Azure DevOps Services |Azure DevOps Server |Azure DevOps Server 2022 |Azure DevOps Server 2020
本文介绍了 PowerShell 脚本如何将业务逻辑添加到 Azure Pipelines。 PowerShell v2 (PowerShell@2) 任务运行 PowerShell 脚本,这些脚本可以访问 Azure DevOps REST API、使用 Azure DevOps 工作项、管理测试或调用其他服务。
可以在 PowerShell 脚本中使用 预定义变量 或 用户定义的变量 。 还可以设置 多作业输出变量 ,使变量可用于其他作业。 有关详细信息,请参阅定义变量。
还可以在 PowerShell 脚本中使用命名参数。 不支持其他类型的参数,例如 开关参数。 有关详细信息,请参阅 如何声明 cmdlet 参数。
PowerShell 脚本任务
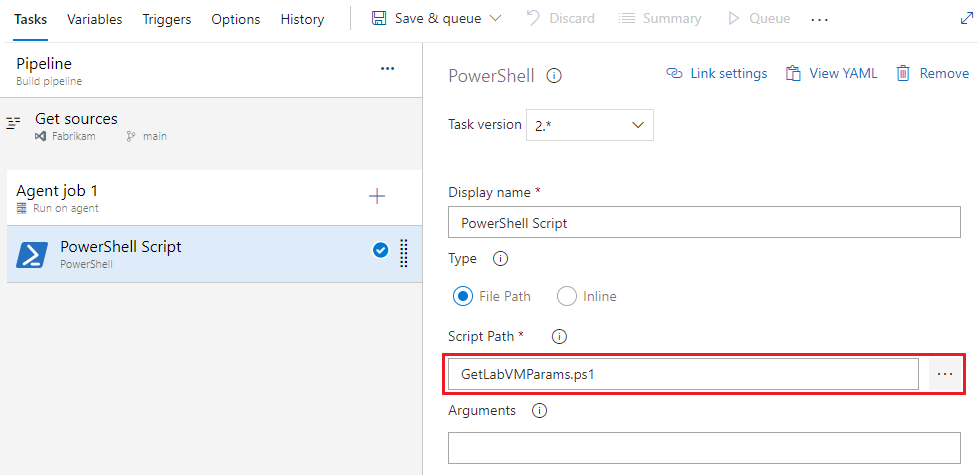
若要使用 PowerShell 脚本,请将 PowerShell v2 (PowerShell@2) 任务添加到管道,然后输入内联 PowerShell 脚本或调用 PowerShell 脚本文件。
此生成使用代码的活动分支。 如果管道运行使用 main 代码的分支,则脚本也使用该 main 分支。
以下示例在属性中使用targetType: 'inline'script并添加内联脚本。
steps:
- task: PowerShell@2
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: Write-Host "Hello world!"
以下示例将 PowerShell@2 步骤添加到 YAML 管道。 该代码调用一个名为 test.ps1 的 PowerShell 脚本文件,该文件位于存储库的根目录中。
steps:
- task: PowerShell@2
inputs:
targetType: 'filePath'
filePath: 'test.ps1'
注意
默认情况下,该 PowerShell@2 任务使用 Windows PowerShell 5.1 进行 Windows 代理,使用适用于 Linux/macOS 代理的 PowerShell 7.x。 若要在 Windows 代理上使用 PowerShell 7.x,必须安装 PowerShell 7.x,并将参数集添加到 pwshtrue。
默认情况下,Microsoft托管代理 已安装 PowerShell 7.x。
还可以将 YAML pwsh 管道添加或 powershell 步骤作为步骤的 PowerShell@2 快捷方式。 快捷方式 pwsh 在 macOS、Linux 或 Windows 上运行 PowerShell 7.x。 快捷方式 powershell 在 Windows 或 Linux 和 macOS 上的 PowerShell 7.x 上运行 Windows PowerShell 5.1。
steps:
- pwsh: test.ps1
steps:
- pwsh: Write-Host Hello
将版本应用于程序集的示例脚本
以下 PowerShell 脚本基于内部版本号对程序集应用版本。 例如,如果生成号格式定义 $(BuildDefinitionName)_$(Year:yyyy).$(Month).$(DayOfMonth)$(Rev:.r) 生成号 生成HelloWorld_2024.07.19.1,则脚本会将版本 2024.07.19.1 应用于程序集。
若要成功运行此脚本,内部版本号格式必须具有四个段。 有关详细信息,请参阅 “运行”或“内部版本号”。
注意
内部版本号也称为运行编号。
使用
name管道根级别的属性在 YAML 管道中自定义生成号定义。name: $(BuildDefinitionName)_$(Year:yyyy).$(Month).$(DayOfMonth)$(Rev:.r)将以下 PowerShell 脚本保存为存储库根目录中的文件。
PowerShell@2向管道添加任务步骤或pwshpowershell快捷方式,并调用 PowerShell 脚本文件相对于工作目录的文件路径。
用于将版本应用到程序集的 PowerShell 脚本:
# Enable -Verbose option
[CmdletBinding()]
# Regular expression pattern to find the version in the build number
$VersionRegex = "\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+"
# If not running on a build server, remind user to set environment variables for debugging
if(-not ($Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY -and $Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER))
{
Write-Error "You must set the following environment variables"
Write-Error "to test this script interactively."
