Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
After you get started with the Azure AI Foundry for Visual Studio Code extension, use Azure AI Foundry Agent Service to build agents. Agents are microservices that:
- Answer questions by using their training data or search other sources with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
- Perform specific actions.
- Automate complete workflows.
Agents combine AI models with tools to access and interact with your data.
Azure AI Foundry developers can stay productive by developing, testing, and deploying agents in the familiar environment of Visual Studio Code (VS Code).
Important
Items marked (preview) in this article are currently in public preview. This preview is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Create and edit an Azure AI agent within the designer view
Follow these steps to create an Azure AI agent:
Deploy a model to use with your agent.
In the Azure AI Foundry Extension view, find the Resources section.
Select the plus (+) icon next to the Agents subsection to create a new AI agent.

Interact with your agent in the designer
After you choose your save location, both the agent .yaml file and the designer view open so that you can edit your AI agent. Perform the following tasks in the agent designer:
In the prompt, enter a name for your agent.
In the dropdown list, select the name of your model deployment. The deployment name is what you chose when you deployed an existing model.
The extension generates the Id value. Configure the following fields:
- Add a description for your agent.
- Set system instructions.
- Configure tools for agent use.
To save the .yaml file, select File > Save on the VS Code menu bar.
Explore the Azure AI agent's .yaml definition
Your AI agent's .yaml file was opened at the same time that the designer was. This file contains the details and setup information for your agent. It's similar to the following .yaml file example:
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://aka.ms/ai-foundry-vsc/agent/1.0.0
version: 1.0.0
name: my-agent
description: Description of the agent
id: ''
metadata:
authors:
- author1
- author2
tags:
- tag1
- tag2
model:
id: 'gpt-4o-1'
options:
temperature: 1
top_p: 1
instructions: Instructions for the agent
tools: []
Add tools to the Azure AI agent
Azure AI Foundry Agent Service has the following set of tools that you can use to interact with your data sources. These tools are available in the Azure AI Foundry for Visual Studio Code extension.
- Grounding with Bing search
- File search
- Code interpreter
- OpenAPI specified tools
- Model Context Protocol (MCP)
For more information about using MCP tools, see Work with Azure AI Foundry Agent Service and MCP server tools in Visual Studio Code (preview).
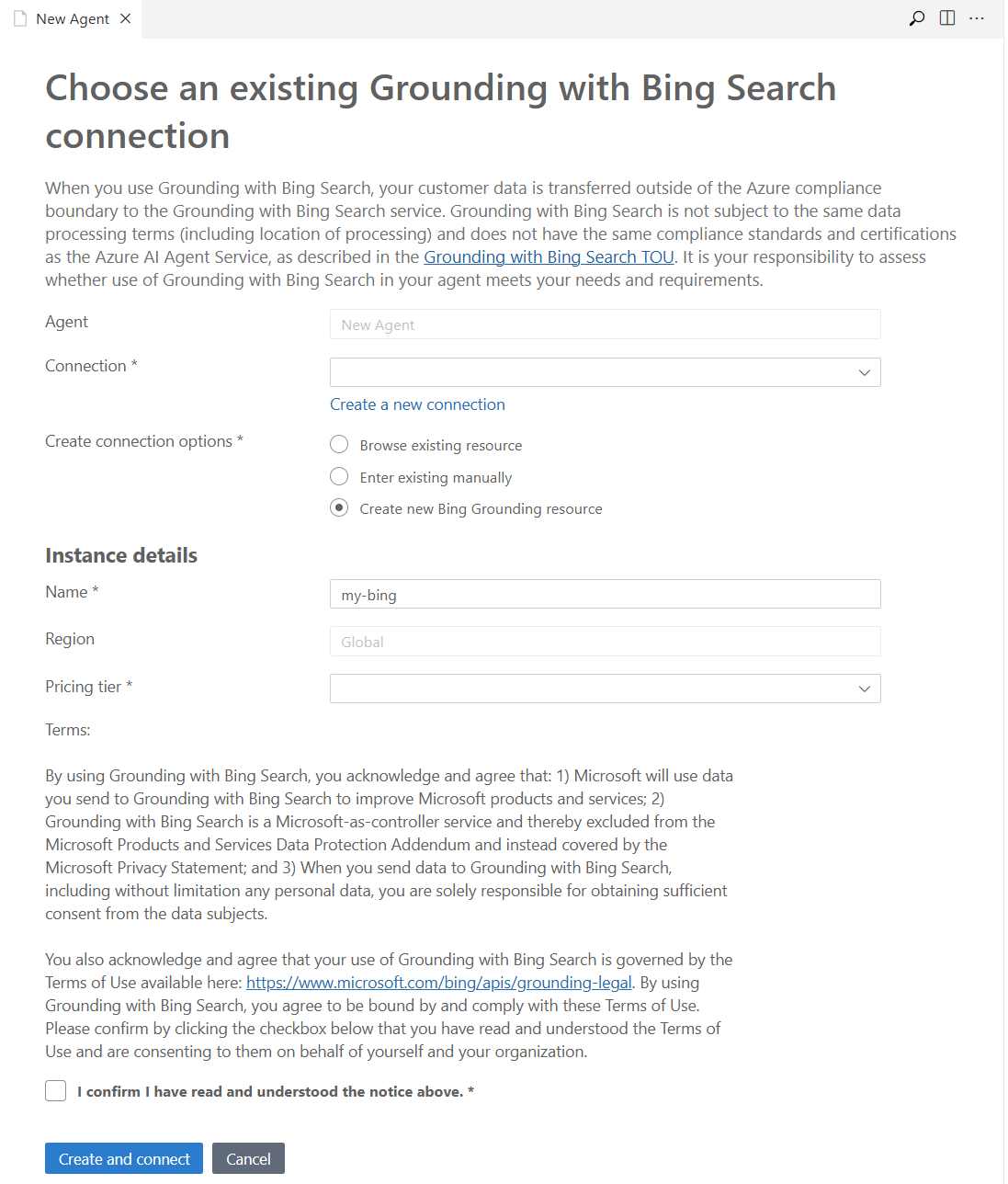
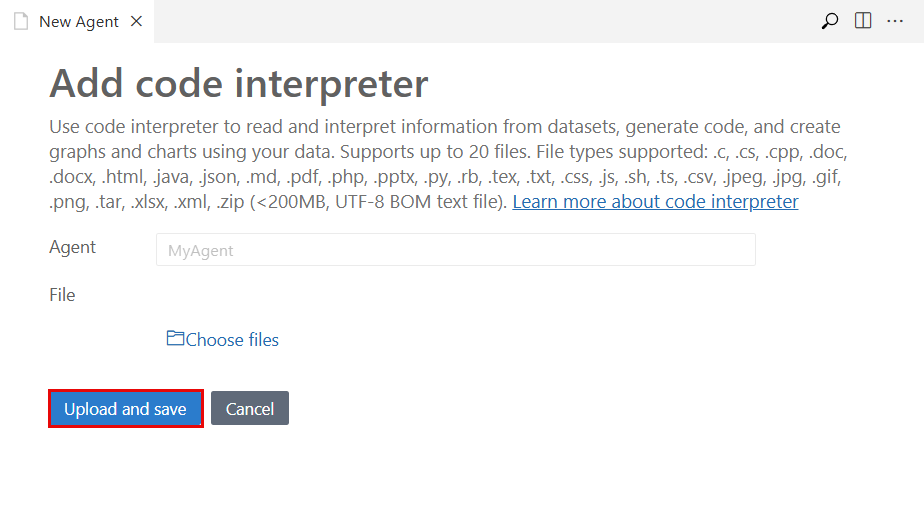
Add a tool to the AI agent
In the designer, in the upper-right corner of the TOOL section, select Add tool. In the dropdown list, select the tool that you want to add.
The designer displays the appropriate pane to configure the tool, as shown in the following images:
After you enter the required information, select Create and connect, Upload and save, or Create Tool. The button varies according to the pane.
