RelativeLayout 用来对子级进行位置和大小调整(相当于布局属性或同级元素而言)。 这样就可以创建可根据设备大小按比例缩放的 UI。 此外,与某些其他的布局类不同,RelativeLayout 能够定位子级,使之重叠。
RelativeLayout 类定义以下属性:
XConstraint,类型为Constraint,是一个附加属性,表示对子级的 X 位置的约束。YConstraint,类型为Constraint,是一个附加属性,表示对子级的 Y 位置的约束。WidthConstraint,类型为Constraint,是一个附加属性,表示对子级的宽度的约束。HeightConstraint,类型为Constraint,是一个附加属性,表示对子级的高度的约束。BoundsConstraint,类型为BoundsConstraint,是一个附加属性,表示对子级的位置和大小的约束。 无法从 XAML 轻松使用此属性。
这些属性由 BindableProperty 对象提供支持,这意味着它们可以作为数据绑定的目标,也可以进行设置样式。 有关附加属性的详细信息,请参阅 Xamarin.Forms 附加属性。
注意
RelativeLayout 中子级的宽度和高度也可以通过子级的 WidthRequest 和 HeightRequest 属性(而不是 WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性)指定。
RelativeLayout 类派生自 Layout<T> 类,后者定义了类型 IList<T> 的 Children 属性。 由于 Children 属性是 Layout<T> 类的 ContentProperty,因此不需要通过 XAML 显式设置。
提示
尽可能避免使用 RelativeLayout。 它会导致 CPU 不得不执行显著更多的工作。
约束
在 RelativeLayout 内,可以使用绝对值或相对值将子级的位置和大小指定为约束。 未指定约束时,子级将定位于布局的左上角。
下表显示了如何在 XAML 和 C# 中指定约束:
| XAML | C# | |
|---|---|---|
| 绝对值 | 绝对约束是通过将 RelativeLayout 附加属性设置为 double 值来指定的。 |
绝对约束由 Constraint.Constant 方法指定,或使用需要 Func<Rectangle> 参数的 Children.Add 重载来指定。 |
| 相对值 | 相对约束是通过将 RelativeLayout 附加属性设置为 ConstraintExpression 标记扩展返回的 Constraint 对象来指定的。 |
相对约束由 Constraint 类的方法返回的 Constraint 对象指定。 |
若要详细了解如何使用绝对值来指定约束,请参阅绝对定位和大小调整。 若要详细了解如何使用相对值来指定约束,请参阅相对定位和大小调整。
在 C# 中,可以通过三个 Add 重载将子级添加到 RelativeLayout。 第一个重载需要 Expression<Func<Rectangle>> 来指定子级的位置和大小。 第二个重载需要适用于 x、y、width 和 height 参数的可选 Expression<Func<double>> 对象。 第三个重载需要适用于 x、y、width 和 height 参数的可选 Constraint 对象。
可以使用 SetXConstraint、SetYConstraint、SetWidthConstraint 和 SetHeightConstraint 方法更改 RelativeLayout 中子级的位置和大小。 每个此类方法的第一个参数都是子级,第二个参数是 Constraint 对象。 此外,SetBoundsConstraint 方法还可用于更改子级的位置和大小。 此方法的第一个参数是子级,第二个参数是 BoundsConstraint 对象。
调整绝对位置和大小
RelativeLayout 可以使用以与设备无关的单位指定的绝对值来定位子级并调整其大小,这些单位显式定义了应将子级放置在布局中的哪个位置。 这是通过将子级添加到 RelativeLayout 的 Children 集合并将每个子级上的 XConstraint、YConstraint、WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性设置为绝对位置和/或大小值来实现的。
警告
使用绝对值调整子级的位置和大小可能会出问题,因为不同设备的屏幕大小和分辨率也不同。 因此,一台设备上的屏幕中心坐标在其他设备上可能会出现偏移。
以下 XAML 显示了一个 RelativeLayout,其子级使用绝对值进行定位:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="RelativeLayoutDemos.Views.StylishHeaderDemoPage"
Title="Stylish header demo">
<RelativeLayout Margin="20">
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="10"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="200"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="5" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="20"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="200"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="5" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="10"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="5"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="65" />
<BoxView Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="20"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="0"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="5"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="65" />
<Label Text="Stylish header"
FontSize="24"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="30"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="25" />
</RelativeLayout>
</ContentPage>
