Hello!
I'am trying to configure my Arduino project in Visual Studio 2022 IDE.
Subject: IntelliSense shows incorrect data model for AVR (2-byte int and pointer).
Environment
- Visual Studio 2022 (version 17.14.16)
- CMake with custom AVR toolchain
- Arduino Mega 2560
- Windows 10 x64
Project structure
│ CMakeLists.txt
│ CMakePresets.json
│
├───cmake
│ │ arduino_core.cmake
│ │ arduino_hex.cmake
│ │ arduino_upload.cmake
│ │ lto.cmake
│ │
│ └───toolchain
│ avr.toolchain.cmake
│ mega.toolchain.cmake
│
└───src
Files
CMakeLists.txt
mega.toolchain.cmake:
set(ARDUINO_BOARD "AVR_MEGA2560")
set(ARDUINO_MCU "atmega2560")
set(ARDUINO_F_CPU "16000000L")
set(ARDUINO_VARIANT "mega")
set(ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_PROTOCOL "wiring")
set(ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_SPEED "115200")
set(ARDUINO_USB Off)
set(ARDUINO_ADDITIONAL_COMPILER_DEFINITIONS "__AVR_ATmega2560__")
include(${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/avr.toolchain.cmake)
avr.toolchain.cmake:
# Enter CMake cross-compilation mode
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Generic)
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR avr)
# User settings with sensible defaults
if(CMAKE_HOST_WIN32)
set(ARDUINO_PATH_DEFAULT "$ENV{LOCALAPPDATA}/Arduino15/packages/arduino")
else()
set(ARDUINO_PATH_DEFAULT "$ENV{HOME}/.arduino15/packages/arduino")
endif()
set(ARDUINO_PATH "${ARDUINO_PATH_DEFAULT}" CACHE PATH
"Path of the Arduino packages folder, e.g. ~/.arduino15/packages/arduino.")
set(ARDUINO_CORE_VERSION "1.8.6" CACHE STRING
"Version of arduino/ArduinoCore-AVR")
set(AVR_GCC_VERSION "7.3.0-atmel3.6.1-arduino7" CACHE STRING
"Full version string of the GCC release shipped with the Arduino core.")
set(AVRDUDE_VERSION "6.3.0-arduino17" CACHE STRING
"Full version string of the avrdude release shipped with the Arduino core.")
set(ARDUINO_VERSION "10815" CACHE STRING
"Arduino IDE version (used for the macro with the same name)")
# Derived paths
set(ARDUINO_AVR_PATH ${ARDUINO_PATH}/hardware/avr/${ARDUINO_CORE_VERSION})
set(ARDUINO_CORE_PATH ${ARDUINO_AVR_PATH}/cores/arduino)
set(ARDUINO_TOOLS_PATH ${ARDUINO_PATH}/tools/avr-gcc/${AVR_GCC_VERSION}/bin)
set(ARDUINO_TOOLS_AVR_PATH ${ARDUINO_PATH}/tools/avr-gcc/${AVR_GCC_VERSION}/avr)
set(ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_PATH ${ARDUINO_PATH}/tools/avrdude/${AVRDUDE_VERSION})
set(ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_CONF ${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_PATH}/etc/avrdude.conf)
# Toolchain paths
find_program(CMAKE_C_COMPILER avr-gcc PATHS "${ARDUINO_TOOLS_PATH}" NO_DEFAULT_PATH
DOC "Path to avr-gcc")
find_program(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER avr-g++ PATHS "${ARDUINO_TOOLS_PATH}" NO_DEFAULT_PATH
DOC "Path to avr-g++")
find_program(CMAKE_OBJCOPY avr-objcopy PATHS "${ARDUINO_TOOLS_PATH}" NO_DEFAULT_PATH
DOC "Path to avr-objcopy")
find_program(CMAKE_SIZE avr-size PATHS "${ARDUINO_TOOLS_PATH}" NO_DEFAULT_PATH
DOC "Path to avr-size")
find_program(ARDUINO_AVRDUDE avrdude PATHS "${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_PATH}/bin" NO_DEFAULT_PATH
DOC "Path to avrdude")
# Only look libraries etc. in the sysroot, but never look there for programs
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PROGRAM NEVER)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_LIBRARY ONLY)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_INCLUDE ONLY)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PACKAGE ONLY)
arduino_core.cmake:
if(NOT ARDUINO_PATH)
message(FATAL_ERROR "Arduino-specific variables are not set. \
Did you select the right toolchain file?")