When you add a tool, you can also add any new assets that it needs. For example, if you add a file search tool, you can use an existing vector store asset or make a new asset for your vector store to host your uploaded files.
Create an Azure AI agent on Azure AI Foundry
Create your agent directly on Azure AI Foundry by using the following steps:
In the designer, select the Create Agent on Azure AI Foundry button.
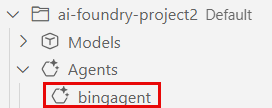
In VS Code, refresh the Azure Resources view. The deployed agent appears in the Agents subsection.
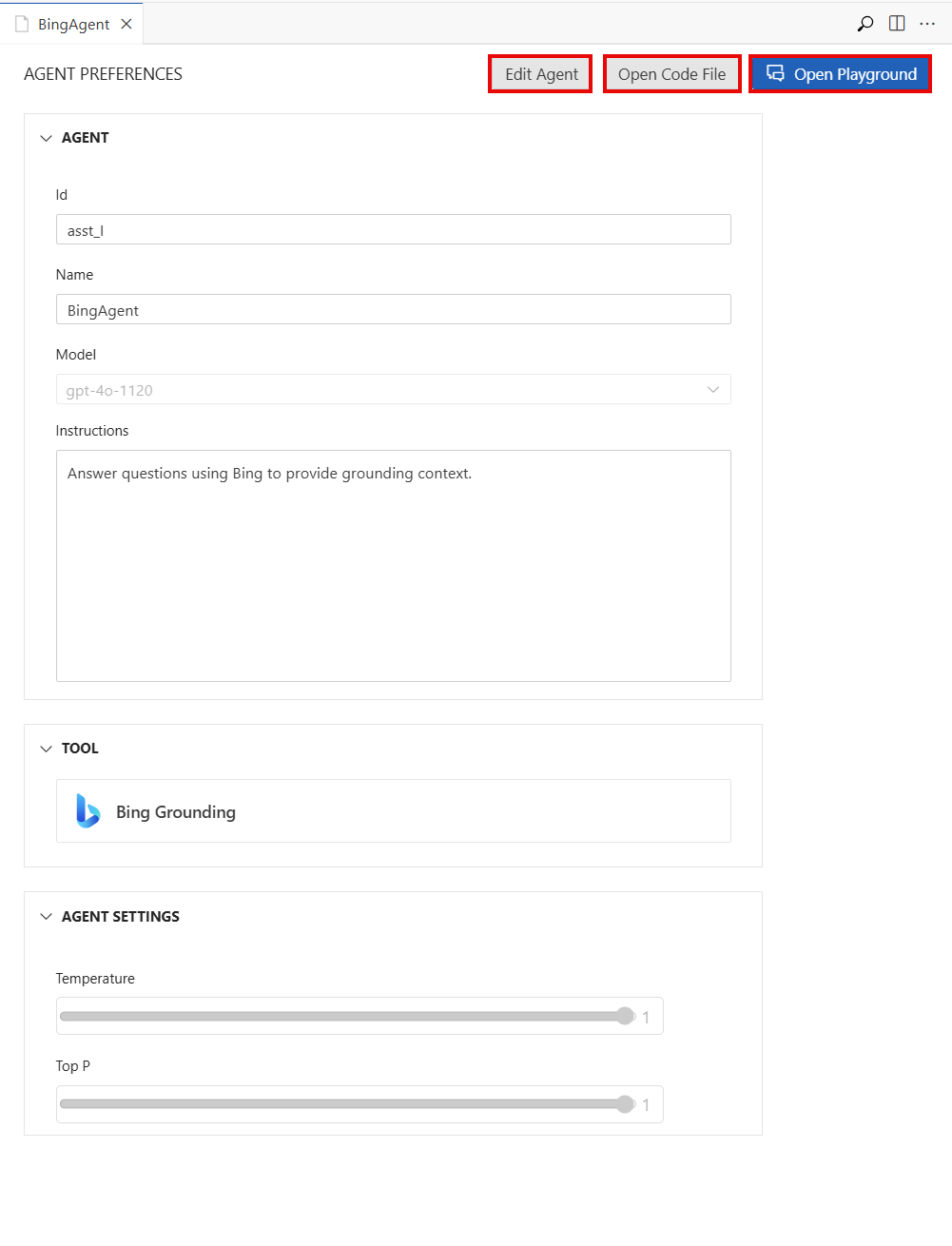
View the details of the deployed AI agent
Selecting the deployed agent opens the AGENT PREFERENCES pane in a view-only mode. You can:
- Select the Edit Agent button to view the agent designer and the .yaml definition of the agent for editing.