在此示例中,每个 BoxView 对象的位置是使用 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加属性中指定的值定义的。 每个 BoxView 的大小是使用 WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性中指定的值定义的。 Label 对象的位置也是使用 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加属性中指定的值定义的。 但是,没有为 Label 指定大小值,因此它不受约束,会自行调整大小。 在所有情况下,绝对值都表示与设备无关的单位。
以下屏幕截图显示布局结果:

等效 C# 代码如下所示:
public class StylishHeaderDemoPageCS : ContentPage
{
public StylishHeaderDemoPageCS()
{
RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout
{
Margin = new Thickness(20)
};
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(0, 10, 200, 5));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(0, 20, 200, 5));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(10, 0, 5, 65));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new BoxView
{
Color = Color.Silver
}, () => new Rectangle(20, 0, 5, 65));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(new Label
{
Text = "Stylish Header",
FontSize = 24
}, Constraint.Constant(30), Constraint.Constant(25));
Title = "Stylish header demo";
Content = relativeLayout;
}
}
在此示例中,使用 Add 重载将 BoxView 对象添加到 RelativeLayout,该重载需要 Expression<Func<Rectangle>> 来指定每个子级的位置和大小。 Label 的位置是使用 Add 重载定义的,该重载需要可选的 Constraint 对象,后者在本例中是由 Constraint.Constant 方法创建的。
注意
一个使用绝对值的 RelativeLayout 可以调整子级的位置和大小,使它们不在布局的边界内。
相对定位和大小调整
RelativeLayout 可以使用布局属性或同级元素的相对值来定位子级并调整其大小。 这是通过使用 Constraint 对象将子级添加到 RelativeLayout 的 Children 集合并将每个子级上的 XConstraint、YConstraint、WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性设置为相对值来实现的。
约束可以是相对于父级或相对于同级的常数。 约束的类型由 ConstraintType 枚举表示,它定义了以下成员:
RelativeToParent,表示相对于父级的约束。RelativeToView,表示相对于视图(或同级)的约束。Constant,表示常数约束。
约束标记扩展
在 XAML 中,可以通过 ConstraintExpression 标记扩展创建 Constraint 对象。 此标记扩展通常用于将 RelativeLayout 中子级的位置和大小与其父级或同级项相关联。
ConstraintExpression 类定义以下属性:
Constant,类型为double,表示约束常数值。ElementName,类型为string,表示要据其计算约束的源元素的名称。Factor,类型为double,表示系数,将按该系数缩放受约束维度(相对于源元素而言)。 此属性的默认值为 1。Property,类型为string,表示源元素上要用在约束计算中的属性的名称。Type,类型为ConstraintType,表示约束的类型。
有关 Xamarin.Forms 标记扩展的详细信息,请参阅 XAML 标记扩展。
以下 XAML 显示了一个 RelativeLayout,其子级受 ConstraintExpression 标记扩展的约束:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
x:Class="RelativeLayoutDemos.Views.RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPage"
Title="RelativeLayout demo">
<RelativeLayout>
<BoxView Color="Red"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}" />
<BoxView Color="Green"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Constant=-40}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}" />
<BoxView Color="Blue"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=Constant, Constant=0}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Constant=-40}" />
<BoxView Color="Yellow"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Constant=-40}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Constant=-40}" />
<!-- Centered and 1/3 width and height of parent -->
<BoxView x:Name="oneThird"
Color="Silver"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToParent, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}" />
<!-- 1/3 width and height of previous -->
<BoxView Color="Black"
RelativeLayout.XConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=X}"
RelativeLayout.YConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Y}"
