Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
Power BI service for business users
Power BI service for designers & developers
Power BI Desktop
Requires Pro or Premium license
This article explains how to interact with the Power BI service to discover data‑driven business insights. It focuses on the everyday tasks and tools available to Power BI business users (sometimes called consumers or readers).
Note
Looking for navigation basics (Home, Browse, Apps, Learning center, workspaces)? Start with Getting around in the Power BI service. Need help locating content on the Home canvas? See Find content from Power BI service Home.
If you're not signed up for the Power BI service, sign up for a free trial before you begin.
Prerequisites
Most interactions in this article assume:
- You have at least a Power BI Pro or Premium Per User (PPU) license, or the content you are viewing is stored in a Premium (or Fabric F64+) capacity that allows free users to consume it. Fabric (Free) users are limited to content in their own My workspace or Premium/Fabric capacity workspaces shared with them.
- The feature has not been disabled by your Power BI / Fabric admin (admins can turn off or restrict capabilities like export, Analyze in Excel, or Q&A for governance).
For details, see Power BI license types and service features by license.
What is Power BI?
Power BI is a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to turn your unrelated sources of data into coherent, visually immersive, and interactive insights. Your data might be a simple Excel spreadsheet or a collection of data from different data sources. No matter, Power BI lets you easily connect to your data sources, visualize (or discover) what's important, and share that with anyone or everyone you want.
Open the Power BI service, in a browser or on a mobile device. You and your colleagues work from the same trusted apps, dashboards, and reports, that update and refresh automatically, so you're always working with the freshest content.
Reading view
There are two modes for interacting with reports in the Power BI service: Editing view and Reading view. If you're a business user, then you're more likely to use Reading view to consume reports created by others. Editing view is used by report designers, who create the reports and share them with you. Reading view is your way to explore and interact with reports created by colleagues.
Select Editing view and Reading view
Most reports open in Reading view. To switch from Reading view to Editing view, select Edit from the action bar. If Edit is grayed out, that means that you don't have permissions to edit the report.
To switch back to Reading view, select Reading view from the action bar.
Even in Reading view, the content isn't static. You can look for trends, explore insights, ask questions in natural language, set up alerts and subscriptions, and export or focus visuals—across devices.
At a glance: What you can do here
| Goal | Feature | Where |
|---|---|---|
| Navigate & open content | Home, Browse, search | Getting around |
| View structured bundles | Apps | Apps |
| Explore multi-page visuals | Reports | Reports |
| Monitor key metrics | Dashboards & tiles | Dashboards |
| Ask questions | Q&A | (Dashboard) Q&A box |
| Get proactive updates | Subscriptions & alerts | Dashboard/report menus |
| Narrow data shown | Filters pane, slicers | Report pages |
| Focus or present | Focus mode, Full screen | Visual menu / View menu |
| Reuse insights elsewhere | Export, Analyze in Excel, PowerPoint | Menus / export options |
For definitions of core building blocks (reports, dashboards, apps) see the linked pages above; this article concentrates on interaction techniques.
Interact in the Power BI service
Collaborate with colleagues
Skip the email. Add a personal comment or start a conversation with colleagues about a dashboard, right there on that dashboard. The comment feature is just one of the ways you can collaborate with others.

Learn more about commenting.
Tip
Commenting (and other collaboration actions) requires Pro or PPU, or that the content resides in a Premium / Fabric capacity workspace that grants you access. See license types.
Subscribe to a dashboard or report
It's not necessary to open Power BI to monitor a dashboard. You can subscribe instead, and Power BI emails you a snapshot of that dashboard on a schedule you set.
