Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Summary
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Release State | General Availability |
| Products | Power BI (Semantic models) Power BI (Dataflows) Fabric (Dataflow Gen2) Power Apps (Dataflows) Dynamics 365 Customer Insights |
| Authentication Types Supported | Anonymous Database Windows |
| Function Reference Documentation | — |
Note
Some capabilities might be present in one product but not others due to deployment schedules and host-specific capabilities.
Note
The Impala connector implementation 2.0 has been in preview since July 2025.
Capabilities Supported
- Import
- DirectQuery (Power BI semantic models)
- Advanced options
- Connection timeout duration
- Command timeout duration
Connect to an Impala database from Power Query Desktop
To connect to an Impala database, take the following steps:
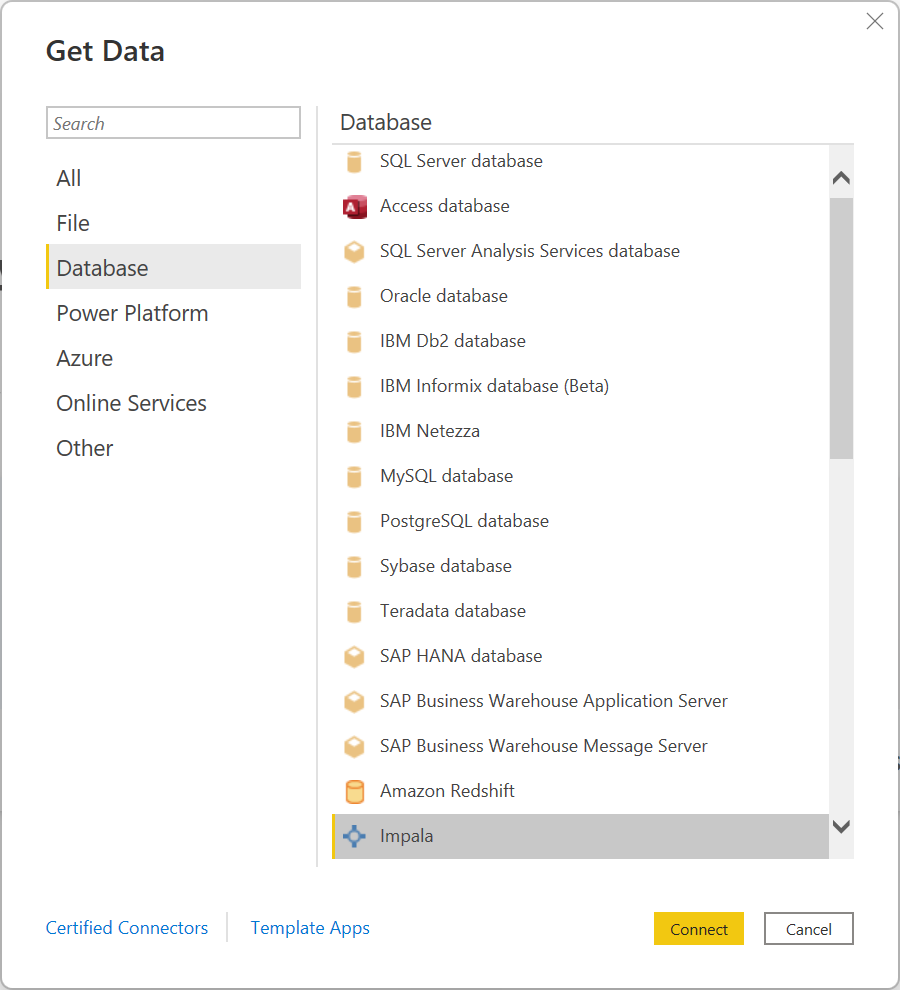
Select Get Data from the Home ribbon in Power BI Desktop.
Select Database from the categories on the left, select Impala on the right, and then select Connect.
In the Impala window that appears, type or paste the name of your Impala server into the box. You can Import data directly into Power BI or you can use DirectQuery. Learn more about using DirectQuery. Then select OK.

When prompted, enter your credentials or connect anonymously. The Impala connector supports Anonymous, Database (user name and password), and Windows authentication.
