Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
The Vulnerability Remediation Agent is currently in a limited public preview and available to only a select group of customers. If you’re interested in gaining access or would like to learn more, please reach out to your sales team for further details and next steps.
In public preview, the Vulnerability Remediation Agent for Security Copilot in Intune uses data from Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management to identify Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) on your managed devices. The results are prioritized for remediation and include step-by-step instructions to guide you in using Intune to remediate the threat. This Copilot Agent can help you reduce the time it takes to investigate, identify, and remediate threats, ultimately improving your organization’s overall security posture.
When the agent runs, it analyzes data from Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management and provides a prioritized list of suggestions that appear in the Intune admin center. You can drill-in to each suggestion to view details that include:
- The count of associated vulnerabilities (CVEs)
- A Copilot-assisted summarized impact analysis
- Suggested actions
- Affected systems
- Exposed devices
- Potential impact
- Step-by-step guidance for using Intune to remediate it
Once you remediate an agent suggestion, you can mark it as applied to have the agent retain a record you can use in tracking remediation actions over time.
Because CVE details and recommended remediation guidance can change over time, subsequent runs of the agent might provide new details, device counts, and remediation steps. As you manage subsequent reports of threats, the record of your previously applied solutions can help you track the change to specific risks based on your previous remediations.
For information about other Security Copilot Agents in Intune and common features, see Security Copilot agents in Microsoft Intune.
Prerequisites
Licensing and plugins
Microsoft Intune Plan 1 subscription - This subscription provides the core Intune capabilities.
Microsoft Security Copilot - Security Copilot must share a Tenant with Intune, and to set up the agent your account must have permission to the workspace for Security Copilot. For more information, see Get started with Microsoft Security Copilot.
Security compute units (SCU) - You must have sufficient SCUs to power Security Copilot workloads, including agents.
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management - This capability is provided by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint P2 or Defender Vulnerability Management Standalone.
Government cloud support
The current release of the Vulnerability Remediation Agent is supported on the public cloud but isn't supported on government clouds.
Supported platforms and applications
The Vulnerability Remediation Agent supports evaluation and recommendations for the following platforms and applications:
- Windows
- Apps in Intune
Role-based access control and permissions
Intune Requirements: To set up the agent or view agent results, admins must be assigned an Intune license and be assigned either a built-in or custom Intune role-based access control (RBAC) role that grants the following permissions:
- Managed apps / read
- Mobile apps / read
- Device configurations / read
The least privileged built-in role that includes these permissions is Read Only Operator.
Microsoft Defender Requirements: The account used by the agent for its identity must be assigned permissions that align with the following Microsoft Defender XDR RBAC configurations. The specific configuration depends on whether your Defender XDR implementation uses Unified RBAC or a granular RBAC configuration:
Unified RBAC: Assign the Microsoft Entra ID Security Reader to the agent's identity account. This role provides read-only access to Defender Vulnerability Management data and automatically enforces device group scoping.
For details about mapping permissions to the Unified RBAC Security Reader role, see Microsoft Entra Global roles access in the Map Microsoft Defender XDR Unified role-based access control (RBAC) article in the Defender documentation.
Granular RBAC: Assign a custom RBAC role with permissions equivalent to the Unified RBAC Security Reader role. For example, the permission View data – Defender Vulnerability Management is required, as it maps to the Unified RBAC permission of Security posture / Posture management / Vulnerability management (read).
Ensure the agent’s identity is scoped in Microsoft Defender to include all relevant device groups. The agent can't access or report on devices outside its assigned scope.
Security Copilot Roles:
- To set up or remove an agent, the admin must be a Copilot owner.
- To work with the installed agent, the admin must be a Copilot contributor.
Important
Data that the agent reports is made visible through agent suggestions. This data might be visible to admins with access to view the agent within the Intune admin center, even when that data is outside the admins assigned Intune roles or scope.
Agent identity
By default, the Vulnerability Remediation Agent runs under the identity and permissions of the admin account that is used to set up the agent. After setup, this identity can be changed.