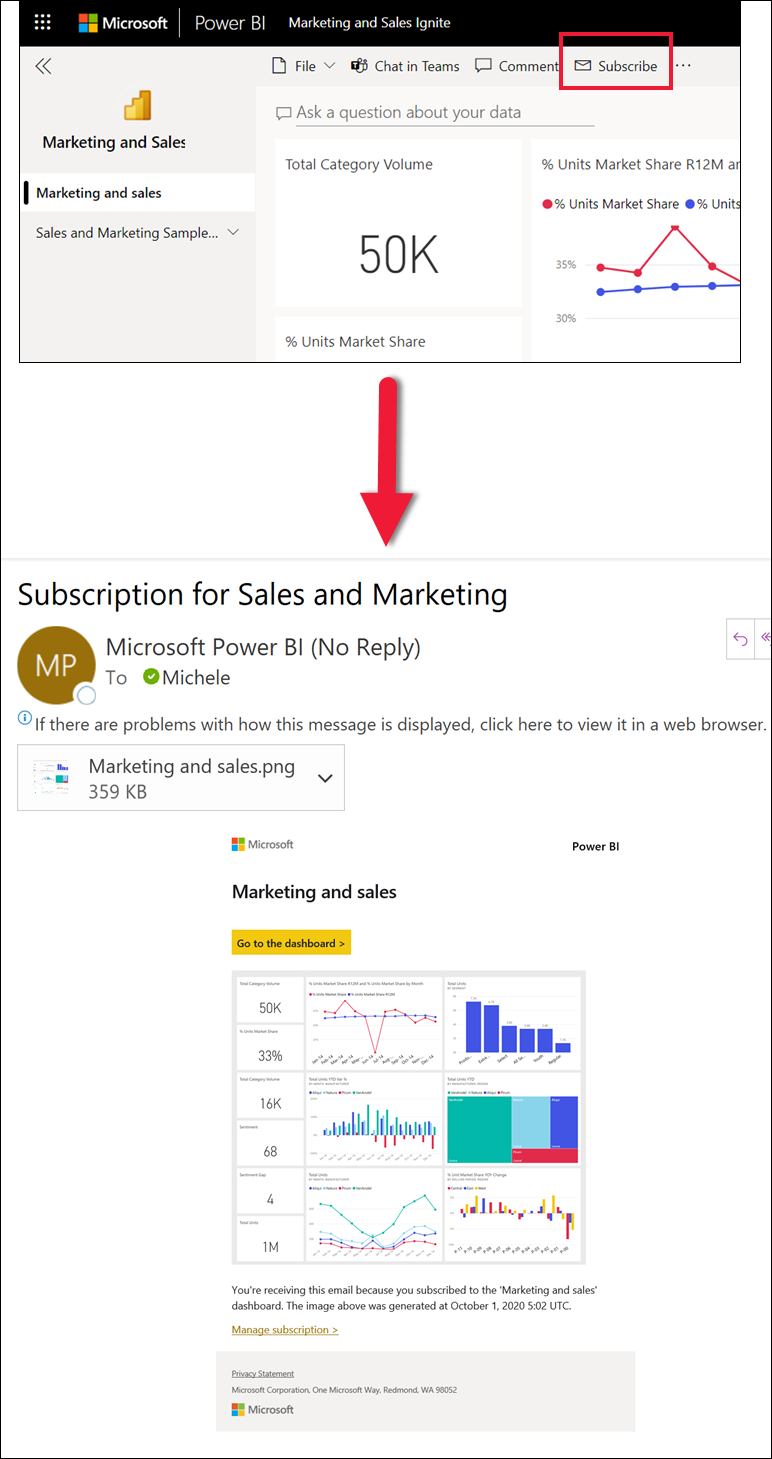
Learn more about Power BI subscriptions.
Note
Subscriptions require a Pro or PPU license unless the content is hosted in a Premium capacity. Admins can disable subscriptions for governance or compliance.
Get alerts when your data reaches a threshold
Your data is live, and your visuals update automatically. If you want to get notified when data changes above or below a threshold you set, use data alerts. Alerts work on gauges, KPIs, and cards.

Power BI sends you an email when the value increases or decreases past the limit you set.