Write-Host '$Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY - For example, enter something like:'
Write-Host '$Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY = "C:\code\Fabrikam\HelloWorld"'
Write-Host '$Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER - For example, enter something like:'
Write-Host '$Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER = "Build HelloWorld_0000.00.00.0"'
exit 1
}
# Make sure path to source code directory is available
if (-not $Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY)
{
Write-Error ("BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY environment variable is missing.")
exit 1
}
elseif (-not (Test-Path $Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY))
{
Write-Error "BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY does not exist: $Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY"
exit 1
}
Write-Verbose "BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY: $Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY"
# Make sure there's a build number
if (-not $Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER)
{
Write-Error ("BUILD_BUILDNUMBER environment variable is missing.")
exit 1
}
Write-Verbose "BUILD_BUILDNUMBER: $Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER"
# Get and validate the version data
$VersionData = [regex]::matches($Env:BUILD_BUILDNUMBER,$VersionRegex)
switch($VersionData.Count)
{
0
{
Write-Error "Couldn't find version number data in BUILD_BUILDNUMBER."
exit 1
}
1 {}
default
{
Write-Warning "Found more than one instance of version data in BUILD_BUILDNUMBER."
Write-Warning "Assuming first instance is version."
}
}
$NewVersion = $VersionData[0]
Write-Verbose "Version: $NewVersion"
# Apply the version to the assembly property files
$files = gci $Env:BUILD_SOURCESDIRECTORY -recurse -include "*Properties*","My Project" |
?{ $_.PSIsContainer } |
foreach { gci -Path $_.FullName -Recurse -include AssemblyInfo.* }
if($files)
{
Write-Verbose "Applying $NewVersion to $($files.count) files."
foreach ($file in $files) {
$filecontent = Get-Content($file)
attrib $file -r
$filecontent -replace $VersionRegex, $NewVersion | Out-File $file
Write-Verbose "$file.FullName - version applied"
}
}
else
{
Write-Warning "Found no files."
}
用于访问 REST API 的示例脚本
以下 PowerShell 脚本使用环境变量来访问 Azure Pipelines REST API 并检索管道定义。
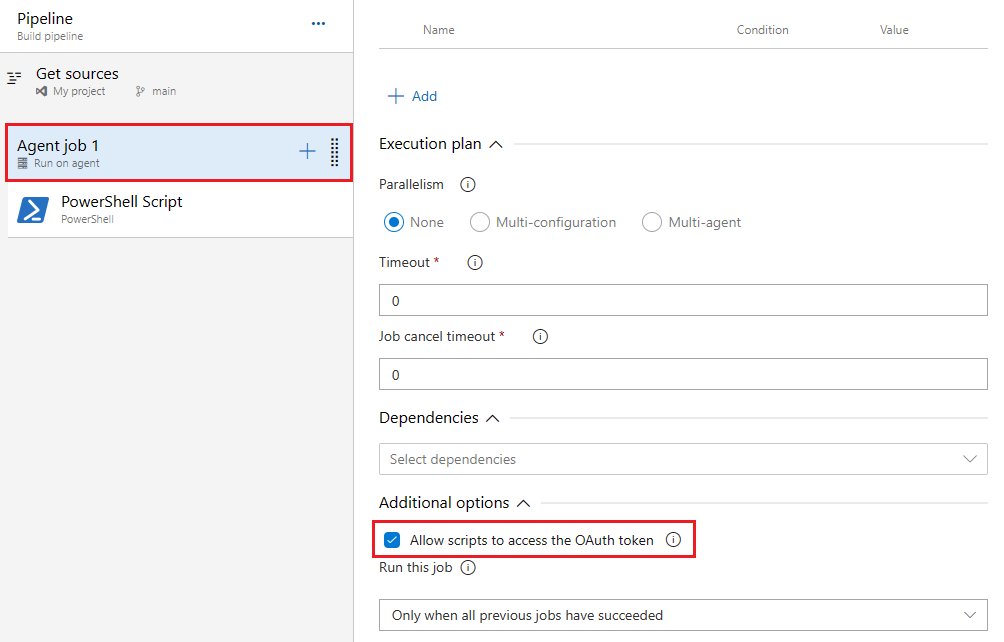
在 YAML 管道中,可以在任务中$env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN定义环境变量PowerShell@2,并在内联脚本中使用它来获取 OAuth 令牌以访问 REST API。
- task: PowerShell@2
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
$url = "$($env:SYSTEM_TEAMFOUNDATIONCOLLECTIONURI)$env:SYSTEM_TEAMPROJECTID/_apis/build/definitions/$($env:SYSTEM_DEFINITIONID)?api-version=5.0"
Write-Host "URL: $url"
$pipeline = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $url -Headers @{
Authorization = "Bearer $env:SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN"
}
Write-Host "Pipeline = $($pipeline | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 100)"
env:
SYSTEM_ACCESSTOKEN: $(System.AccessToken)