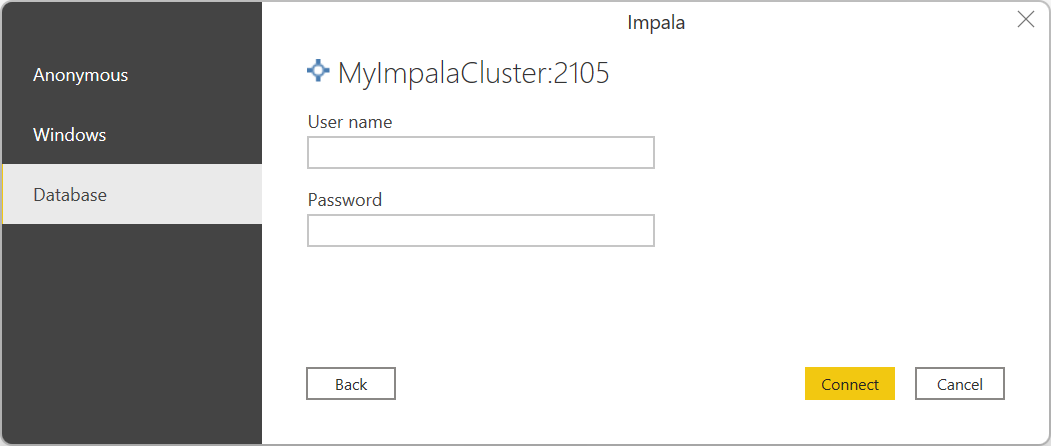
For more information about authentication methods, go to Authentication with a data source.
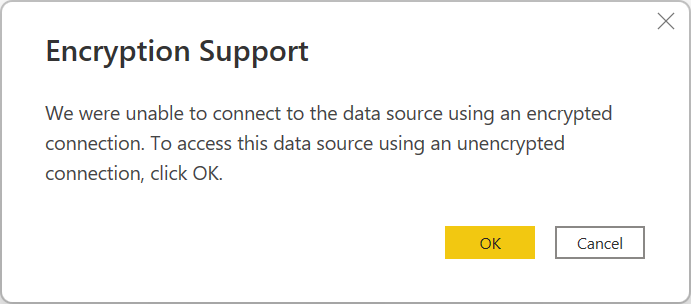
Note
If the connection isn't encrypted, you'll be prompted with the following message. Select OK if you want to use an unencrypted connection.
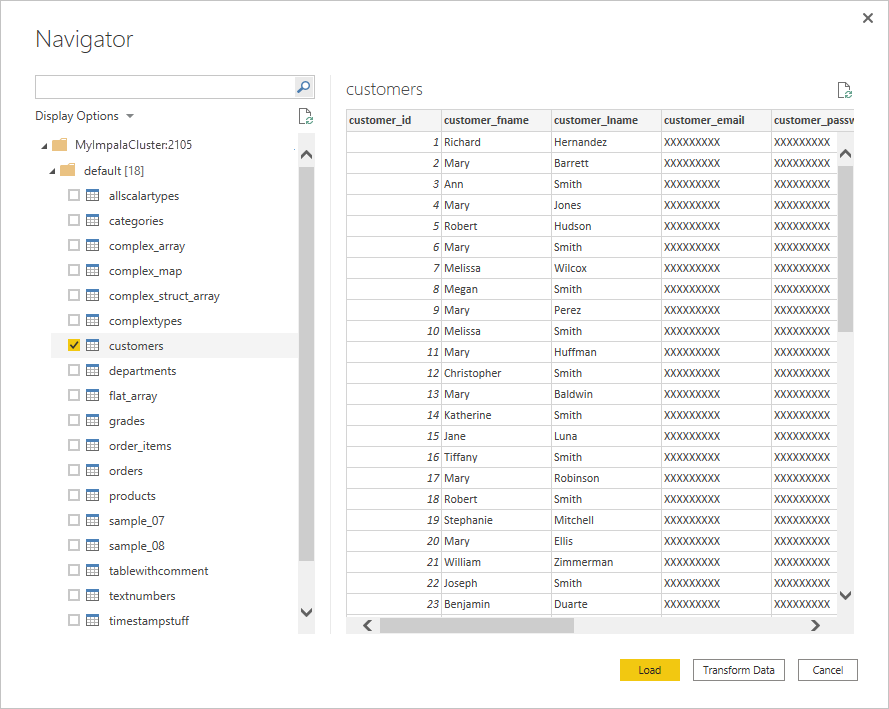
After you connect, a Navigator window appears and displays the data that's available on the server. Either select Load to load the data or Transform Data to continue transforming the data in the Power Query editor.
Connect to an Impala database from Power Query Online
To connect to an Impala database, take the following steps:
Select the Impala option in the connector selection.
In Connect to data source, provide the name of the server and a port number if required.