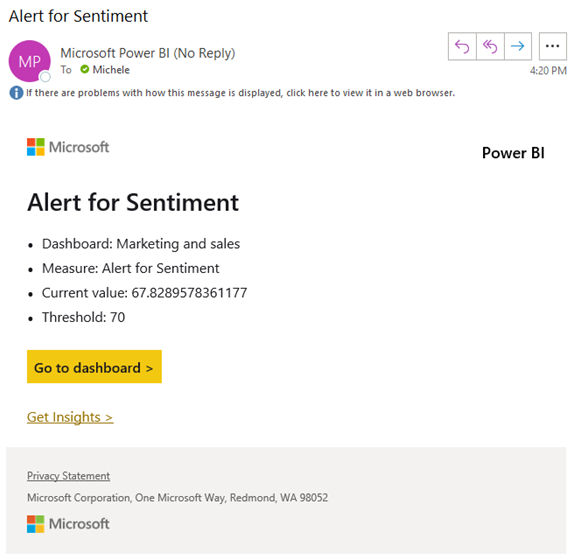
Learn more about Power BI alerts.
Important
Data alerts work only on certain dashboard tile types (KPI, gauge, card) and not on report visuals directly. They require at least a Pro license unless the dashboard is in a Premium capacity. Alerts also respect row-level security (RLS) and only evaluate data the user is authorized to view.
Use Q&A to ask questions using natural language
Sometimes the fastest way to get an answer from your data is to ask a question using natural language. The Q&A question box is available at the top of your dashboard. For example, "show me count of large opportunities by sales stage as a funnel."
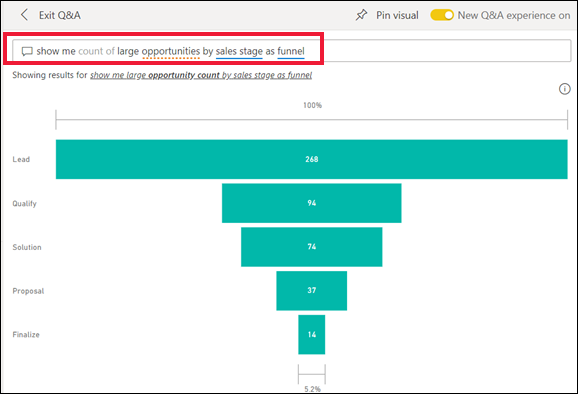
Learn more about Power BI Q&A.
Tip
Q&A availability can be limited or turned off by an admin or the dataset owner (semantic model). Some older dialogs might still display the term dataset instead of semantic model—the concepts are the same for the purposes of this article.
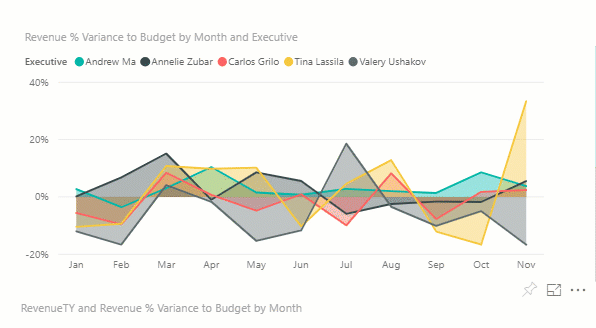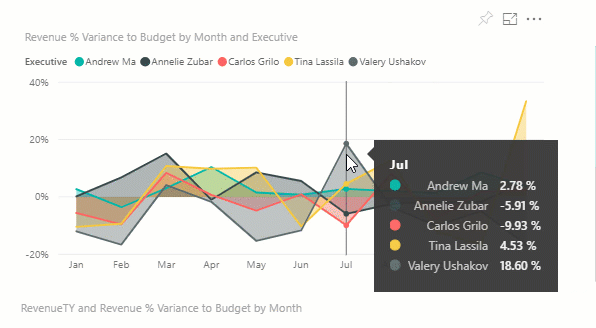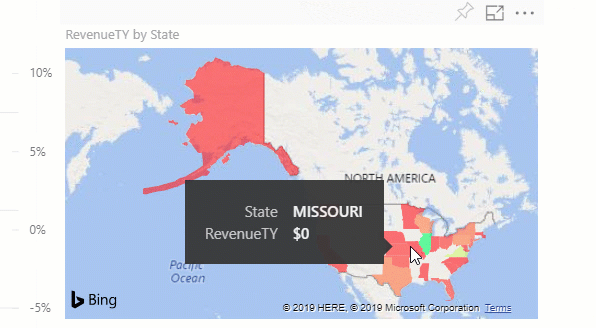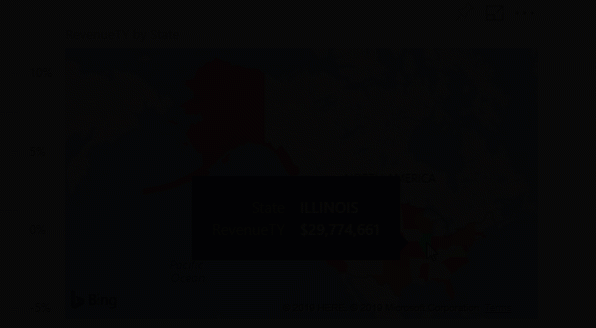
Display details on a visualization
Visuals are made up of datapoints, and by hovering over a datapoint, you can view the details.