Changing the identity doesn’t affect the agent’s run history, which remains available.
The Agent behavior is limited to the permissions of the user identity that the agent runs under.
The agent persistently runs in the identity and permissions of the Intune admin account that is assigned as the agent’s identity.
The agent identity refreshes with each agent run and expires if the agent doesn't run for 90 consecutive days. When the expiration date nears, each Copilot owner and Copilot contributor receives a warning banner about renewal of the agent identity when they view the agent overview page. If the agent authentication expires, subsequent agent runs fail until authentication is renewed. For more information about renewing authentication, see Renew the agent later in this article.
Important
When the agent authentication is renewed, the agent begins use of the credentials of the individual who clicks on the Renew authentication button.
Limitations
An admin must manually start the agent. Once the agent starts, there are no options to stop or pause it.
Only start the agent from within the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Associated CVEs contain the count of CVEs on devices with Windows client operating system editions but excludes devices with Windows Server Editions. CVEs are classified as Low, Medium, High, and Critical according to the CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) scale.
Exposed device list includes only devices found in Microsoft Entra, and that aren't Windows Server editions.
Agent doesn't support scope tags in public preview.
Only the user who sets up the agent can view session details in the Microsoft Security Copilot portal.
Getting started
Complete the setup process to start the Vulnerability Remediation Agent for the first time:
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center with an account that has the required RBAC permissions and access to your tenants Security Copilot workspace.
On the Home screen of the admin center, find the Get started with Security Copilot banner and select the Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview) tile. The admin center opens the Endpoint security > Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview) page:
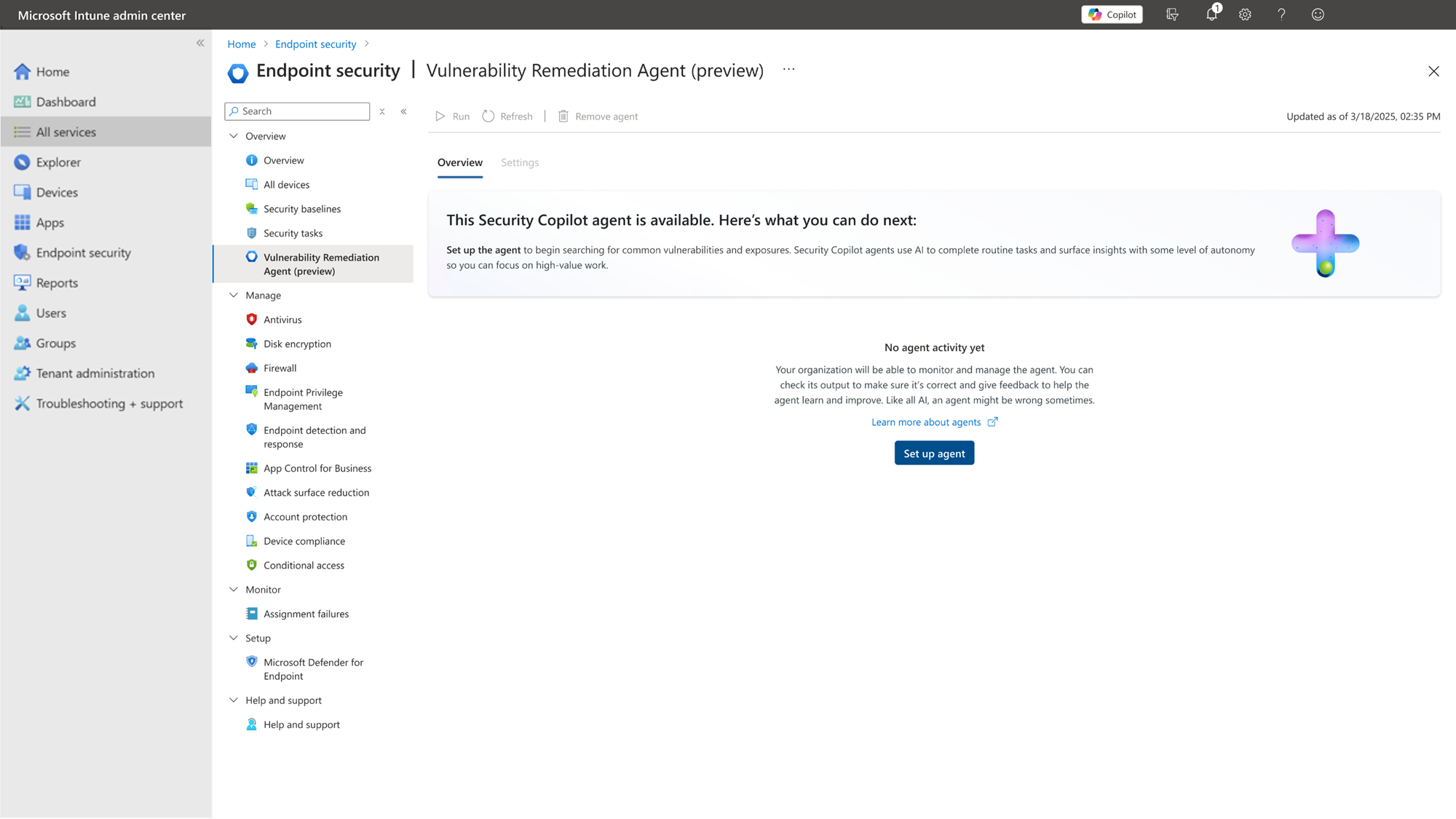
Select Set up Agent to open the set-up pane. This pane displays details about the agent but doesn’t require any configuration. Review the details to ensure requirements are in place, and then select Start agent to close the set-up pane and start the first run of the agent.
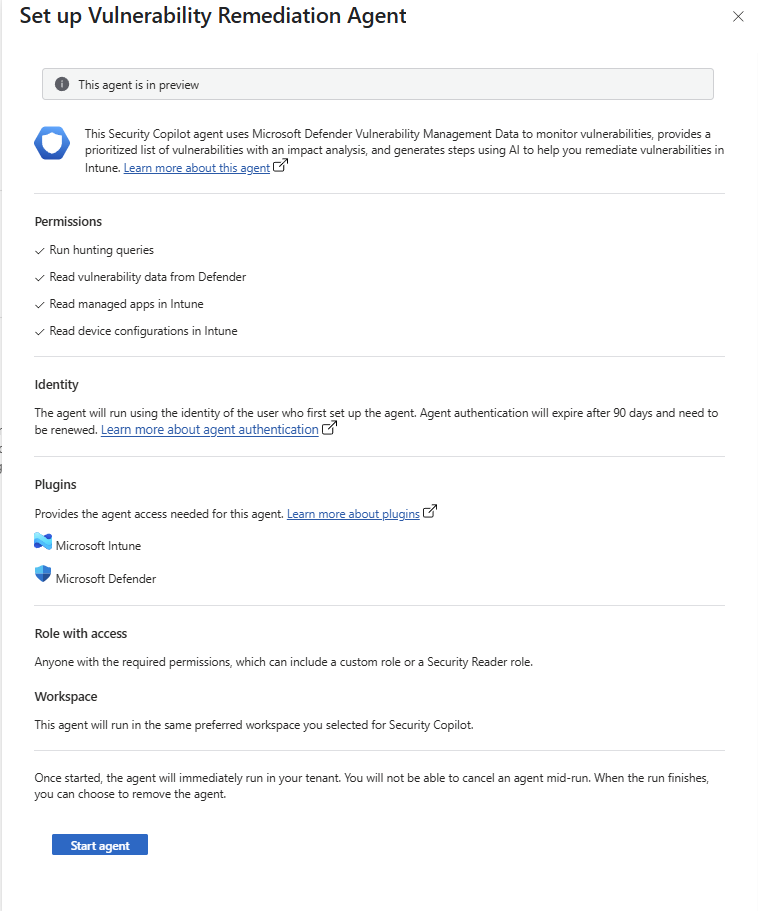
The agent runs until it finishes and then displays its results in the Vulnerability Remediation Agent pane of the admin center.