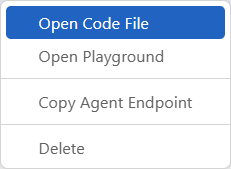
- Select the Open Code File button to create a sample code file that uses the agent.
- Select the Open Playground button to open the agent playground.
Edit and update the deployed AI agent
On the AGENT PREFERENCES pane, select the Edit Agent button. The agent designer opens with the agent's .yaml file.
Edit the agent's configuration, such as the model, tools, and instructions.
After you finish editing, select the Update Agent on Azure AI Foundry button to save your changes.
Create a sample code file
Right-click your deployed agent, and then select the Open Code File option. Or, on the AGENT PREFERENCES pane, select the Open Code File button.
In the Choose your preferred SDK dropdown list, select your preferred SDK for the agent code file, and then select the Enter key.
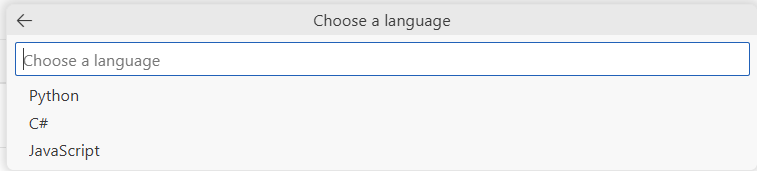
In the Choose a language dropdown list, select your preferred language for the agent code file, and then select the Enter key.