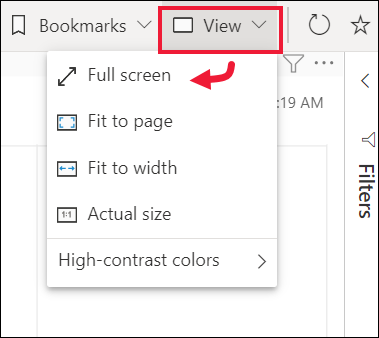
Adjust the display dimensions
Reports are viewed on many different devices, with varying screen sizes and aspect ratios. The default rendering may not be what you want to see on your device.
To adjust, from the upper right menu bar select the View icon and choose one of the display options.
![]()
See how all the visuals on a page are interconnected
Cross-highlight and cross-filter the related visualizations on a report page. The visualizations on a single report page are all "connected" to each other. What this means is that if you select one or more values in one visualization, other visualizations that use that same value change based on your selection.
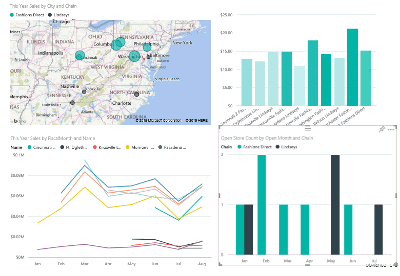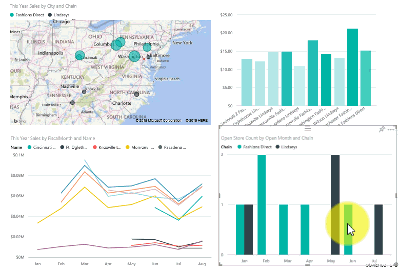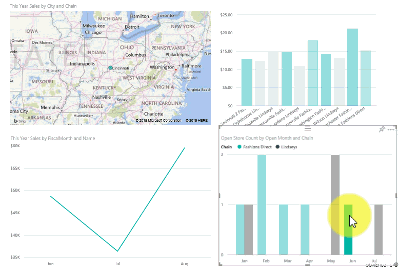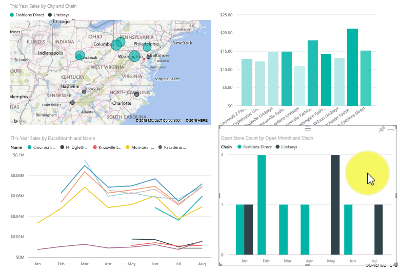
Learn more about visual interactions.
Update the filters used in the report
Open the Filters pane to reveal the filters applied to the page, report, and visualization.