Manage vulnerabilities and the agent
After the agent completes its initial run, admins can review and manage the Vulnerability Remediation Agent suggestions In the Intune admin center. Go to Endpoint security > Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview). By default, the agent page opens to the Overview tab. On this tab, admins can view the prioritized list of vulnerabilities, drill in for more details and remediation steps, and view the agent run history.
The other available tab is Settings tab, which provides limited details about the agent’s configuration.
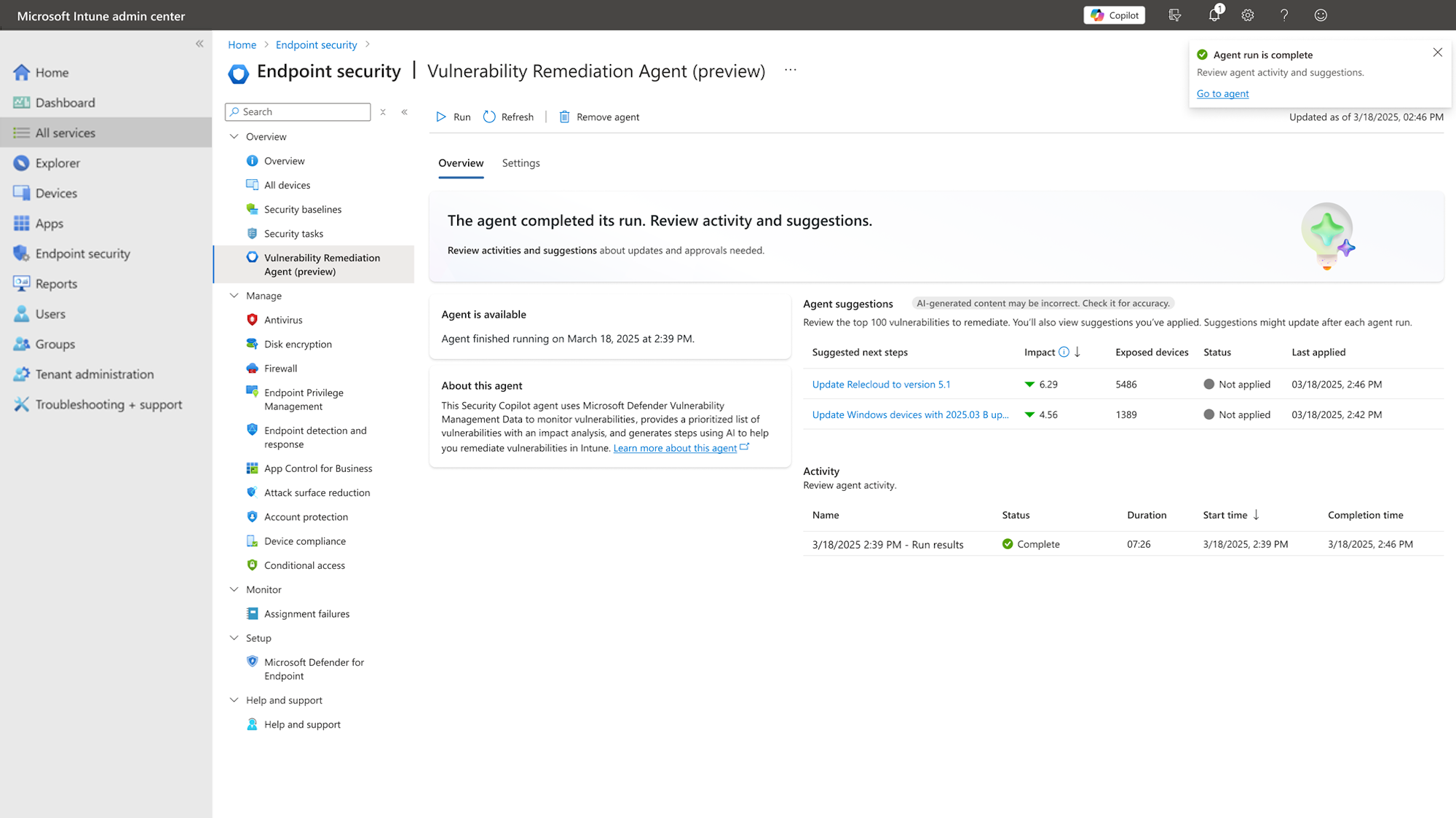
Overview tab
After the Vulnerability Remediation Agent completes a run, the Overview tab updates with the agents prioritized list of top vulnerabilities.