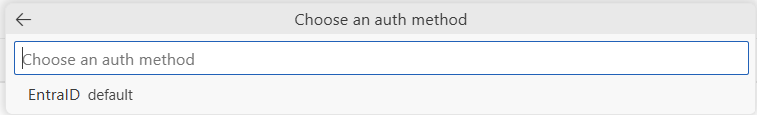
In the Choose an auth method dropdown list, select your preferred authentication method for the agent code file, and then select the Enter key.
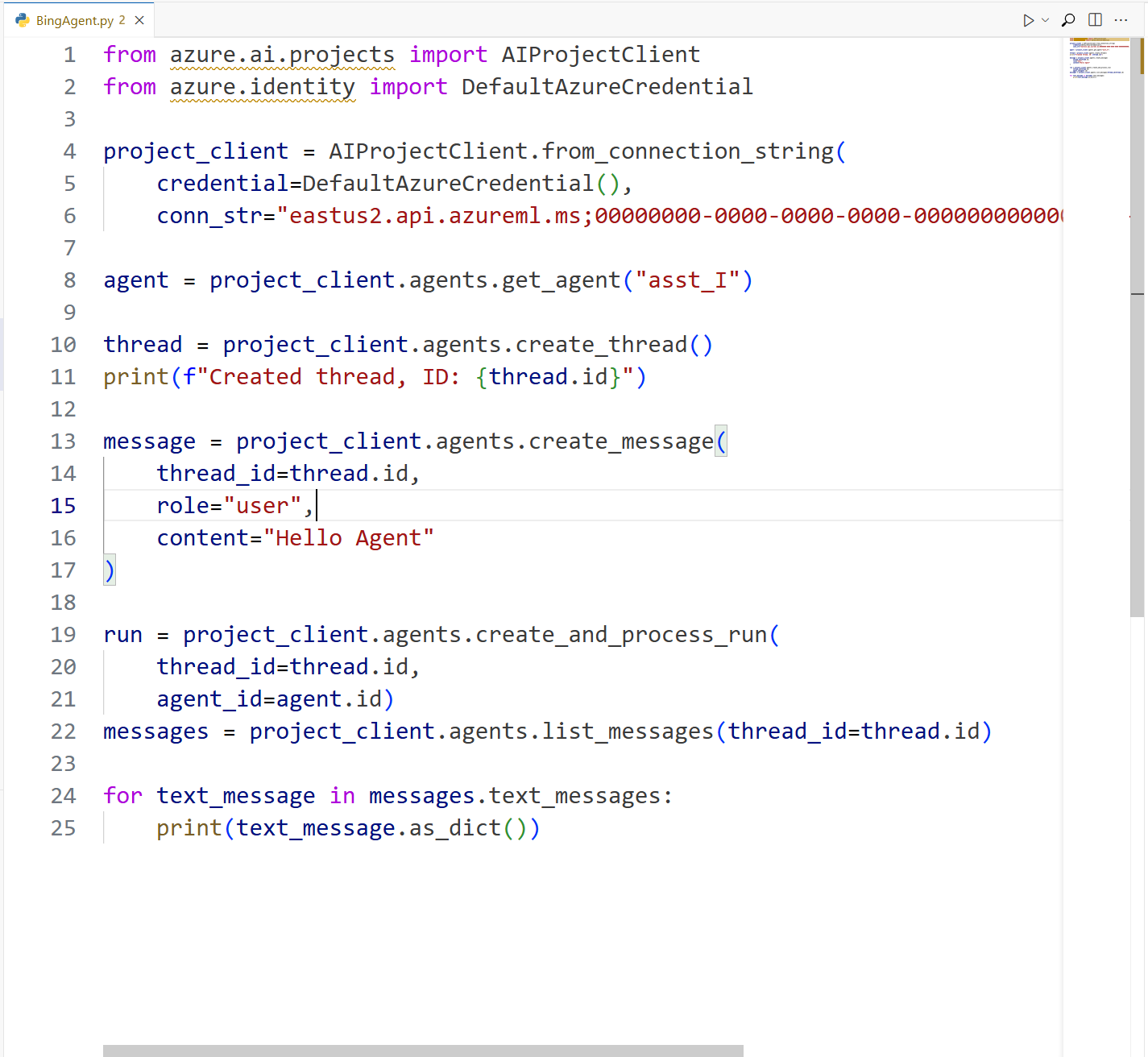
Explore the sample code file
The following Python sample code file demonstrates a basic call to interact with the agent through the Azure AI Foundry Projects API.
Interact with agents by using the agent playground
Right-click your deployed agent, and then select the Open Playground option.
Alternatively, select the Agent Playground link in the Tools subsection, and then select your agent from the dropdown list.
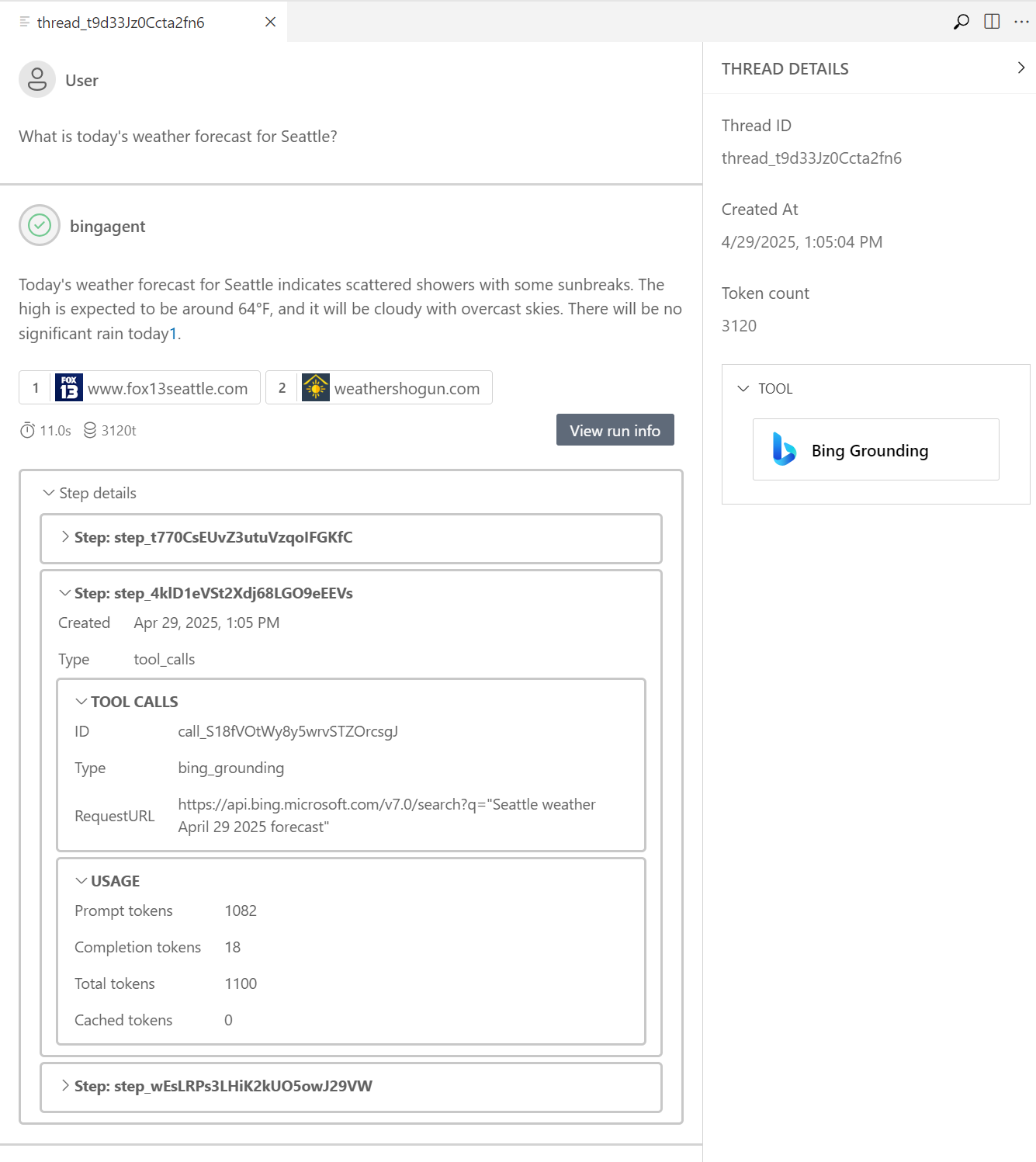
This step opens the Agent Playground pane and starts a thread with your agent so that you can send messages.
Enter your prompt and view the outputs.
This example uses Bing Grounding to illustrate a web search for information. The agent uses the model and tools that you configured in the agent designer. The source of the information appears in the section for agent annotations.
Explore threads
The Threads subsection displays the threads created during a run with your agent. In the Azure Resources view, expand the Threads subsection to view the list.
Keep these terms in mind as you explore threads:
A thread is a conversation session between an agent and a user. Threads store messages and automatically handle truncation to fit content into a model's context.
A message is a single interaction between the agent and the user. Messages can include text, images, and other files. Messages are stored as a list on the thread.
A run is a single execution of an agent. Each run can have multiple threads, and each thread can have multiple messages. The agent uses its configuration and a thread's messages to perform tasks by calling models and tools. As part of a run, the agent appends messages to the thread.
View thread details
To view the THREAD DETAILS pane, select a thread.