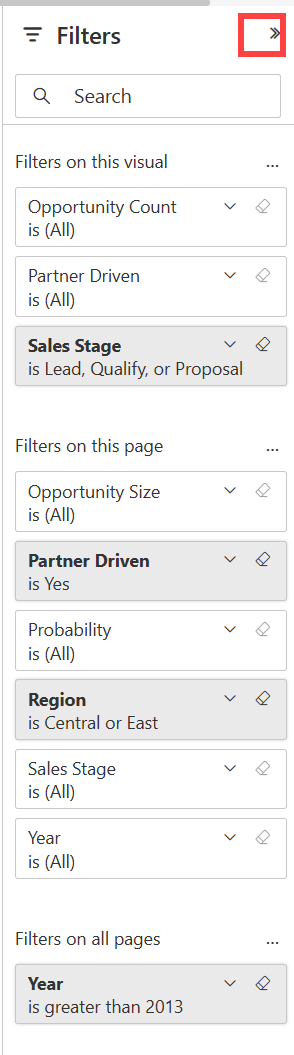
If the report has filters applied, they'll display in the Filters pane. Make changes to the filters to see the effect on the visuals. Save your changes, or use the ![]() to revert to the default report page state.
to revert to the default report page state.
Zoom in on individual visuals
Hover over a visual and select the Focus mode icon ![]() . When you view a visualization in Focus mode, it expands to fill the entire report canvas.
. When you view a visualization in Focus mode, it expands to fill the entire report canvas.
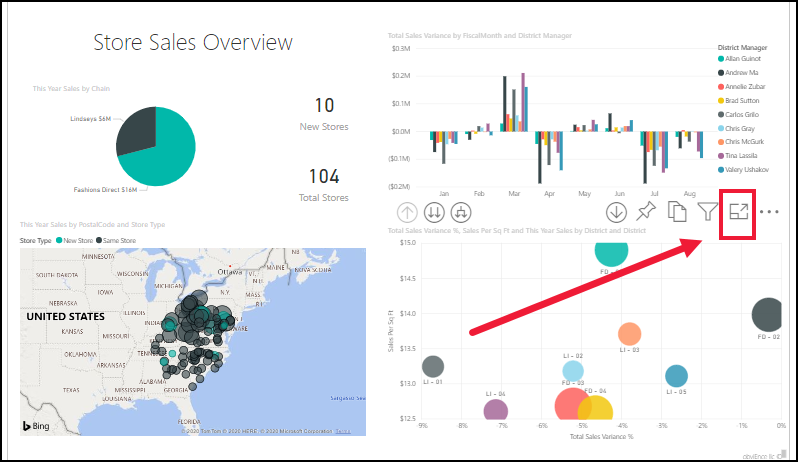
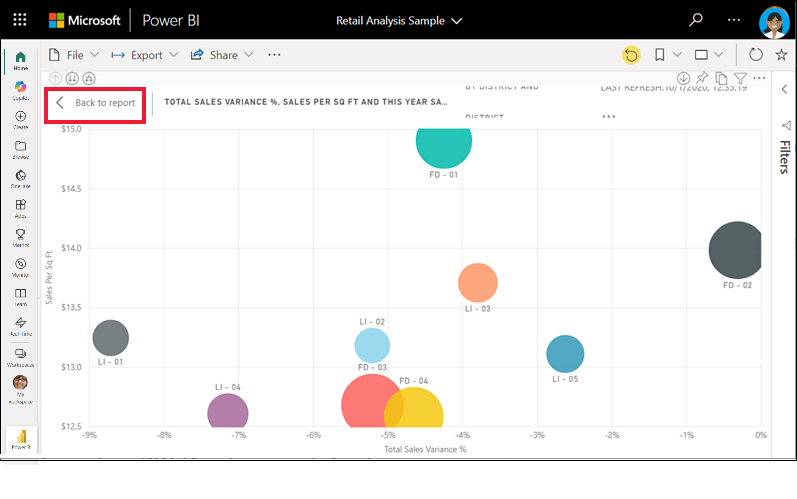
To display that same visualization without the distraction of menu bars, filter pane, and other chrome--select Full screen from the View dropdown.