The following information is available on this tab:
- The agent’s availability and run status
- Agent suggestions, which are the prioritized list of vulnerabilities.
- The list of past agent activity.
Agent suggestions
Agent suggestions are a prioritized list of the top vulnerabilities identified based on the data from Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management. This information can differ slightly from the same information you can view in the Microsoft Defender console.
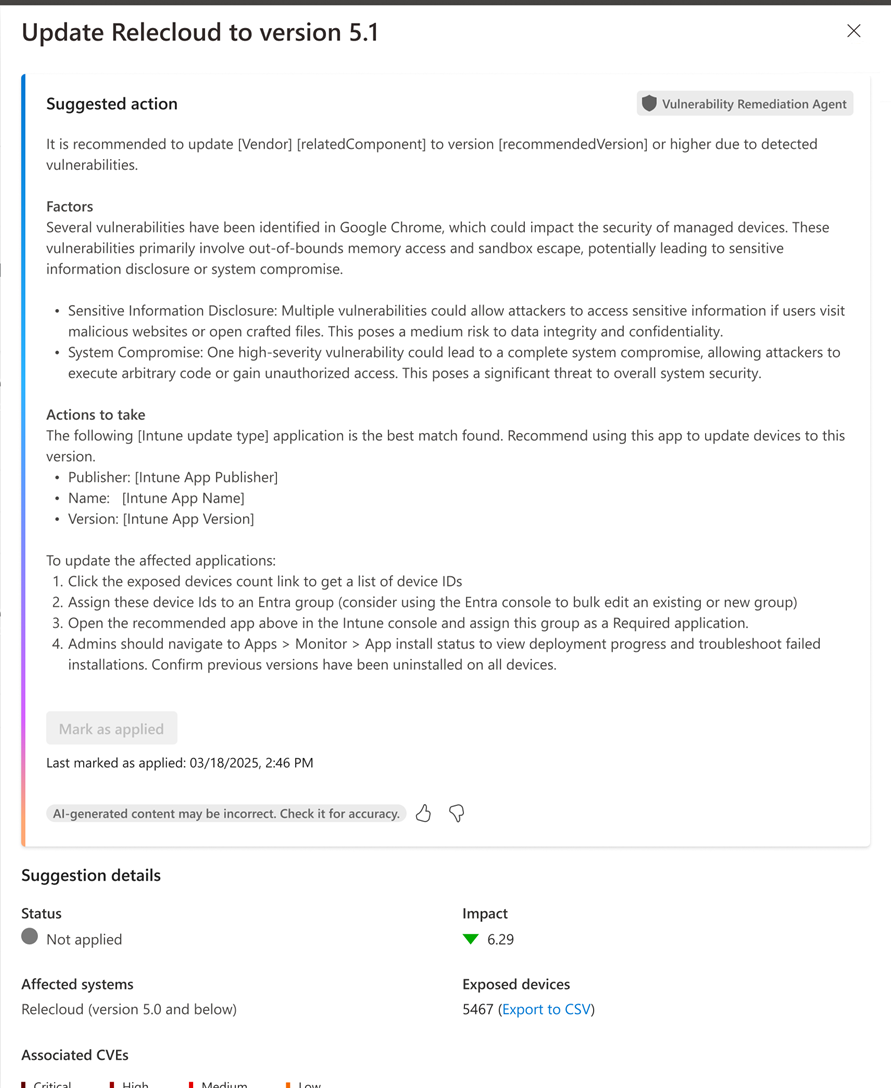
This list also displays the following column details:
Suggested next steps: Each suggested next step is a link that opens a Suggested action pane.