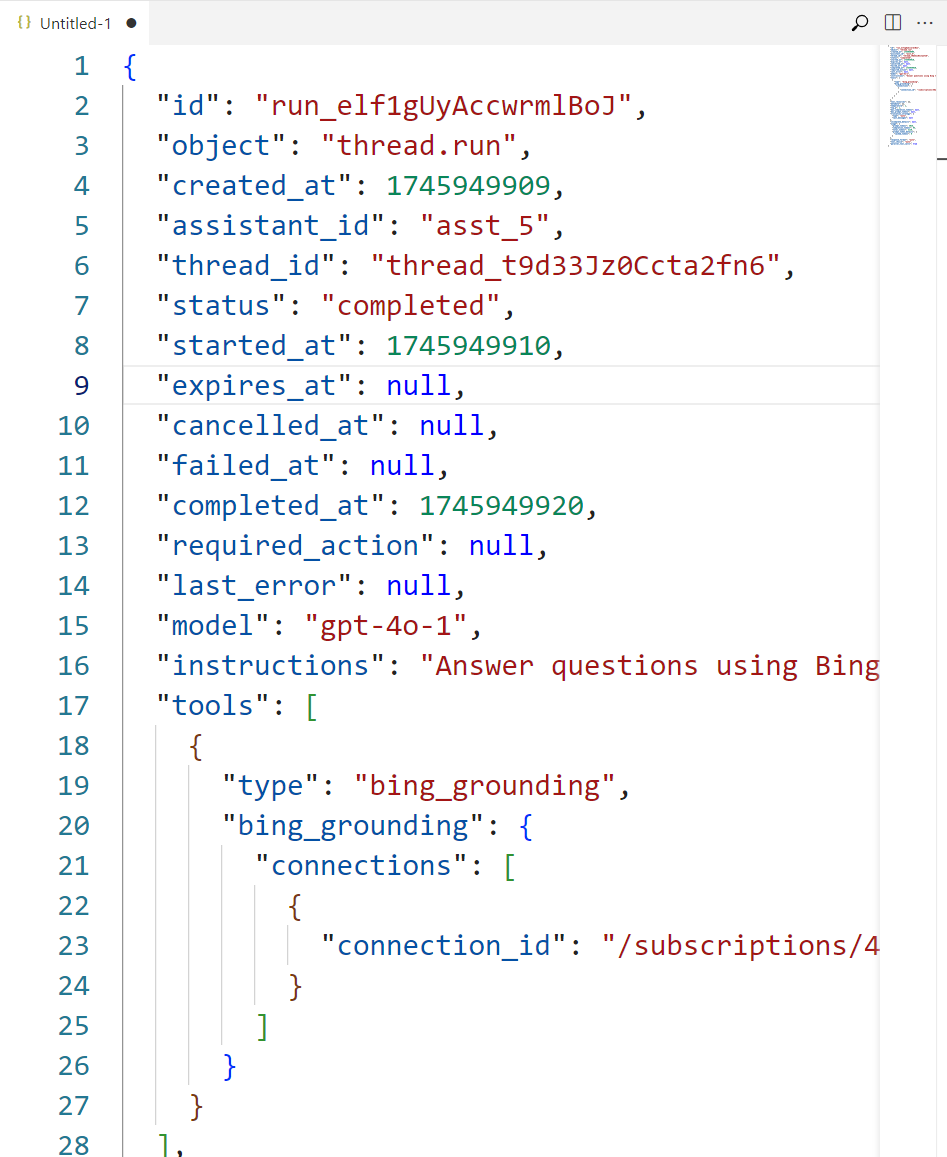
View run details
To view run information in a JSON file, select the View run info button on the THREAD DETAILS pane. The following screenshot shows an example JSON file.
Work with multi-agent workflows
You can use the Azure AI Foundry for Visual Studio Code extension to create multi-agent workflows. A multi-agent workflow is a sequence of agents that work together to accomplish a task. Each agent in the workflow can have its own model, tools, and instructions.
Create a new multi-agent workflow
Open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P).
Run this command:
>Azure AI Foundry: Create a New Multi-agent Workflow.Select a programming language.
Select a folder where you want to save your new workflow.
Enter a name for your workflow project.
A new folder is created with the necessary files for your multi-agent workflow project, including a sample code file to get you started.
Install dependencies
Install the required dependencies for your multi-agent workflow project. The dependencies vary based on the programming language that you selected when you created the project.
