Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Index aliases are currently in public preview and available under supplemental terms of use.
In Azure AI Search, an index alias is a secondary name for a search index. You can create an alias that maps to a search index and substitute the alias name in places where you would otherwise reference an index name. This gives you flexibility if you ever need to change which index your application is pointing to. Instead of updating the references to the index name in your production code, you can just update the mapping for your alias.
You can create and manage aliases in Azure AI Search service via HTTP requests (POST, GET, PUT, DELETE) against a given alias resource. Aliases are service level resources and maintained independently from search indexes. Once a search index is created, you can create an alias that maps to that search index.
Before using an alias, your application sends requests directly to hotel-samples-index.
POST /indexes/hotel-samples-index/docs/search?api-version=2025-08-01-preview
{
"search": "pool spa +airport",
"select": "HotelId, HotelName, Category, Description",
"count": true
}
After using an alias, your application sends requests to my-alias, which maps to hotel-samples-index.
POST /indexes/my-alias/docs/search?api-version=2025-08-01-preview
{
"search": "pool spa +airport",
"select": "HotelId, HotelName, Category, Description",
"count": true
}
Supported scenarios
You can only use an alias with document operations or to get and update an index definition.
Aliases can't be used to delete an index, or test text tokenization, or be referenced as the targetIndexName on an indexer or knowledge source.
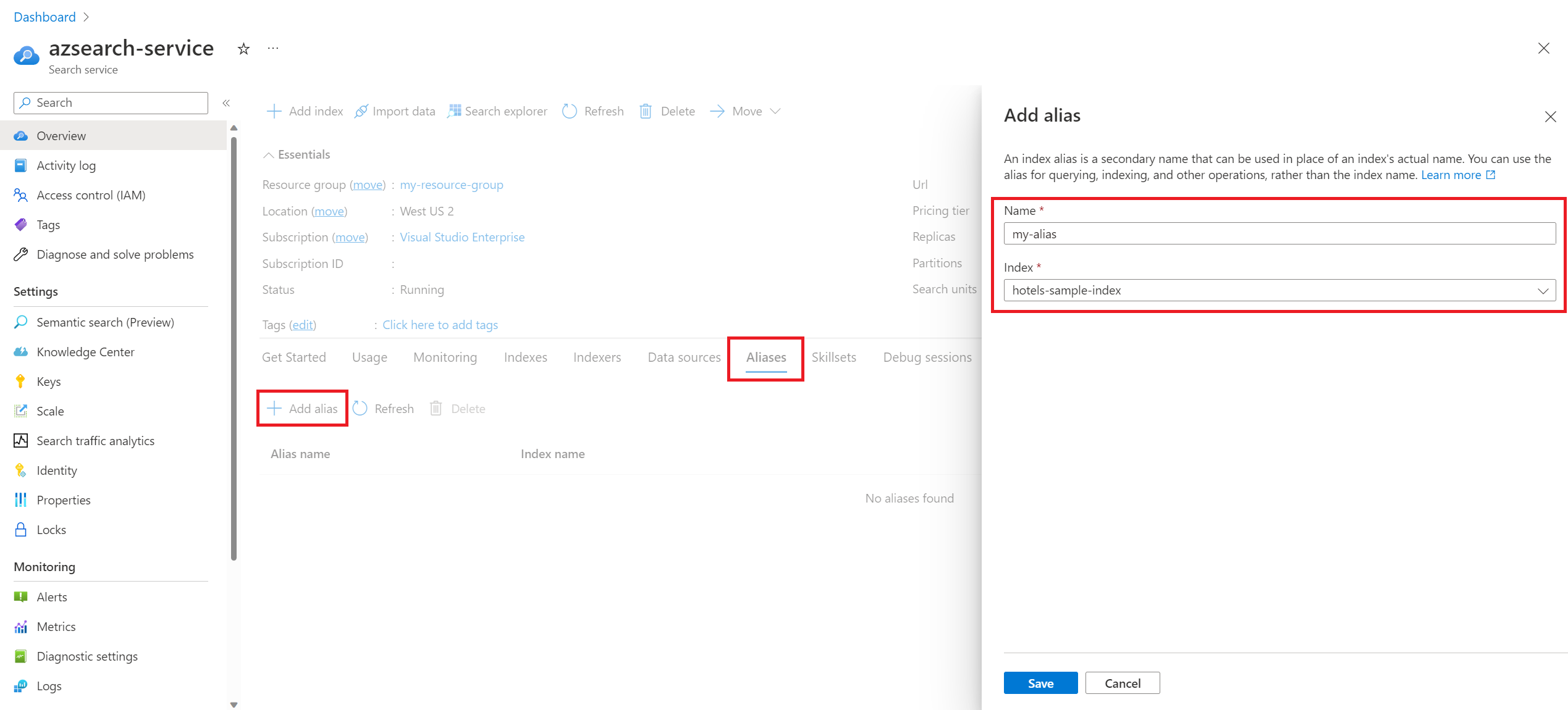
Create an index alias
Creating an alias establishes a mapping between an alias name and an index name. If the request is successful, the alias can be used for indexing, querying, and other operations.
Updating an alias allows you to map that alias to a different search index. When you update an existing alias, the entire definition is replaced with the contents of the request body. In general, the best pattern to use for updates is to retrieve the alias definition with a GET, modify it, and then update it with PUT.
You can create an alias using the preview REST API, the preview SDKs, or through the Azure portal. An alias consists of the name of the alias and the name of the search index that the alias is mapped to. Only one index name can be specified in the indexes array.
The maximum number of aliases that you can create varies by pricing tier. For more information, see Service limits.
You can use the Create or Update Alias (REST preview) to create an index alias.
POST /aliases?api-version=2025-08-01-preview
{
"name": "my-alias",
"indexes": ["hotel-samples-index"]
}
Send requests to an index alias
Aliases can be used for all document operations including querying, indexing, suggestions, and autocomplete.
This query sends the request to my-alias, which is mapped to an actual index on your search service.
POST /indexes/my-alias/docs/search?api-version=2025-08-01-preview
{
"search": "pool spa +airport",
"searchMode": any,
"queryType": "simple",
"select": "HotelId, HotelName, Category, Description",
"count": true
}
Get an alias definition
This request returns a list of existing alias objects by name.
GET https://[service name].search.windows.net/aliases?api-version=[api-version]&$select=name
api-key: [admin key]
This request returns an alias definition
GET https://[service name].search.windows.net/aliases/my-alias?api-version=[api-version]
api-key: [admin key]
Update an alias
The most common update to an alias is changing the index name when the underlying index is replaced with a newer version.
PUT is required for alias updates as described in Create or Update Alias (REST preview).
PUT /aliases/my-alias?api-version=2025-08-01-preview
{
"name": "my-alias",
"indexes": ["hotel-samples-index2"]
}
An update to an alias may take up to 10 seconds to propagate through the system so you should wait at least 10 seconds before deleting the index that the alias was previously mapped to.
If you attempt to delete an index that is currently mapped to an alias, the operation will fail with 400 (Bad Request) and an error message stating that the alias(es) that's mapped to that index must be deleted or mapped to a different index before the index can be deleted.