Suggested action: On the Suggested action pane, you can find the following information:
- Details about the associated vulnerabilities (for Intune managed devices).
- Suggested actions to take to remediate the threat.
- A Configurations section that details available settings from the Intune settings catalog that you can deploy to help reduce your device attack surface against vulnerabilities.
- An option to mark the remediation as Applied.
Remediation guidance falls into the following categories:
Apps - To remediate apps the agent might recommend deployment of an updated app, or of an Intune profile to help manage what the app can do or be used to do that represents a threat.
Windows – To remediate Windows vulnerabilities, common recommendations include deployment of a quality update policy or the expedited deployment of a quality update policy using Windows update rings to resolve the threat.
When a recommendation involves a Windows update, the agent guidance includes details about the use of update rings to help manage a more controlled rollout of the update.
Important
Some suggested Windows updates recommendations begin with Expedite. The agent uses this format when the CVE’s Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) score reaches a risk value of 9.0 or greater. For this level of risk, the agent recommends expediting these updates to your devices immediately. To help you deploy these more critical updates, the guidance includes how to use Expedited installation of quality updates, to more rapidly deploy the recommended update.
In the Configurations section, the agent provides details for creating a device configuration policy by using available settings from the settings catalog. This guidance is provided to help you reduce your attack surface against the vulnerabilities and includes:
- A list of the relevant settings you can configure through an Intune settings catalog policy. Only settings that are relevant to the vulnerability are listed.
- Each setting is presented with the recommended configuration.
- Selecting the citation icon next to a setting displays that settings description. That description can also include a link to content for the underlying device Configuration Service Provider (CSP) that the setting represents.
If there are no recommended device configuration settings to deploy, the Configurations section indicates that no recommended settings catalog policy configurations are available.
The following image shows the Configurations section from a Suggested action pane for a Windows 11 update task:
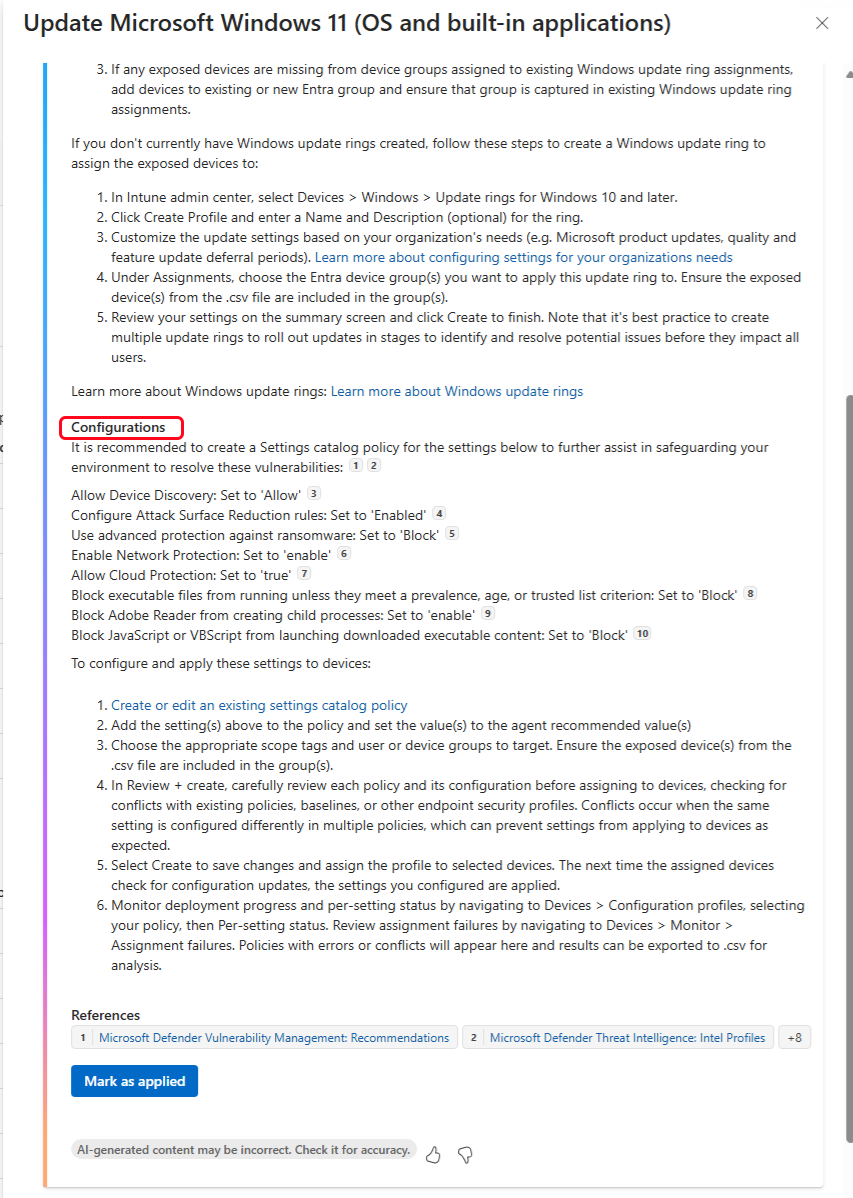
After an admin reviews agent suggestions and applies a recommended remediation, they can self-attest to applying those remediations by selecting Mark as applied. This action confirms that the remediation steps are complete. Marking a suggestion as applied doesn’t trigger any device changes by the agent but does add a timestamp called Last marked as applied to the suggestion that identifies the time of that attestation.
