Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To improve the security of the Operator Nexus platform, managed identities are now supported for Operator Nexus Clusters. Managed identities provide a secure way for applications to access other Azure resources and eliminate the need for users to manage credentials. Additionally, Operator Nexus now has a user provided resource model. In addition to improved security, this shift provides a consistent user experience across the platform.
Managed identities are used with the following user resources provided on Operator Nexus Clusters:
- Storage Accounts used for the output of Bare Metal run-* commands.
- Key Vaults used for credential rotation.
- Log Analytics Workspaces (LAW) used to capture some metrics.
To learn more about managed identities in Azure, see Managed identities for Azure resources. Operator Nexus Clusters support multiple User Assigned Managed Identities (UAMI) or one system assigned managed identity (SAMI). A combination of one or more UAMIs and a SAMI is also supported.
While a user can choose to use either managed identity type, UAMIs are recommended. They allow users to preconfigure resources with the appropriate access to the UAMI in advance of Operator Nexus Cluster creation or updating. The same UAMI can be used for all resources, or if users want fine grained access, they can define UAMIs for each resource.
For information on using the API to update Cluster managed identities, see Update Cluster Identities.
Prerequisites
- Install Azure CLI.
- Install the latest version of the appropriate Azure CLI extensions.
- Storage Account managed identity support requires the
2024-07-01or later version of the NetworkCloud API. - Key Vault and Log Analytics Workspace managed identity support requires the
2025-02-01or later version of the NetworkCloud API.
Operator Nexus Clusters with User Assigned Managed Identities (UAMI)
It's a best practice to first define all of the user provided resources (Storage Account, LAW, and Key Vault), the managed identities associated with those resources and then assign the managed identity the appropriate access to the resource. If these steps aren't done before Cluster creation, the steps need to be completed before Cluster deployment.
The impacts of not configuring these resources for a new Cluster are as follows:
- Storage Account: Cluster creation fails as there's a check to ensure that
commandOutputSettingsexists on the Cluster input. - LAW: Cluster deployment fails as the LAW (Log Analytics Workspace) is required to install software extensions during deployment.
- Key Vault: Credential rotations fail as there's a check to ensure write access to the user provided Key Vault before performing credential rotation.
Updating the Cluster can be done at any time. Changing the LAW settings causes a brief disruption in sending metrics to the LAW as the extensions that use the LAW need to be reinstalled.
The following steps should be followed for using UAMIs with Nexus Clusters and associated resources.
- Create the UAMI or UAMIs
- Create the resources and assign the UAMI to the resources
- Create or update the Cluster to use User Assigned Managed Identities and user provided resources
- Deploy the Cluster (if new)
Create the UAMI or UAMIs
- Create the UAMI or UAMIs for the resources in question. For more information on creating the managed identities, see Manage user-assigned managed identities.
Create the resources and assign the UAMI to the resources
UAMI Storage Accounts setup
- Create a storage account, or identify an existing storage account that you want to use. See Create an Azure storage account.
- Create a blob storage container in the storage account. See Create a container.
- Assign the
Storage Blob Data Contributorrole to users and the UAMI that need access to the run-* command output. See Assign an Azure role for access to blob data. - To limit access to the Storage Account to a select set of IP or virtual networks, see Configure Azure Storage firewalls and virtual networks.
- The IPs for all users executing run-* commands need to be added to the Storage Account's
Virtual Networksand/orFirewalllists. - Ensure
Allow Azure services on the trusted services list to access this storage account.underExceptionsis selected.
- The IPs for all users executing run-* commands need to be added to the Storage Account's
UAMI Log Analytics Workspaces setup
- Create a Log Analytics Workspace (LAW), or identify an existing LAW that you want to use. See Create a Log Analytics Workspace.
- Assign the
Log Analytics Contributorrole to the UAMI for the log analytics workspace. See Manage access to Log Analytics workspaces.
UAMI Key Vault setup
- Create a Key Vault, or identify an existing Key Vault that you want to use. See Create a Key Vault.
