Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
A SQL operator (preview), also called a SQL code editor, is a new data transformation capability in Microsoft Fabric eventstreams. SQL operators provide a code editing experience where you can easily define your own custom data transformation logic by using simple SQL expressions. This article describes how to use a SQL operator for data transformations in an eventstream.
Note
Eventstream artifact names that include an underscore (_) or dot (.) are not compatible with SQL operators. For the best experience, create a new eventstream without using underscores or dots in the artifact name.
Prerequisites
- Access to a workspace in the Fabric capacity license mode or the trial license mode with Contributor or higher permissions.
Add a SQL operator to an eventstream
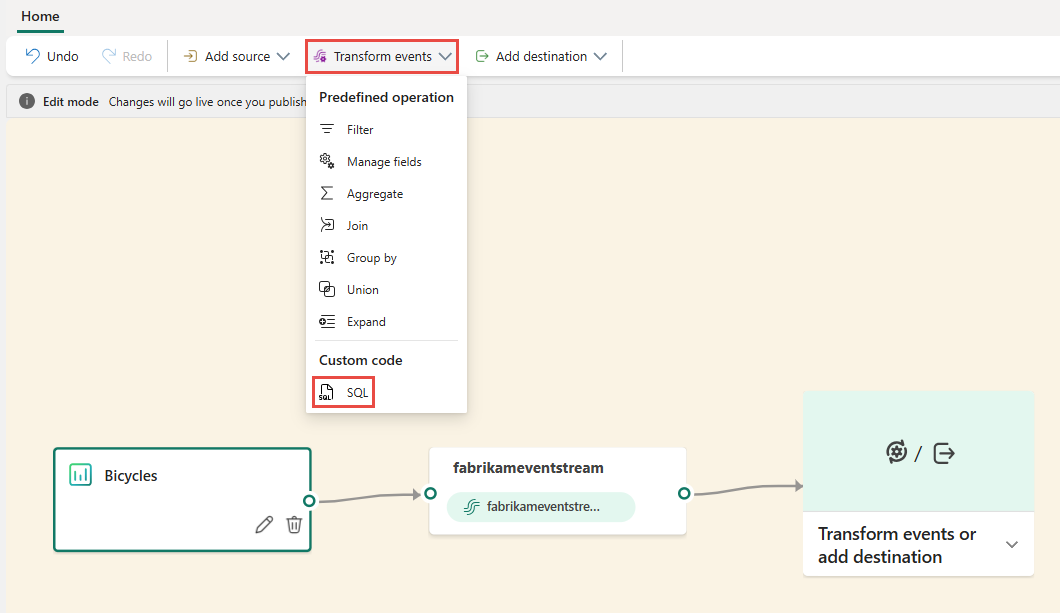
To perform stream processing operations on your data streams by using a SQL operator, add a SQL operator to your eventstream by using the following instructions:
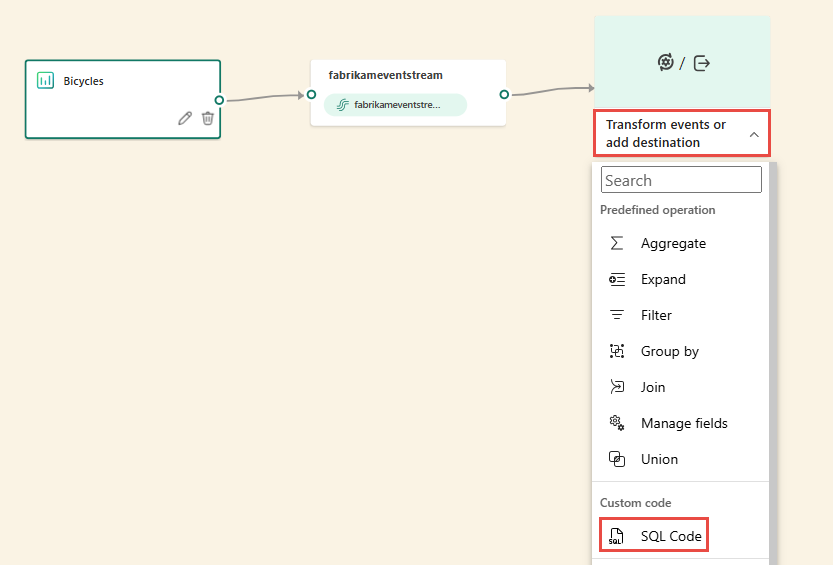
Create a new eventstream. Then add a SQL operator to it by using one of the following options:
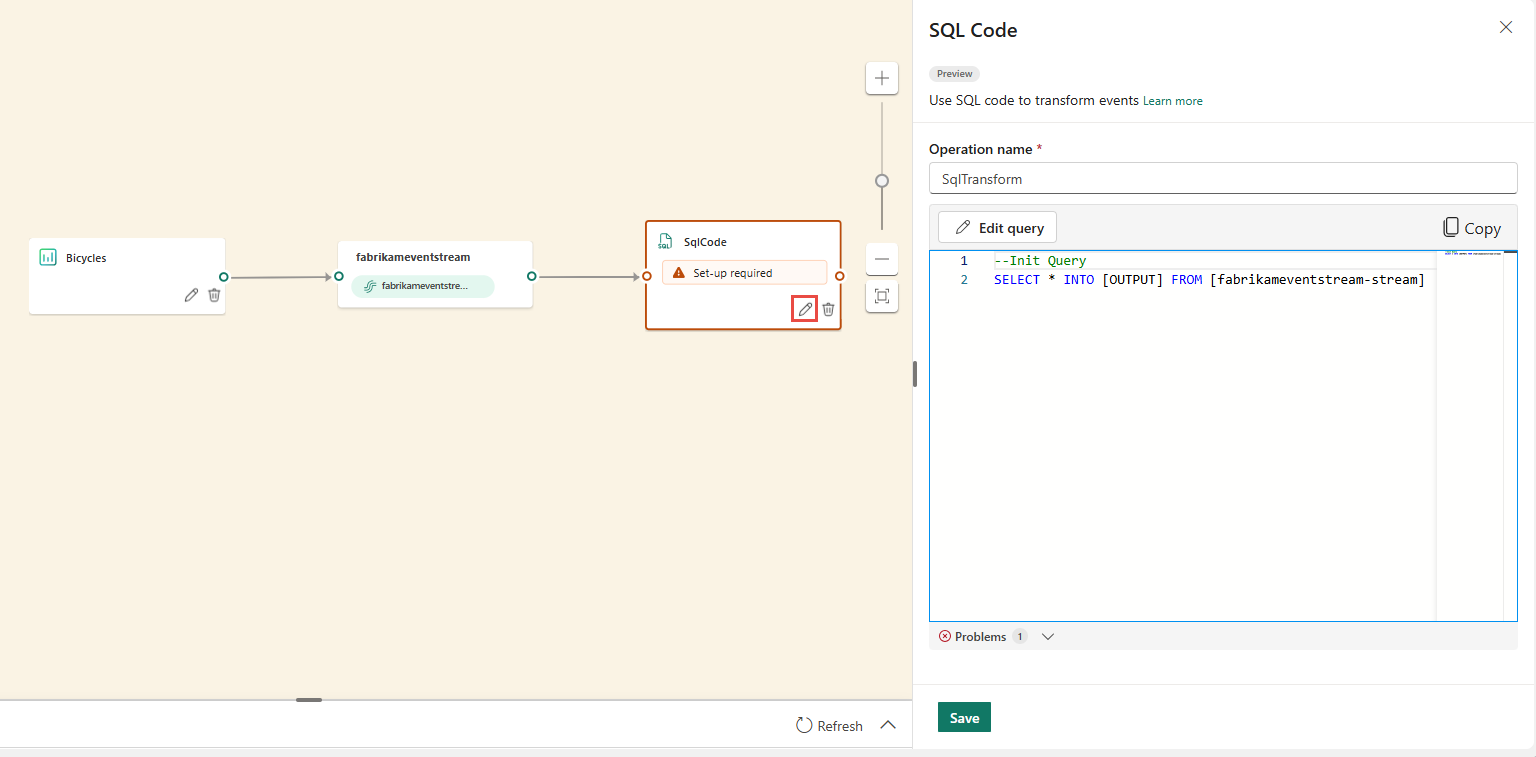
A new SQL node is added to your eventstream. Select the pencil icon to continue setting up the SQL operator.
On the SQL Code pane, specify a unique name for the SQL operator node in the eventstream.