With subsequent runs of the agent, suggestions might be updated. If the previous suggestion was marked as applied, admins can self-attest to applying the more recent suggestions by selecting Make update as applied. This action updates the Last marked as applied timestamp to the current time.
While optional, marking a suggested action as applied helps track when a suggested remediation was implemented. Recommendations marked as applied persist in the agent suggestions list, serving as a baseline for future runs of the agent, allowing you to compare new results and changes for that same vulnerability.
Impact: This value is the potential impact the exposure score as identified by Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management.
Exposed devices: The count of affected devices. The associated CVEs number count shown by the agent is only for devices with Windows client operating system editions and doesn't include server editions. The devices listed in the export to .csv removes any devices not found in Microsoft Entra.
Tip
The agent doesn't support scope tags during the public preview.
Status: By default, a reported vulnerability has its status set to Not applied. An admin can drill into a reported vulnerability to review and deploy the suggested remediation, and then select the option to mark that suggestion as applied, which changes the status of the agent’s suggestion to Applied. Mark as applied confirms that an admin attests to having completed the remediation steps. No action is taken on devices by the agent.
Last applied: This value identifies the date and time that an admin selected the option to mark the remediation guidance as applied.
Activity
This section tracks the current and past run activity of the agent. When the agent is still actively running, the Status column displays Run in progress. The status column displays Complete for past agent runs.
Settings tab
On the Vulnerability Remediation Agent Settings tab, admins can view the existing details about the current configuration of the agent. You can also view details about the agents Identity, and choose to assign a different identity to run the agent.
Run the agent
To manually run the Vulnerability Remediation Agent, in the Intune admin center, go to Endpoint security > Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview) and on the Overview tab, select Start agent. This option isn’t available until after the agent is set-up and completes its first run.
When an agent run starts, the agent runs until it completes its evaluation. It can’t be stopped or paused.
Each time the agent runs, it runs under the identity and permissions of the Intune administrator that its been configured to use.