- Enable the Key Vault for Role Based Access Control (RBAC). See Enable Azure RBAC permissions on Key Vault.
- Assign the
Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role (Preview)role to the UAMI for the Key Vault. See Assign role.- The role definition ID for the Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role is
44f0a1a8-6fea-4b35-980a-8ff50c487c97. This format is required if using the Azure command line to do the role assignment.
- The role definition ID for the Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role is
- To limit access to the Key Vault to a select set of IP or virtual networks, see Configure Azure Key Vault firewalls and virtual networks.
- The IPs for all users requiring access to the Key Vault need to be added to the Key Vault's
Virtual Networksand/orFirewalllists. - Ensure the
Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall.underExceptionsis selected.
- The IPs for all users requiring access to the Key Vault need to be added to the Key Vault's
Create or update the Nexus Cluster to use User Assigned Managed Identities and user provided resources
Define the UAMI(S) on the Cluster
When creating or updating a Cluster with a user assigned managed identity, use the --mi-user-assigned parameter along with the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) resource identifier of the UAMI. If you wish to specify multiple UAMIs, list the UAMIs' Azure Resource Manager (ARM) resource identifiers with a space between them. Each UAMI that's used for a Key Vault, LAW, or Storage Account must be provided in this list.
When creating the Cluster, you specify the UAMIs in --mi-user-assigned and also define the resource settings. Updating the Cluster to set or change a UAMI should also include the resource settings changes to associate the UAMI to the resource.
UAMI Storage Account settings
The --command-output-settings data construct is used to define the Storage Account where run command output is written. It consists of the following fields:
container-url: The URL of the storage account container that is to be used by the specified identities.identity-resource-id: The user assigned managed identity resource ID to use. Mutually exclusive with a system assigned identity type.identity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseUserAssignedIdentity.overrides: Optional. An array of override objects that can be used to override the storage account container and identity to use for specific types of run commands. Each override object consists of the following fields:command-output-type: The type of run command to override.container-url: The URL of the storage account container to use for the specified command type.identity-resource-id: The user assigned managed identity resource ID to use for the specified command type.identity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseUserAssignedIdentity.
Valid command-output-type values are:
BareMetalMachineRunCommand: Output from theaz networkcloud baremetalmachine run-commandcommand.BareMetalMachineRunDataExtracts: Output from theaz networkcloud baremetalmachine run-data-extractcommand.BareMetalMachineRunDataExtractsRestricted: Output from theaz networkcloud baremetalmachine run-data-extracts-restrictedcommand.BareMetalMachineRunReadCommands: Output from theaz networkcloud baremetalmachine run-read-commandcommand.StorageRunReadCommands: Output from theaz networkcloud storageappliance run-read-commandcommand.
Run command output is written to the storage account container defined in the overrides for the specific command type, using the associated identity for that override. If no matching override is found, the default container-url and identity-resource-id from the command output settings is used.
UAMI Log Analytics Workspace settings
The --analytics-output-settings data construct is used to define the LAW where metrics are sent. It consists of the following fields:
analytics-workspace-id: The resource ID of the analytics workspace that is to be used by the specified identity.identity-resource-id: The user assigned managed identity resource ID to use. Mutually exclusive with a system assigned identity typeidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseUserAssignedIdentity.
UAMI Key Vault settings
The --secret-archive-settings data construct is used to define the Key Vault where rotated credentials are written. It consists of the following fields:
identity-resource-id: The user assigned managed identity resource ID to use.identity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseUserAssignedIdentity.vault-uri: The URI for the key vault used as the secret archive.
UAMI Cluster create command examples
Example 1: This example is an abbreviated Cluster create command that uses one UAMI across the Storage Account, LAW, and Key Vault.
az networkcloud cluster create --name "clusterName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
...
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
--command-output-settings identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer" \
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
--secret-archive-settings vault-uri="https://mykv.vault.azure.net/" \
identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI"
Example 2: This example is an abbreviated Cluster create command that uses two UAMIs. The Storage Account and LAW use the first UAMI and the Key Vault uses the second.
az networkcloud cluster create --name "clusterName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
...
