Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can clone an existing Azure IoT Operations instance to create a new instance with the same configuration and settings. Cloning is useful for creating a backup of your instance or for setting up a new instance with the same configuration for testing or development purposes.
Use-case scenarios for clone include:
- Disaster recovery: Create a backup of your Azure IoT Operations instance that can be used to restore the instance if there's a disaster.
- Testing and development: Set up a new Azure IoT Operations instance with the same configuration as an existing instance for testing or development purposes.
- Migration: Move your Azure IoT Operations instance to a new cluster or resource group by cloning the instance to the new location.
- Scaling: Create multiple instances of your Azure IoT Operations instance to handle increased workload or to distribute the load across multiple instances.
Note
The clone feature is in preview and under development.
Prerequisites
An Azure IoT Operations instance deployed to a cluster. For more information, see Deploy Azure IoT Operations.
Azure CLI installed on your development machine. This scenario requires Azure CLI version 2.53.0 or higher. Use
az --versionto check your version andaz upgradeto update if necessary. For more information, see How to install the Azure CLI.The Azure IoT Operations extension for Azure CLI. Clone is currently compatible with the following IoT Operations instance version range:
1.0.34>=,<1.2.0. Use the following command to update or install the extension. Replace<VERSION_NUMBER>with a version that is compatible with your instance.az extension add --upgrade --name azure-iot-ops --version <VERSION_NUMBER>
Clone command overview
Use the az iot ops clone command to create a new Azure IoT Operations instance based on an existing one.
The clone command analyzes an Azure IoT Operations instance and reproduces it in an infrastructure-as-code manner via ARM templates. You can apply the output of clone to another connected cluster, which is referred to as replication. You can also save the clone to a local directory for later use and perform some configuration changes before applying it to a cluster.
The clone operation consists of three main components: the model, which is the source instance, the target, which is the destination instance, and the template. The following diagram illustrates the clone flow. The clone command analyzes the source instance and replicates it via IaC/ARM template. The replicated definition is applied to one or more destination clusters.
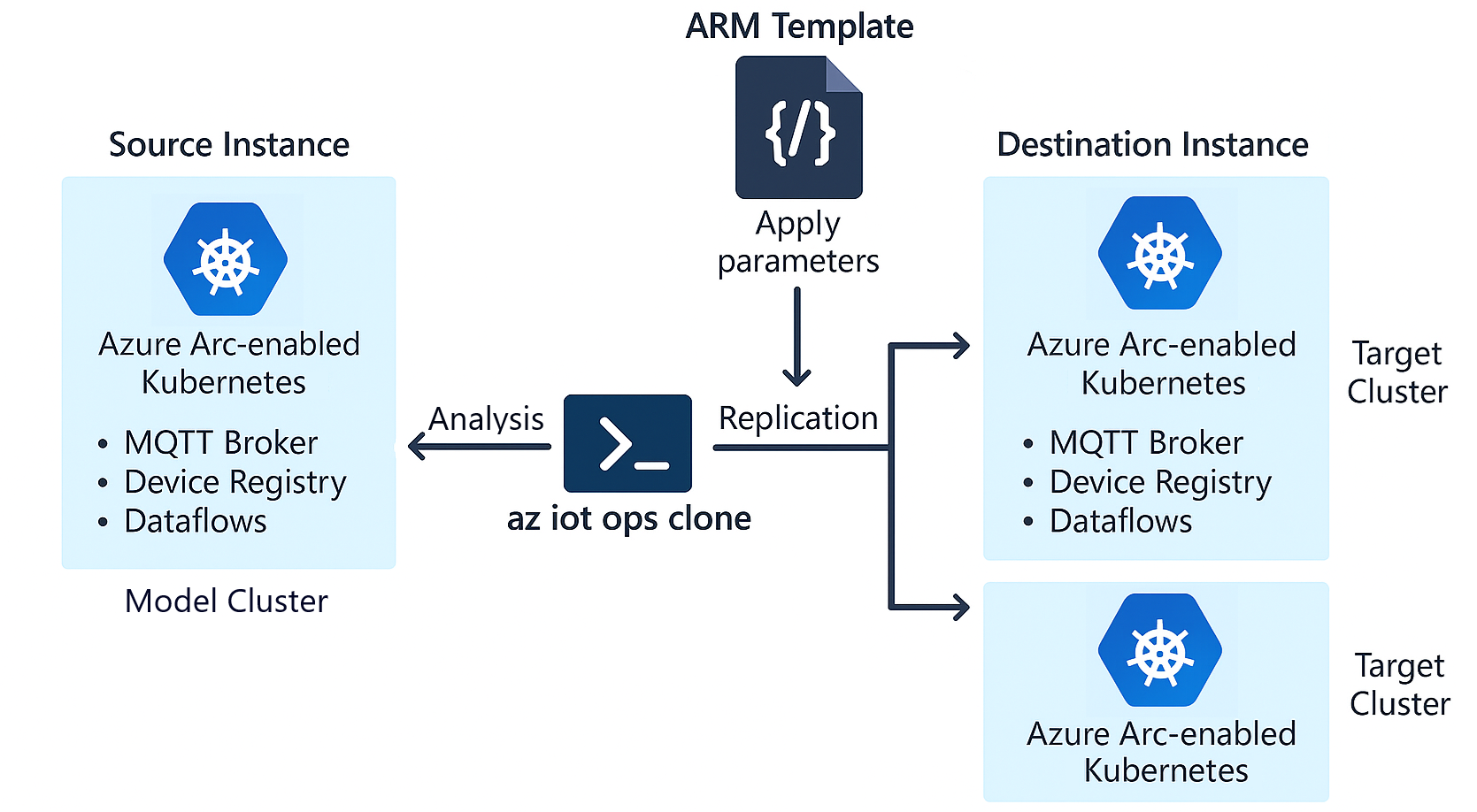
Clone model
The model is the instance you are cloning from. It is the source of truth for the clone operation. To identify the model, enter the following parameters:
--name/-n: The model instance name.--resource-group/-g: The resource group that contains the model instance.
