Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
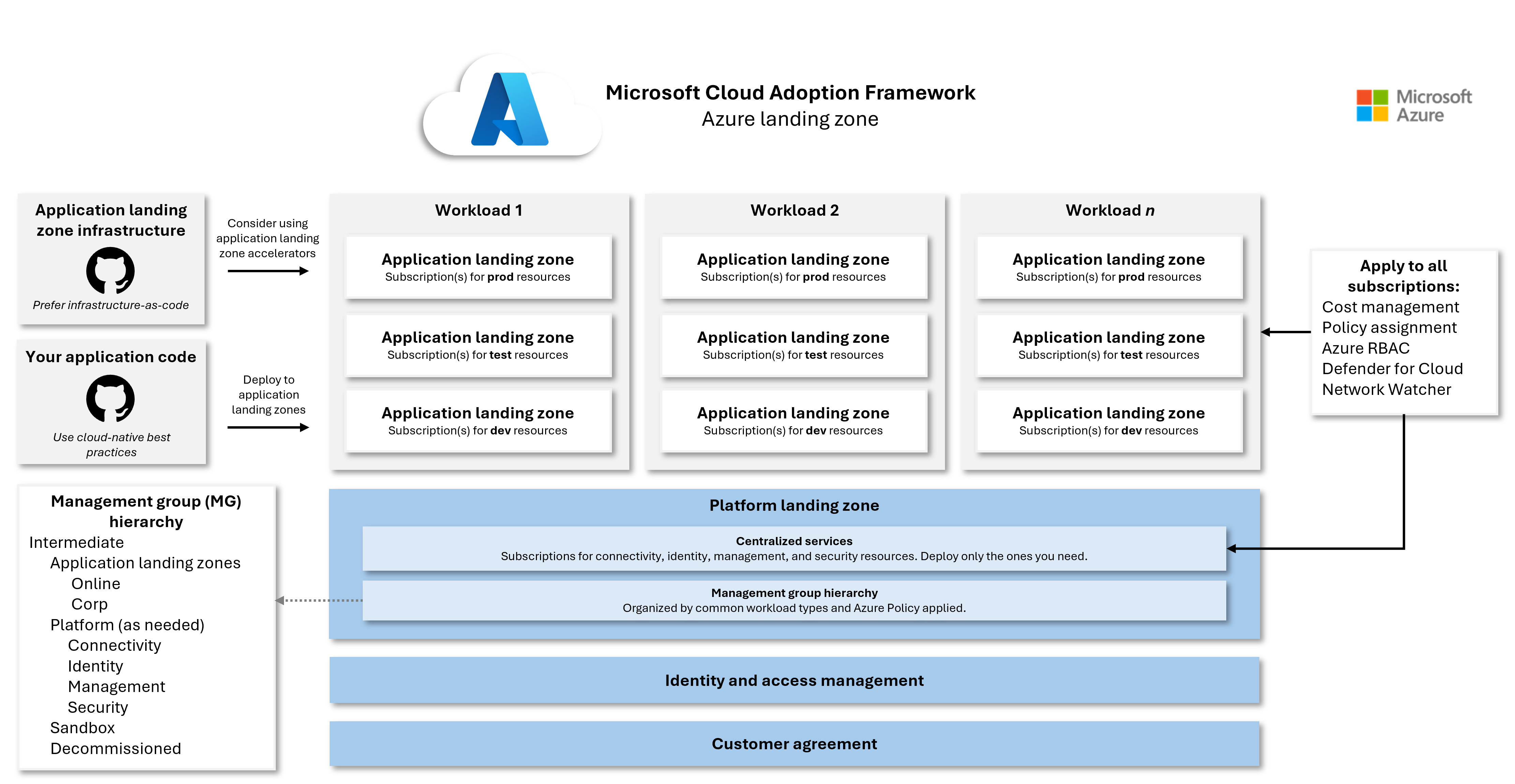
Before you can deploy workloads in Azure, it's important to prepare the underlying environment that supports them. This foundational setup is known as an Azure landing zone is the recommended starting point to build your Azure environment. An Azure landing zone is a structured approach that helps you build a scalable, secure, and governed cloud environment from the start.
An Azure landing zone helps you address key considerations such as identity and access management, customer agreements, and the configuration of core platform services. It provides a consistent framework for organizing both shared infrastructure and application-specific resources. At the heart of this model are two types of landing zones:
Platform landing zone
The platform landing zone serves as the backbone of your Azure environment. It establishes governance and central services that apply across your organization. Its functionality includes a management group hierarchy with Azure Policy enforcement across subscriptions. There are also dedicated subscriptions for connectivity, identity, management, and security shared services.
Depending on your organization's size and cloud maturity, you might choose to implement all, some, or none of these centralized services. For smaller or cloud-native teams, a lightweight approach might be sufficient.
Application landing zone
An application landing zone is for workload resources. A workload should have an application landing zone for each environment (development, testing, or production). Each application landing zone consists of one or more subscriptions to accommodate scaling and service limits. They are nested under appropriate management groups, such as "Online" or "Corp," to inherit Azure Policy definitions from the parent management group(s). This structure ensures that workloads are deployed in a controlled and consistent manner, while still allowing flexibility for individual workload needs.
Configurations that apply across all subscriptions
Whether a subscription belongs to the platform or an application landing zone, certain configurations should be enabled universally. These configurations include: Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Cost Management, Network Watcher, and Microsoft Defender for Cloud. These services help maintain visibility, security, and operational control across your entire Azure environment.
Azure landing zone journey
As you work through the Ready guide, think of your progress as a journey toward creating a fully operational Azure landing zone. This journey unfolds in four major phases, each with supporting processes and tools:
1. Bootstrap your environment
Whether you’re starting fresh (Greenfield) or modernizing an existing setup (Brownfield), the first step is to create the subscriptions that will host your resources. Implementing a new Azure landing zone environment based on best practices usually requires multiple subscriptions. You can create these subscriptions manually, programmatically, or by using automated vending modules:
2. Deploy platform landing zone components
Next, accelerate the deployment of your platform resources based on the Azure landing zone conceptual architecture. These components establish governance and shared services such as management group hierarchy, policy enforcement, connectivity, security, and monitoring. Deployment options include the Azure portal, Bicep, and Terraform:
3. Subscription vending process
Once your platform is in place, you’ll need to create individual application landing zones within your Azure tenant. A subscription vending solution is recommended to automate this process. Vending helps deploy subscriptions along with core resources such as networking. Both Bicep and Terraform modules are available:
4. Deploy application landing zone components
Finally, deploy the components that support your workloads. Multiple application landing zone accelerators are available to provide reference architectures and implementation guidance for scenarios such as Azure Virtual Desktop, SAP, and Azure Kubernetes. These accelerators help prepare application landing zones in an Azure landing. See the CAF cloud adoption scenarios.