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myFirstUAMI" "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/mySecondUAMI" \
--command-output-settings identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myFirstUAMI" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer" \
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myFirstUAMI" \
--secret-archive-settings vault-uri="https://mykv.vault.azure.net/" \
identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/mySecondUAMI"
Cluster update examples
Updating a Cluster is done as a single step. Update the cluster to include the UAMI in the --mi-user-assigned field and the corresponding --identity-resource-id for the Storage Account, LAW, or Key Vault.
If there are multiple UAMIs in use, the full list of UAMIs must be specified in the --mi-user-assigned field when updating. If a SAMI is in use on the Cluster and you're adding a UAMI, you must include --mi-system-assigned in the update command. Failure to include existing managed identities causes them to be removed.
For LAW and Key Vault, transitioning from the existing data constructs to the new constructs that use managed identities can be done via a Cluster Update.
Example 1: Add a UAMI to a Cluster and assign the UAMI (myUAMI) to the secret archive settings (Key Vault). If this Cluster had a SAMI defined, the SAMI would be removed.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
--secret-archive-settings identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
vault-uri="https://keyvaultname.vault.azure.net/"
Example 2: Add UAMI mySecondUAMI to a Cluster that already has myFirstUAMI, which is retained, and update the Cluster to assign mySecondUAMI to the command output settings (Storage Account).
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myFirstUAMI" "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/mySecondUAMI" \
--command-output-settings identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/mySecondUAMI" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer"
Example 3: Update a Cluster that already has a SAMI and add a UAMI and assign the UAMI to the log analytics output settings (LAW). The SAMI is retained.
Caution
Changing the LAW settings causes a brief disruption in sending metrics to the LAW as the extensions that use the LAW might need to be reinstalled.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
--mi-system-assigned \
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="UserAssignedIdentity" \
identity-resource-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI"
View the principal ID for the User Assigned Managed Identity
The identity resource ID can be found by selecting "JSON view" on the identity resource; the ID is at the top of the panel that appears. The container URL can be found on the Settings -> Properties tab of the container resource.
The Azure CLI is another option for viewing the identity and the associated principal ID data within the cluster.
Example:
az networkcloud cluster show --ids /subscriptions/<Subscription ID>/resourceGroups/<Cluster Resource Group Name>/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/<Cluster Name>
Output:
"identity": {
"type": "UserAssigned",
"userAssignedIdentities": {
"/subscriptions/subscriptionID/resourcegroups/<resourceGroupName>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<userAssignedIdentityName>": {
"clientId": "00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444",
"principalId": "bbbbbbbb-cccc-dddd-2222-333333333333"
}
}
},
Operator Nexus Clusters with a System Assigned Managed Identity
Using a System Assigned Managed Identity (SAMI) follows a slightly different pattern from UAMIs. While the user provided resources (Storage Account, LAW and Key Vault) should be included in the Cluster creation command or template, the SAMI doesn't exist until the Cluster is created. After Cluster creation, users need to query the Cluster to get the SAMI, assign the correct privileges to the SAMI for each resource before deploying the Cluster.
For a new Cluster, these steps need to be completed before Cluster deployment. The impacts of not configuring these resources by deployment time for a new Cluster are as follows:
- Storage Account: Cluster creation fails as there's a check to ensure that
commandOutputSettingsexists on the Cluster input. - LAW: Cluster deployment fails as the LAW is required to install software extensions during deployment.
- Key Vault: Credential rotations fail as there's a check to ensure write access to the user provided Key Vault before performing credential rotation.
Updating the Cluster can be done at any time. Changing the LAW settings causes a brief disruption in sending metrics to the LAW as the extensions that use the LAW need to be reinstalled.
The following steps should be followed for using UAMIs with Nexus Clusters and associated resources.