Install the following packages from the source:
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/agent-framework.git
pip install -e agent-framework/python/packages/azure-ai -e agent-framework/python/packages/core
Prerequisites
To run the sample multi-agent workflow C# project, ensure that you have an Azure AI Foundry project or an Azure OpenAI resource.
Setup and installation
Download and install the .NET 9 SDK from the official .NET website.
Go to your project directory and run this command to get the necessary NuGet packages:
dotnet restoreThe sample workflow project creates an .env file with the necessary environment variables. Create or update the .env file with your Azure OpenAI credentials:
# Your Azure OpenAI endpoint AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT=https://<your-openai-resource>.openai.azure.com/ # Your Azure OpenAI API key AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-api-key> # Your model deployment name in Azure OpenAI MODEL_DEPLOYMENT_NAME=<your-model-deployment-name>Important
Never commit the .env file to version control. Add it to your .gitignore file.
Run your multi-agent workflow locally
Before you run dotnet run locally, set up the required environment variables. You can get these values from the Azure AI Foundry portal.
Set up your environment variables based on your operating system:
$env:AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT="https://your-resource-name.openai.azure.com/" $env:MODEL_DEPLOYMENT_NAME="your-deployment-name" $env:AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key"Run the application by using the following commands:
dotnet build dotnet run
Update the .env file in the root directory of your project and add the following environment variables:
AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT=https://your-resource-name.openai.azure.com/
AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY=your-api-key
MODEL_DEPLOYMENT_NAME=your-deployment-name
Run the application by using this command:
python workflow.py
Visualize multi-agent workflow execution
By using the Azure AI Foundry for Visual Studio Code extension, you can visualize the interactions between agents and how they collaborate to achieve your desired outcome.
Enable visualization in your workflows by adding the following code snippet:
from agent_framework.observability import setup_observability
setup_observability(vs_code_extension_port=4317) # Default port is 4317
To monitor and visualize your multi-agent workflow execution in real time (currently available for Python interactive mode only):
Open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P).
Run this command:
>Azure AI Foundry: Visualize the Multi-Agent Workflow.
A new tab opens in VS Code to display the execution graph. The visualization updates itself automatically as your workflow progresses, to show the flow between agents and their interactions.
Port conflicts
If you find any port conflicts, change the visualization port by setting the FOUNDRY_OTLP_PORT environment variable. Update the observability port in the workflow.py file accordingly.
For example, to change the port to 4318, use this command:
export FOUNDRY_OTLP_PORT=4318
In workflow.py, update the port number in the observability configuration:
setup_observability(vs_code_extension_port=4318)
Clean up resources
The Azure resources that you created in this article are billed to your Azure subscription. If you don't expect to need these resources in the future, delete them to avoid incurring more charges.
Delete your agents
Tip
Because you can customize the left pane in the Azure AI Foundry portal, you might see different items than shown in these steps. If you don't see what you're looking for, select ... More at the bottom of the left pane.
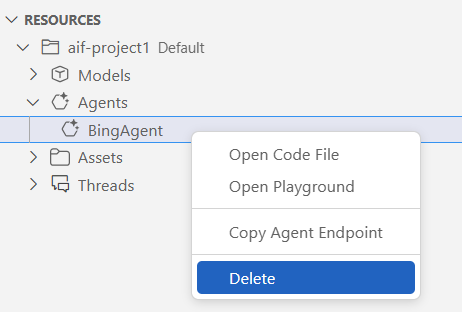
In the Azure AI Foundry portal, on the left menu, select Agents.
Select the agent that you want to delete, and then select Delete.
Delete your models
In VS Code, refresh the Azure Resources view. Expand the Models subsection to display the list of deployed models.
Right-click the deployed model that you want to delete, and then select Delete.
Delete your connected tools
Open the Azure portal.
Select the Azure resource group that contains the tool.
Select the Delete button.
Related content
- Learn about the tools that you can use with Azure AI agents, such as file search or code interpreter.