Renew the agent
If the agent remains unused for 90 days, the agent authorization can expire. As the agent authorization period approaches expiration, Intune raises an alert that's visible to each Copilot owner and Copilot contributor in a warning banner on the agent overview page. The warning alerts Copilot owners and contributors to the end of the authorized period and prompts for the renewal of the agent identity. If the agent authentication expires, subsequent agent runs fail until reauthentication. Renewal of the agent authentication can be performed before the expiration and after expiration.
To reauthorize the agent identity, select Renew authentication. After renewal, the warning banner disappears, and a toast notification appears to validate that renewal is successful.
Important
When the agent authentication is renewed, the agent uses the credentials of the individual who selects Renew authentication. If you don't want the identity to change, make sure the user who authorizes renewal is the same user who the agent identity was already under.
Change the agent identity
By default, the agent runs under the identity of the administrative user who set up the agent in the tenant. After setup, the agent identity can change when a different user renews the agent, and by editing the agent settings to explicitly assign a new agent identity.
A change of the agent identity doesn’t affect the agent’s run history.
To assign a new identity, in the Intune admin center, go to Endpoint security > Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview) and select the Settings tab. Under Identity, you can see the current user account that the agent runs under. Select Choose another identity to open an account sign-in prompt. Select and then authenticate a new account to use as the agents identity.
Important
Agent behavior is limited to the level of permissions that are assigned to the identity of the user the agent runs under. When the user whose identity the agent runs under has insufficient permissions, the agent fails to run.
Remove the agent
To remove the Vulnerability Remediation Agent, in the Intune admin center , go to Endpoint security > Vulnerability Remediation Agent (preview) and select Remove agent. After an admin accepts the prompt, the agent is removed, and the agent pane is restored to its original state.
Note
To remove the agent instance, the admin account must have the Owner role in Security Copilot. An account with the Contributor role can run the agent and view results but can't manage the agent instance.
Warning
When an agent is removed, all existing agent suggestions are deleted. This includes details about suggestions that were marked as Applied.
Later, an admin can run through the agent set-up to reinstall it.
Vulnerability Remediation Agent logs
During the public preview, there are limited logs available for the agent.
All agent management, create, delete, run, and any permission failures are available in Security Copilot logs. Logging of discovered vulnerabilities or when a remediation was applied aren't available. Instead, use the options to mark a remediated vulnerability as Applied.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Error: You don’t have access to this agent – Licenses
Details: You don’t have the licenses needed to access this agent.
Review the prerequisites for the license and plugin requirements for this agent and ensure license assignments and related product license and configurations are available in your tenant.
Error: You don’t have access to this agent – Workspace
Details: You aren’t part of the workspace needed to access this agent.
This message indicates that your account doesn't have permission to view or use the Security Copilot workspace, which is configured at the time Security Copilot is added to your Tenant. Contact the administrator who installed or manages your Security Copilot subscription for assistance in gaining access, and see Understand authentication in Microsoft Security Copilot.
Error: You don’t have access to this agent – Permissions
Details: You don’t have the permissions needed to access this agent.
Review the prerequisites for the role-based access control permission required to use this agent. Work with an Intune Administrator to assign your account the required permissions.
Error: The agent encountered an error and didn't finish the run. Try running the agent again.
Details: The agent instance failed to start or successfully complete its run. Details of the failure can't be identified. Despite failing to run or complete, admins can continue to view and manage the agent suggestions from past runs.
If the agent continues to fail, it's possible that its lost authorization for its identity account and can't run until it’s reauthorized. Possible reasons for a loss of authorization include but aren't limited to:
- The agent’s authorization period of 90 days was reached.
- The user account that the agent was installed with is subject to a policy that requires periodic reauthentication.
- An access token has been revoked.
During the public preview, agent reauthorization requires that the agent is removed and then set up again.
Warning
When an agent is removed, all existing agent suggestions are deleted. This includes details about suggestions that were marked as Applied.
Related content
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management Security Copilot agents in Microsoft Intune Microsoft Security Copilot