Cluster Creation:
- Create the user provided resources
- Create the Cluster with a SAMI and specify the resources that use the SAMI
- Get the SAMI by querying the Cluster
- Update the resources and assign the SAMI to the resources
- Deploy the Cluster
Cluster Update:
- Create the user provided resources
- Add a SAMI via Cluster update
- Get the SAMI by querying the Cluster
- Update the resources and assign the SAMI to the resources
- Update the Cluster with the user provided resources information
Initial user provided resources creation
This section provides external links for the user resource setup that needs to occur before Cluster creation.
Initial Storage Accounts setup
- Create a storage account, or identify an existing storage account that you want to use. See Create an Azure storage account.
- Create a blob storage container in the storage account. See Create a container.
Initial Log Analytics Workspaces setup
- Create a Log Analytics Workspace (LAW), or identify an existing LAW that you want to use. See Create a Log Analytics Workspace.
Initial Key Vault setup
- Create a Key Vault, or identify an existing Key Vault that you want to use. See Create a Key Vault.
Create the Cluster with a SAMI and user provided resources
When creating a Cluster with a system assigned managed identity, use the --mi-system-assigned parameter. The Cluster creation process generates the SAMI information. The user provided resources are also defined at the time of Cluster creation.
SAMI Storage Account settings
The --command-output-settings data construct is used to define the Storage Account where run command output is written. It consists of the following fields:
container-url: The URL of the storage account container that is to be used by the specified identities.identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.
SAMI Log Analytics Workspace settings
The --analytics-output-settings data construct is used to define the LAW where metrics are sent. It consists of the following fields:
analytics-workspace-id: The resource ID of the analytics workspace that is to be used by the specified identity.identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.
SAMI Key Vault settings
The --secret-archive-settings data construct is used to define the Key Vault where rotated credentials are written. It consists of the following fields:
identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.vault-uri: The URI for the key vault used as the secret archive.
SAMI Cluster create command example
Example: This example is an abbreviated Cluster create command that specifies a SAMI and uses the SAMI for each of the user provided resources.
az networkcloud cluster create --name "clusterName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
...
--mi-system-assigned \
--command-output-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer"
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
--secret-archive-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
vault-uri="https://keyvaultname.vault.azure.net/"
Add a SAMI via Cluster update
When updating a Cluster with a system assigned managed identity, use the --mi-system-assigned parameter. The Cluster update process generates the SAMI information. The user provided resources are updated later to use the SAMI once the appropriate role assignments are made.
Important
When updating a Cluster with a UAMI or UAMIs in use, you must include the existing UAMIs in the --mi-user-assigned identity list when adding a SAMI or updating. If a SAMI is in use on the Cluster and you're adding a UAMI, you must include --mi-system-assigned in the update command. Failure to do so causes the respective managed identities to be removed.
These examples are for updating an existing Cluster to add a SAMI.
Example 1: This example updates a Cluster to add a SAMI. Any UAMIs defined on the Cluster are removed.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
--mi-system-assigned
Example 2: This example updates a Cluster to add a SAMI and keeps the existing UAMI, myUAMI.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
--mi-user-assigned "/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/myUAMI" \
--mi-system-assigned
Get the SAMI by querying the Cluster
The identity resource ID can be found by selecting "JSON view" on the identity resource in the Azure portal.
The CLI can also be used to view the identity and the associated principal ID data within the cluster.
Note the principalId of the identity that is used when granting access to the resources.
Example:
az networkcloud cluster show --ids /subscriptions/<Subscription ID>/resourceGroups/<Cluster Resource Group Name>/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/<Cluster Name>
System-assigned identity example:
"identity": {
"principalId": "aaaaaaaa-bbbb-cccc-1111-222222222222",
"tenantId": "aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee",
"type": "SystemAssigned"
},
Update the resources and assign the SAMI to the resources
These updates are applicable post Cluster creation or update to ensure that the SAMI has the appropriate role assignments and the resources are configured properly for Operator Nexus usage.
SAMI Storage Accounts setup
- Assign the
Storage Blob Data Contributorrole to users and the SAMI that need access to the run-* command output. See Assign an Azure role for access to blob data. - To limit access to the Storage Account to a select set of IP or virtual networks, see Configure Azure Storage firewalls and virtual networks.