Clone target
The target is where you want to replicate or save the clone definition. You can apply a clone to one, all, or no targets. If you don't provide any target options, the process terminates after outputting a summary of in-scope resources. To identify the target, enter one of the following parameters:
--to-cluster-id: Provide the full Azure resource ID of the target cluster where you want to replicate the cloned instance. When you use this option, the clone command deploys the version of Azure IoT Operations specified in the clone definition to the target cluster, and then applies all relevant resources to complete the deployment. Automatic federation of user-assigned managed identity (UAMI) credentials is currently supported only when cloning to a cluster target.--to-dir: Provide a local directory path to replicate the clone definition to disk, where it can be deployed with existing ARM deployment tools with or without modification. If you inspect the clone definition, you see various parameterization in play to ease some customization.
Important
When selecting a target resource group, consider using a resource group that doesn't contain an existing IoT Operations installation and is separate from the model's resource group. By default, the clone definition preserves resource names from the model instance. If the target and model share the same resource group and you change the custom location, resource name conflicts may occur.
Clone template
The clone command generates an ARM template that describes the resources to be created in the target. The template is generated based on the resources in the model instance and their configuration. Enter the following optional parameters to customize the template:
Clone template customization parameters
You can use the following optional parameters to customize the generated ARM template:
--mode: Specifies how sub-deployments are organized in the template.- When
nestedmode is used (the default), all sub-deployments are self-contained within the root deployment file. - When
linkedmode is used, asset-related sub-deployments are split out and stored as separate files, which are then linked by the root deployment. Uselinkedmode if your instance contains a large number of namespace devices, namespace assets, root assets, and asset endpoint profiles to improve scalability and manageability. You don't need to specify this parameter unless you require this separation for large deployments.
- When
--param: Allows you to override built-in default parameters, such aslocation,instanceName, oradrNamespaceId, using the formatkey=value. Use--helpto display the full list of keys.
Clone an instance
To clone an instance, use the az iot ops clone command with the appropriate parameters to specify the source instance and the target location.
Before you begin, set your default subscription to the same subscription the model instance is in. Otherwise, you need to append
--subscriptionevery time you run anaz iot ops clonecommand.az account set -s $MODEL_SUBSCRIPTION_IDTo get your cluster resource ID, run:
az resource show --name <CLUSTER_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --resource-type "Microsoft.Kubernetes/connectedClusters" --query id --output tsvTo clone an instance and replicate to a target arc-connected cluster using default options, run:
az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-cluster-id <CLUSTER_ID>To customize the replication to another cluster, use
--paramand specify the parameters you want to change in the formatkey=value. For example, to change the location of the cloned instance, run:az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-cluster-id <CLUSTER_ID> --param location=eastusTo clone an instance to a local disk, use the
--to-dirparameter to specify the directory where you want to save the clone definition. This option produces a standard ARM template to be manipulated or deployed at your discretion.az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-dir <DIRECTORY>Tip
To clone an instance to the current directory, run
--to-dir .To clone and replicate an instance to a target cluster and save to file in the same operation, run:
az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-cluster-id <CLUSTER_ID> --to-dir <DIRECTORY>To clone an instance to a cluster, but splitting and serially applying asset related sub-deployments, use
--mode linked.The parameter offers the highest degree of scale when the model instance contains a significant number of asset related resources.az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-cluster-id <CLUSTER_ID> --mode linkedTo clone an instance to disk in linked mode, where each linked asset and/or asset endpoint profile template can be deployed separately from the root template.
az iot ops clone --name <INSTANCE_NAME> --resource-group <RESOURCE_GROUP> --to-dir . --mode linked
Considerations and limitations
- Automatic identity federation is currently supported with
--to-cluster-idoption only. - Resource sync rules aren't captured.
- While the required role assignment between the IoT Operations system managed identity and target schema registry is handled by clone, any other system managed identity role assignments aren't covered.
- Clone is a cloud-side operation. The cluster isn't directly interacted with. Cluster secrets are synced from cloud via secure settings, which encompass secret provider classes and secret sync cloud resources. If the model cluster has user created elements such as configmaps that are referenced in the model IoT Operations solution, those elements need to be re-applied against the target cluster.