aaaaaaaa-0000-1111-2222-bbbbbbbbbbbb",
"category": "gear-surf-surfboards"
}
payload = {
"$set": new_document
}
result = collection.update_one(filter, payload, upsert=True);
Read a document
Perform a point read operation by using both the unique identifier (id) and shard key fields. Use collection.find_one to efficiently retrieve the specific item.
filter = {
"_id": "bbbbbbbb-1111-2222-3333-cccccccccccc",
"category": "gear-surf-surfboards"
}
existing_document = collection.find_one(filter)
Query documents
Perform a query over multiple items in a container using collection.find. This query finds all items within a specified category (shard key).
filter = {
"category": "gear-surf-surfboards"
}
matched_documents = collection.find(filter)
for document in matched_documents:
# Do something with each item
Explore your data
Use the Visual Studio Code extension for Azure Cosmos DB to explore your MongoDB data. You can perform core database operations including, but not limited to:
- Performing queries using a scrapbook or the query editor
- Modifying, updating, creating, and deleting documents
- Importing bulk data from other sources
- Managing databases and collections
For more information, see How-to use Visual Studio Code extension to explore Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB data.
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the sample application or resources, remove the corresponding deployment and all resources.
azd down --force --purge