- The IPs for all users executing run-* commands need to be added to the Storage Account's
Virtual Networksand/orFirewalllists. - Ensure
Allow Azure services on the trusted services list to access this storage account.underExceptionsis selected.
- The IPs for all users executing run-* commands need to be added to the Storage Account's
SAMI Log Analytics Workspaces setup
- Assign the
Log Analytics Contributorrole to the SAMI for the log analytics workspace. See Manage access to Log Analytics workspaces.
SAMI Key Vault setup
- Enable the Key Vault for Role Based Access Control (RBAC). See Enable Azure RBAC permissions on Key Vault.
- Assign the
Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role (Preview)role to the SAMI for the Key Vault. See Assign role.- The role definition ID for the Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role is
44f0a1a8-6fea-4b35-980a-8ff50c487c97. This format is required if using the Azure command line to do the role assignment.
- The role definition ID for the Operator Nexus Key Vault Writer Service Role is
- To limit access to the Key Vault to a select set of IP or virtual networks, see Configure Azure Key Vault firewalls and virtual networks.
- The IPs for all users requiring access to the Key Vault need to be added to the Key Vault's
Virtual Networksand/orFirewalllists. - Ensure the
Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall.underExceptionsis selected.
- The IPs for all users requiring access to the Key Vault need to be added to the Key Vault's
Update the Cluster with the user provided resources information
This step is only required after updating a Cluster to add a SAMI and should be performed after updating the resources to assign the SAMI the appropriate role or roles.
SAMI Storage Account update settings
The --command-output-settings data construct is used to define the Storage Account where run command output is written. It consists of the following fields:
container-url: The URL of the storage account container that is to be used by the specified identities.identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.
SAMI Log Analytics Workspace update settings
The --analytics-output-settings data construct is used to define the LAW where metrics are sent. It consists of the following fields:
analytics-workspace-id: The resource ID of the analytics workspace that is to be used by the specified identity.identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.
SAMI Key Vault update settings
The --secret-archive-settings data construct is used to define the Key Vault where rotated credentials are written. It consists of the following fields:
identity-resource-id: Not required when using a SAMIidentity-type: The type of managed identity that's being selected. UseSystemAssignedIdentity.vault-uri: The URI for the key vault used as the secret archive.
SAMI Cluster update examples
Updating a Cluster follows the same pattern as create. If you need to change the UAMI for a resource, you must include it in both the --mi-user-assigned field and corresponding --identity-resource-id for the Storage Account, LAW or Key Vault. If there are multiple UAMIs in use, the full list of UAMIs must be specified in the --mi-user-assigned field when updating.
For LAW and Key Vault, transitioning from the existing data constructs to the new constructs that use UAMI can be done via a Cluster Update.
Example 1: Add or update the command output settings (Storage Account) for a Cluster.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--command-output-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer"
Example 2: Add or update the log analytics output settings (LAW) for a Cluster.
Caution
Changing the LAW settings causes a brief disruption in sending metrics to the LAW as the extensions that use the LAW need to be reinstalled.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
Example 3: Add or update the secret archive settings (Key Vault) for a Cluster.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--secret-archive-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
vault-uri="https://keyvaultname.vault.azure.net/"
Example 4: This example combines all three resources using a SAMI into one update.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "clusterName" --resource-group "resourceGroupName" \
--command-output-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
container-url="https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer"
--analytics-output-settings analytics-workspace-id="/subscriptions/subscriptionId/resourceGroups/resourceGroupName/providers/microsoft.operationalInsights/workspaces/logAnalyticsWorkspaceName" \
identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
--secret-archive-settings identity-type="SystemAssignedIdentity" \
vault-uri="https://keyvaultname.vault.azure.net/"
Update Cluster identities via APIs
Cluster managed identities can be assigned via CLI. The unassignment of the identities can be done via API calls.
Note, <APIVersion> is the API version 2024-07-01 or newer.