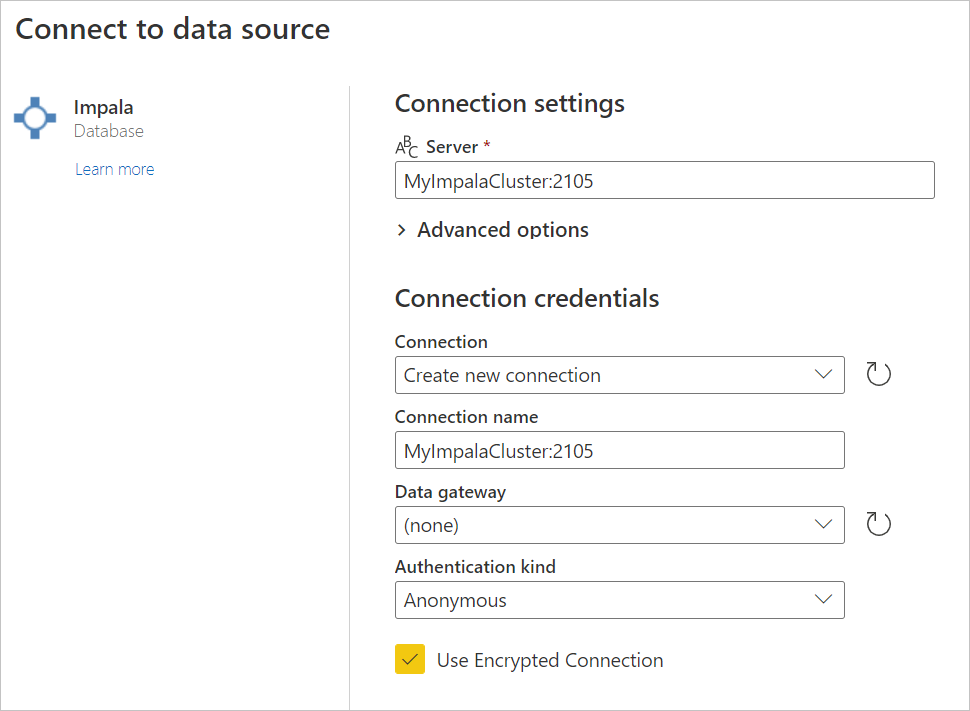
If required, select the name of your on-premises data gateway.
If this is the first time you're connecting to this Impala database, select the type of credentials for the connection in Authentication kind.
Enter your credentials.
Select Use Encrypted Connection if you want to use an encrypted connection, or clear the option if you want to use an unencrypted connection.
Select Next to continue.
In Navigator, select the data you require, then select Transform data to transform the data in the Power Query editor.
Connect using advanced options
Power Query provides a set of advanced options that you can add to your query if needed. The following table lists all of the advanced options you can set in Power Query.
| Advanced option | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection timeout duration | Specifies the maximum time Power Query will wait for a connection to complete. You can enter another value to keep the connection open longer. |
| Command timeout duration | Specifies the maximum time a command is allowed to run before Power Query abandons the call. |
Impala connector implementation 2.0
In August 2025, we introduced a new implementation for the Impala connector to enhance the integration with Impala. We recommend that you upgrade your Power BI Desktop and the on-premises data gateway to the latest version to benefit from the most current capabilities.
Provide us feedback to help us continue improving the connector.
The Impala connector implementation 2.0 is built using the open-source Arrow Database Connectivity (ADBC) driver. ADBC provides a set of standard interfaces for interacting with Arrow data, which is especially efficient at fetching large datasets with minimal overhead and no serialization or copying. The ADBC driver also incorporates security enhancements such as memory safety and garbage collection.
Additionally, collaboration with the open-source community enables more rapid updates, utilizing modern tools and secure development lifecycle (SDL) processes. To enable you to take advantage of these performance and security enhancements, all newly created connections automatically use the 2.0 implementation starting August 2025. During the transition period, you can test the 2.0 implementation by updating your existing queries and adding the Implementation="2.0" flag in Impala.Database as follows. After the transition, connections that don't specify an implementation will be automatically updated to the 2.0 implementation.
Source = Impala.Database("impalavm.centralus.cloudapp.azure.com", [Implementation="2.0"
To aid with diagnosing any potential issue, you can find the Implementation and DriverType details in your Mashup logs like the following example. If you encounter any issue during the transition, contact support.
{
"Start": "2024-11-02T00:14:02.7968686Z",
"Action": "Engine/Module/Impala/IO/Impala/Implementation",
"ResourceKind": "Impala",
"ResourcePath": "impalavm.centralus.cloudapp.azure.com",
"HostProcessId": "29200",
"Implementation": "2.0",
"DriverType": "ADBC",
"ProductVersion": "2.139.0.0 (Main)+eda56ecd858054173a4d11db9c63a6da5cf92a99",
"ActivityId": "106f16b6-cfbb-4853-9f20-ed45486486d2",
"Process": "Microsoft.Mashup.Container.NetFX45",
"Pid": 38560,
"Tid": 1,
"Duration": "00:00:00.0000291"
}
To remain on the previous connector implementation temporarily (while troubleshooting), specify Implementation="1.0" in your queries.
Considerations and limitations
Here are a few considerations and limitations to keep in mind with the Impala connector:
- The Impala connector is supported on the on-premises data gateway, using any of the three supported authentication mechanisms.
- The Impala connector uses the Impala driver, which limits the size of string types to 32K by default.
- The Impala connector doesn't support overridding the Realm option for Kerberos authentication.