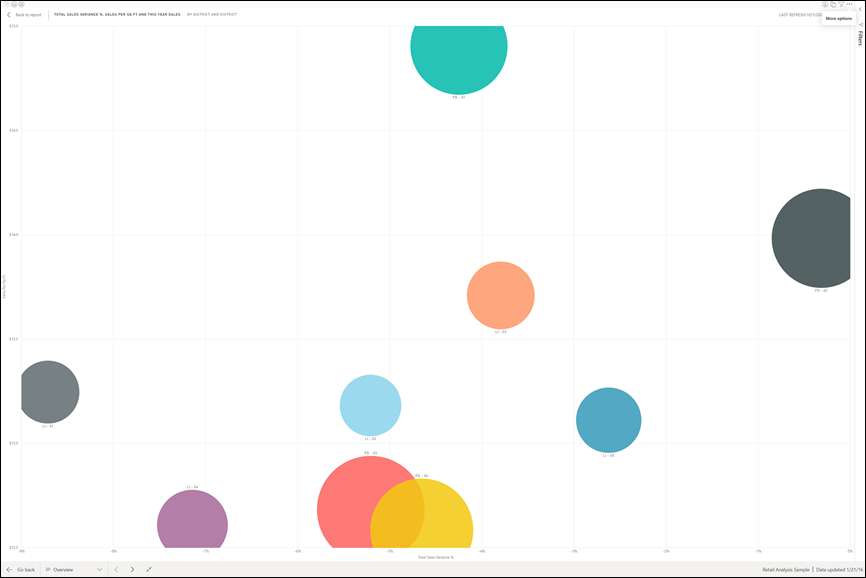
Learn more about focus mode and full screen mode.
Sort a visualization
Visuals on a report page can be sorted and saved with your changes applied.
Hover over a visual to make it active, and select More options (...) to open sorting options.
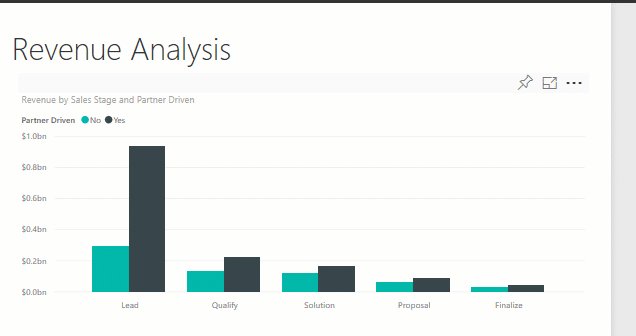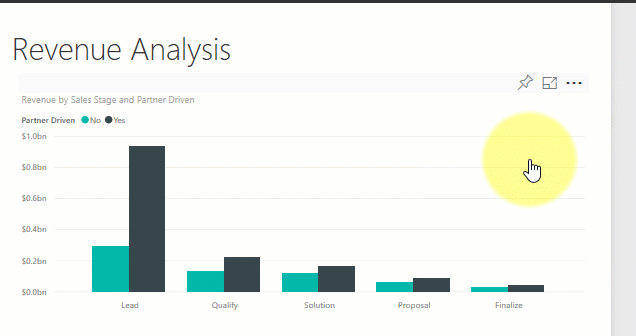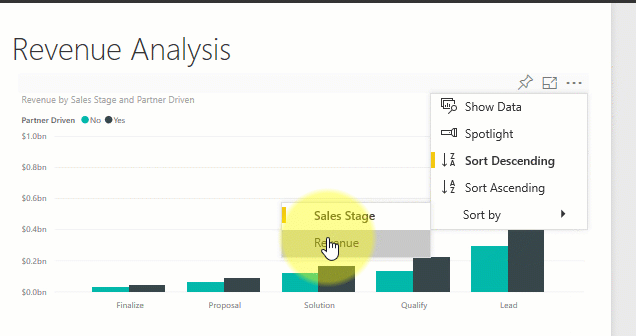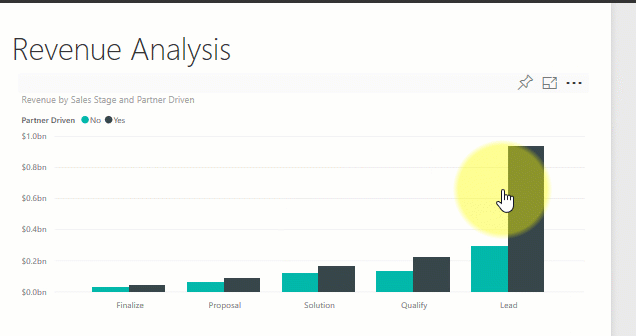
Learn more about sorting visuals.