To remove all managed identities, execute:
az rest --method PATCH --url /subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$CLUSTER_RG/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME?api-version=<APIVersion> --body "{\"identity\":{\"type\":\"None\"}}"If both User-assigned and System-assigned managed identities were added, the User-assigned can be removed by updating the
typetoSystemAssigned:az rest --method PATCH --url /subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$CLUSTER_RG/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME?api-version=<APIVersion> --body @~/uai-body.jsonThe request body (uai-body.json) example:
{ "identity": { "type": "SystemAssigned" } }If both User-assigned and System-assigned managed identities were added, the System-assigned can be removed by updating the
typetoUserAssigned:az rest --method PATCH --url /subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$CLUSTER_RG/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME?api-version=<APIVersion> --body @~/uai-body.jsonThe request body (uai-body.json) example:
{ "identity": { "type": "UserAssigned", "userAssignedIdentities": { "/subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$UAI_RESOURCE_GROUP/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/$UAI_NAME": {} } } }If multiple User-assigned managed identities were added, one of them can be removed by executing:
az rest --method PATCH --url /subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$CLUSTER_RG/providers/Microsoft.NetworkCloud/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME?api-version=<APIVersion> --body @~/uai-body.jsonThe request body (uai-body.json) example:
{ "identity": { "type": "UserAssigned", "userAssignedIdentities": { "/subscriptions/$SUB_ID/resourceGroups/$UAI_RESOURCE_GROUP/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/$UAI_NAME": null } } }
Field deprecations and replacements
This section is a reference for the deprecated resource fields and their replacements. All fields are found on the Cluster resource except for the Cluster Manager managed identity used for the deprecated key vault method. This list also assumes that an associated managed identity is defined on the Cluster that corresponds with the managed identity for the resource.
identity-resource-id is only required when using a UAMI. It shouldn't be specified if using a SAMI for the resource.
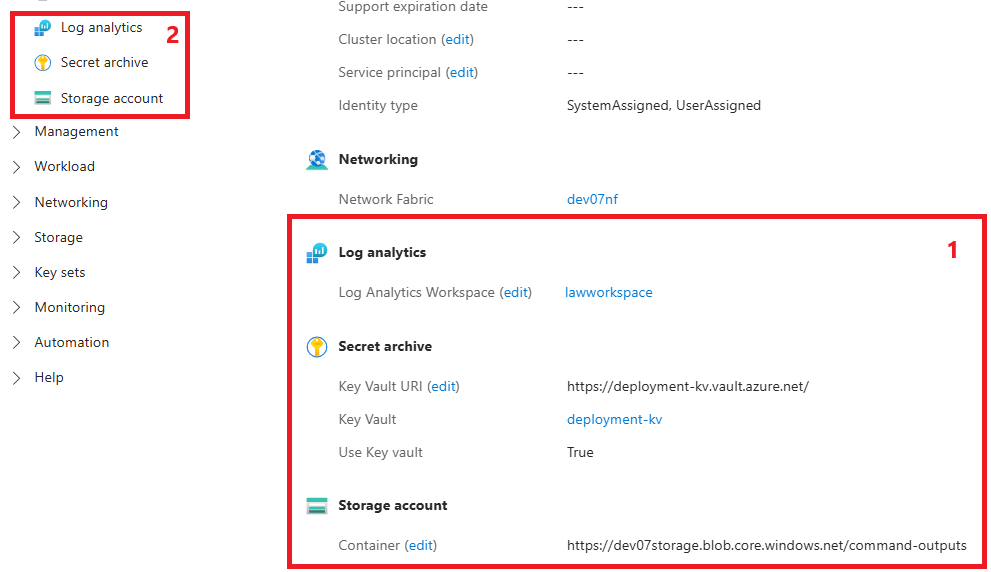
Cluster Overview
Cluster Overview in the Azure portal reflects the new data fields.