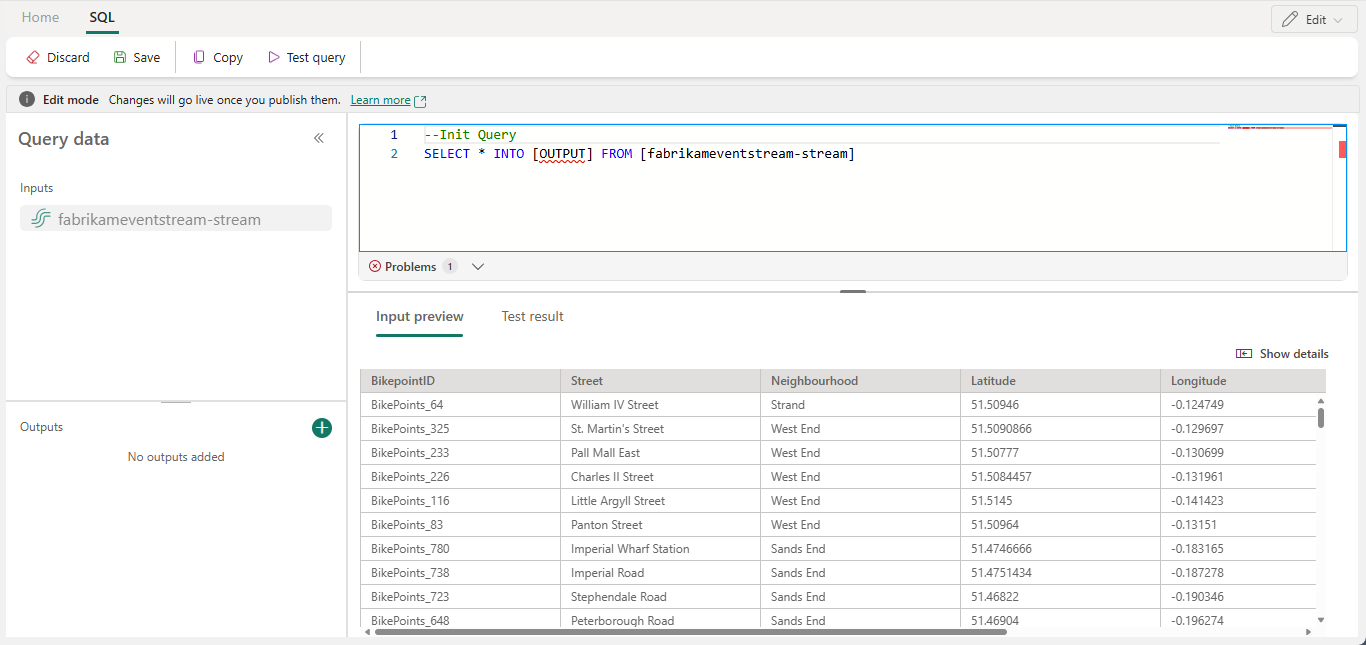
Edit the query in the query area, or select Edit query to enter the full-screen code editor view.
The full-screen code editor mode features an input/output explorer pane on the left side. The code editor section is adjustable, so you can resize it according to your preferences. The preview section at the bottom enables you to view both your input data and your query's test result.
Select the text in the Outputs section, and then enter a name for the destination node. The SQL operator supports all Real-Time Intelligence destinations, including an eventhouse, lakehouse, activator, or stream.
Specify an alias or name for the output destination where the data processed through the SQL operator is written.

Add SQL query for the required data transformation.
An eventstream is built on top of Azure Stream Analytics, and it supports the same query semantics of the Stream Analytics query language. To learn more about the syntax and usage, see Azure Stream Analytics and Eventstream Query Language Reference.
Here's the basic query structure:
SELECT column1, column2, ... INTO [output alias] FROM [input alias]This query example shows the detection of high temperatures in a room every minute:
SELECT System.Timestamp AS WindowEnd, roomId, AVG(temperature) AS AvgTemp INTO output FROM input GROUP BY roomId, TumblingWindow(minute, 1) HAVING AVG(temperature) > 75This query example shows a
CASEstatement to categorize temperature:SELECT deviceId, temperature, CASE WHEN temperature > 85 THEN 'High' WHEN temperature BETWEEN 60 AND 85 THEN 'Normal' ELSE 'Low' END AS TempCategory INTO CategorizedTempOutput FROM SensorInputOn the ribbon, use the Test query command to validate the transformation logic. Test query results appear on the Test result tab.
When you finish testing, select Save on the ribbon to get back to the eventstream canvas.
On the SQL Code pane, if the Save button is enabled, select it to save the settings.
Configure the destination.
Limitations
The SQL operator is designed to centralize all your transformation logic. As a result, you can't use it alongside other built-in operators within the same processing path. Chaining multiple SQL operators in a single path is also not supported. Additionally, the SQL operator can send output data to only the destination node in the topology.
Currently, authoring eventstream topologies is supported only through the user interface. REST API support for the SQL operator isn't available yet.