RelativeLayout.WidthConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Width, Factor=0.33}"
RelativeLayout.HeightConstraint="{ConstraintExpression Type=RelativeToView, ElementName=oneThird, Property=Height, Factor=0.33}" />
</RelativeLayout>
</ContentPage>
在此示例中,每个 BoxView 对象的位置是通过设置 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加属性来定义的。 第一个 BoxView 的 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加属性设置为常数,即绝对值。 其余的 BoxView 对象都通过使用至少一个相对值来设置其位置。 例如,黄色 BoxView 对象将 XConstraint 附加属性设置为其父级(RelativeLayout)的宽度减去 40。 同样,此 BoxView 将 YConstraint 附加属性设置为其父级的高度减去 40。 这可确保黄色 BoxView 显示在屏幕的右下角。
注意
未指定大小的 BoxView 对象会自动通过 Xamarin.Forms 将大小调整为 40x40。
名为 oneThird 的银色 BoxView 位于中心位置(相对于其父级而言)。 它的大小也是相对于其父级的,是其宽度和高度的三分之一。 这是通过将 XConstraint 和 WidthConstraint 附加属性设置为父级 (RelativeLayout) 的宽度乘以 0.33 来实现的。 同样,将 YConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性设置为父级的高度乘以 0.33。
黑色相对于该黑色BoxView的位置和大小oneThirdBoxView。 这是通过将其 XConstraint 和 YConstraint 附加属性分别设置为同级元素的 X 和 Y 值来实现的。 同样,它的大小设置为其同级元素宽度和高度的三分之一。 这是通过将其 WidthConstraint 和 HeightConstraint 附加属性分别设置为同级元素的 Width 和 Height 值并将其乘以 0.33 来实现的。
以下屏幕截图显示了生成的布局:
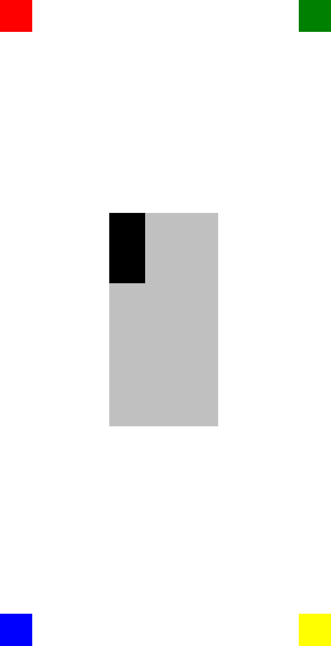
约束对象
Constraint 类定义了以下公共静态方法,这些方法返回 Constraint 对象:
Constant,将子级约束为某个使用double指定的大小。FromExpression,使用 Lambda 表达式来约束子级。RelativeToParent,根据父级的大小来约束子级。RelativeToView,根据视图的大小来约束子级。
此外,BoundsConstraint 类还定义了一个方法 (FromExpression),该方法返回一个 BoundsConstraint,后者使用 Expression<Func<Rectangle>> 约束子级的位置和大小。 该方法可用于设置 BoundsConstraint 附加属性。
以下 C# 代码显示了一个 RelativeLayout,其子级受 Constraint 对象约束:
public class RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPageCS : ContentPage
{
public RelativePositioningAndSizingDemoPageCS()
{
RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout();
// Four BoxView's
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Red },
Constraint.Constant(0),
Constraint.Constant(0));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Green },
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width - 40;
}), Constraint.Constant(0));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Blue },
Constraint.Constant(0),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height - 40;
}));
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Yellow },
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width - 40;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height - 40;
}));
// Centered and 1/3 width and height of parent
BoxView silverBoxView = new BoxView { Color = Color.Silver };
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
silverBoxView,
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToParent((parent) =>
{
return parent.Height * 0.33;
}));
// 1/3 width and height of previous
relativeLayout.Children.Add(
new BoxView { Color = Color.Black },
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.X;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Y;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Width * 0.33;
}),
Constraint.RelativeToView(silverBoxView, (parent, sibling) =>
{
return sibling.Height * 0.33;
}));
Title = "RelativeLayout demo";
Content = relativeLayout;
}
}
在此示例中,使用 Add 重载将子级添加到 RelativeLayout,该重载需要一个适用于 x、y、width 和 height 参数的可选 Constraint 对象。
注意
一个使用相对值的 RelativeLayout 可以调整子级的位置和大小,使它们不在布局的边界内。