- The Overview Properties section contains read only views for
Log analytics,Secret archive(Key Vault), andStorage account.- Selecting
editnext to each resource takes you to the resource specific page within Operator Nexus and allows for updating the resource & managed identity information.
- Selecting
- The
Settingsnavigation menu provides links to manage each of the resources.
Note
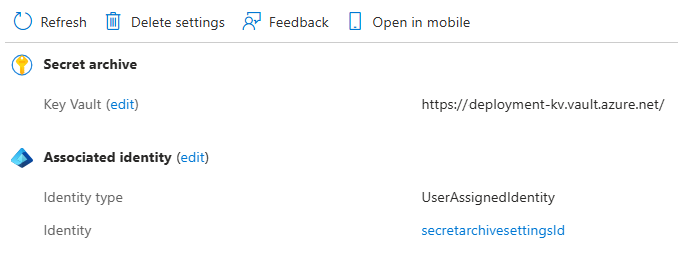
The Secret Archive example reflects an instance where the Cluster was updated to populate secretArchiveSettings with the Key Vault URI and associated managed identity, but the legacy secretArchive fields remain populated. The Overview reflects both fields from a display perspective but the system only uses the secretArchiveSettings. If just secretArchiveSettings is populated, then only Key Vault URI is populated. The Key Vault field would be empty.
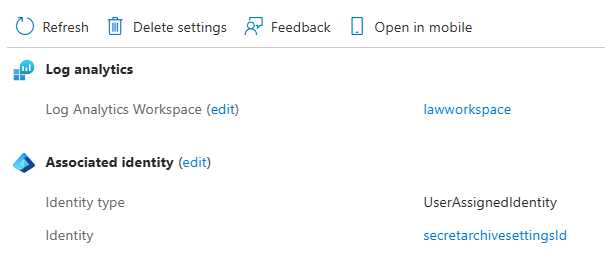
Log Analytics Workspace
Deprecated Fields: analytics-workspace-id
The LAW information is provided and viewed via the analytics-output-settings data construct.
Replacing Fields:
analytics-output-settings:
analytics-workspace-id
identity-type
identity-resource-id
The input format (LAW Azure Resource Manager (ARM) resource ID) is the same between the deprecated analytics-workspace-id field and the analytics-workspace-id within analytics-output-settings. The system updates the deprecated analytics-workspace-id field with the analytics-output-settings:analytics-workspace-id field. Updating the deprecated was done for backwards compatibility purposes during the transition period when moving from using the Service Principal to managed identity for authentication. It no longer has any use but is still present.
Key Vault
Deprecated Fields:
cluster-secret-archive:
use-key-vault
key-vault-id
The Cluster Manager managed identity is used for authentication.
Replacing Fields:
The Key Vault information is provided and viewed via the secret-archive-settings data construct. The Cluster managed identity is used in this construct.
secret-archive-settings:
vault-uri
identity-type
identity-resource-id
vault-uri in secret-archive-settings is the URI for the Key Vault being specified versus the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) resource ID that is specified for key-vault-id. The same managed identity that was specified for the Cluster Manager can be used on the Cluster.
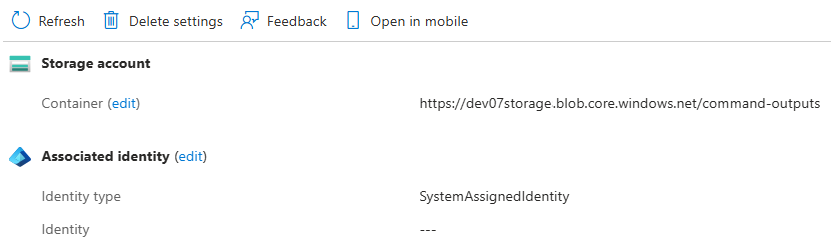
Storage Account
Deprecated Fields: N/A - Previously, the Storage Account was automatically created as part of Cluster Manager creation and didn't require customer input.
Replacing Fields:
The Storage Account information is provided and viewed via the command-output-settings data construct.
command-output-settings:
container-url
identity-type
identity-resource-id