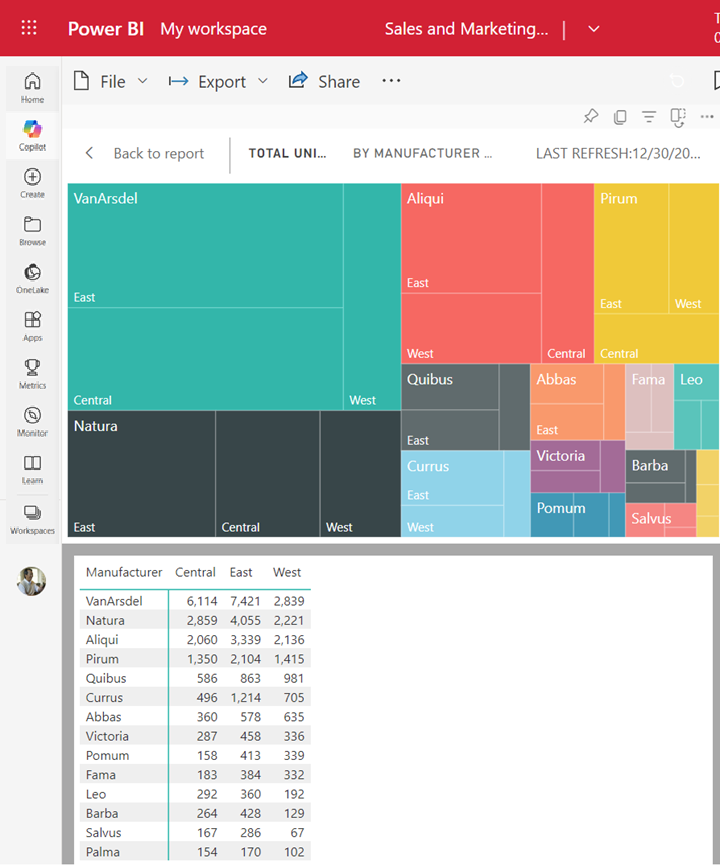
Show the data used to create a visualization
A Power BI visualization is constructed using data from underlying semantic models. If you're interested in seeing behind-the-scenes, Power BI lets you display the data that is being used to create the visual. When you select Show as a table, Power BI displays the data below (or next to) the visualization.
With a visual active, select More options (...) and choose Show as a table.
Export data to Excel
In addition to showing the data that is used to create a visual, you can also export that data and view it in Microsoft Excel. When you export to Excel, you're creating a separate document, a spreadsheet that isn't part of Power BI. Any changes that you make in the Excel file don't impact the data in Power BI. Whether you want to take a closer look at the data, or you want to use the data in another application or for another purpose, Power BI gives you that flexibility. For more information, visit Export the data that was used to create a visualization.
Exporting isn't limited to individual visuals; you can export entire reports to Excel or PowerPoint to share with your colleagues. For more information, see Analyze in Excel and Power BI in PowerPoint.
Note
Export / Analyze in Excel and PowerPoint features can be disabled by your admin. Export respects security: row-level security (RLS), object-level security (OLS), and any applied filters/slicers at the time of export. Large exports are subject to service limits.
This article is a quick overview of just some of the things business users can do with the Power BI service.
Clean up resources
If you connected to an app, from the nav pane, select Apps to open the Apps content list. Hover over the app to delete, and select the trashcan icon.
If you imported or connected to a Power BI sample report, from the nav pane, open My workspace. Using the tabs at the top, locate the dashboard, report, and semantic model, and select the trashcan icon for each.