endif()
# Basic compilation flags
add_library(ArduinoFlags INTERFACE)
target_compile_options(ArduinoFlags INTERFACE
"-fno-exceptions"
"-ffunction-sections"
"-fdata-sections"
"$<$<COMPILE_LANGUAGE:CXX>:-fno-threadsafe-statics>"
"-mmcu=${ARDUINO_MCU}"
)
target_compile_definitions(ArduinoFlags INTERFACE
"F_CPU=${ARDUINO_F_CPU}"
"ARDUINO=${ARDUINO_VERSION}"
"ARDUINO_${ARDUINO_BOARD}"
"ARDUINO_ARCH_AVR"
"${ARDUINO_ADDITIONAL_COMPILER_DEFINITIONS}"
)
target_link_options(ArduinoFlags INTERFACE
"-mmcu=${ARDUINO_MCU}"
"-fuse-linker-plugin"
"LINKER:--gc-sections"
)
target_compile_features(ArduinoFlags INTERFACE cxx_std_11 c_std_11)
# Arduino Core
add_library(ArduinoCore STATIC
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Arduino.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Client.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial_private.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/IPAddress.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/PluggableUSB.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Print.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Printable.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Server.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Stream.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/USBAPI.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/USBCore.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/USBDesc.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Udp.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/WCharacter.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/WString.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/binary.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/new.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_private.h
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/abi.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/CDC.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial0.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial1.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial2.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial3.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/HardwareSerial.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/IPAddress.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/main.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/new.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/PluggableUSB.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Print.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Stream.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/Tone.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/USBCore.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/WMath.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/WString.cpp
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/hooks.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/WInterrupts.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_analog.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_digital.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_pulse.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_shift.c
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}/wiring_pulse.S
)
target_link_libraries(ArduinoCore PUBLIC ArduinoFlags)
target_compile_features(ArduinoCore PUBLIC cxx_std_11 c_std_11)
target_include_directories(ArduinoCore PUBLIC
${ARDUINO_CORE_PATH}
${ARDUINO_AVR_PATH}/variants/${ARDUINO_VARIANT}
${ARDUINO_TOOLS_AVR_PATH}/include
)
if(ARDUINO_USB)
target_compile_definitions(ArduinoCore PUBLIC
USB_VID=${ARDUINO_USB_VID}
USB_PID=${ARDUINO_USB_PID}
USB_MANUFACTURER=\"Unknown\"
USB_PRODUCT=\"${ARDUINO_USB_PRODUCT}\"
)
endif()
arduino_hex.cmake:
# Transforms the target.elf file into target.eep (EEPROM) and target.hex files.
# Also prints the size of each section in target.elf.
function(arduino_avr_hex target)
set_target_properties(${target} PROPERTIES SUFFIX ".elf")
add_custom_command(TARGET ${target} POST_BUILD
COMMAND ${CMAKE_SIZE} ARGS
-A "$<TARGET_FILE:${target}>"
USES_TERMINAL)
add_custom_command(TARGET ${target} POST_BUILD
BYPRODUCTS ${target}.eep
COMMAND ${CMAKE_OBJCOPY} ARGS
-O ihex -j .eeprom
--set-section-flags=.eeprom=alloc,load
--no-change-warnings --change-section-lma
.eeprom=0
"$<TARGET_FILE:${target}>"
${target}.eep)
add_custom_command(TARGET ${target} POST_BUILD
BYPRODUCTS ${target}.hex
COMMAND ${CMAKE_OBJCOPY} ARGS
-O ihex -R .eeprom
"$<TARGET_FILE:${target}>"
${target}.hex)
endfunction()
arduino_upload.cmake:
# Creates a target upload-target that uses avrdude to upload target.hex to the
# given serial port.
function(arduino_avr_upload target port)
add_custom_target(upload-${target}
COMMAND ${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE}
-C${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_CONF}
-p${ARDUINO_MCU}
-c${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_PROTOCOL}
-P${port}
-b${ARDUINO_AVRDUDE_SPEED}
-D
"-Uflash:w:$<TARGET_FILE_BASE_NAME:${target}>.hex:i"
USES_TERMINAL)
add_dependencies(upload-${target} ${target})
endfunction()
lto.cmake:
# Enables interprocedural optimization (link-time optimization) globally if
# available.
include(CheckIPOSupported)
check_ipo_supported(RESULT ipo_supported OUTPUT ipo_error)
if(ipo_supported)
set(CMAKE_INTERPROCEDURAL_OPTIMIZATION TRUE)
else()
message(STATUS "IPO / LTO not supported: ${ipo_error}")
endif()
CMakePresets.json:
{
"version": 3,
"configurePresets": [
{
"name": "arduino-minsizerel",
"displayName": "Arduino MinSizeRel",
"description": "Arduino Project",
"generator": "Ninja",
"binaryDir": "${sourceDir}/out/build/${presetName}",
"installDir": "${sourceDir}/out/install/${presetName}",
"toolchainFile": "${sourceDir}/cmake/toolchain/mega.toolchain.cmake",
"cacheVariables": {
"CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE": "MinSizeRel",
"CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD": "14",
"CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED": true,
"CMAKE_C_STANDARD": "11",
"CMAKE_C_STANDARD_REQUIRED": true
},
"vendor": {
"microsoft.com/VisualStudioSettings/CMake/1.0": {
"enableClangTidyCodeAnalysis": false,
"enableMicrosoftCodeAnalysis": false,
"intelliSenseMode": "linux-gcc-x64"
}
}
}
]
}
test.cpp:
#include <Arduino.h>
void setup()
{
int i = 0;
void* pointer = 0;
}
void loop()
{
}
Problem
The project builds successfully, but IntelliSense behaves incorrectly.
- On the AVR platform, both int and pointers are 2 bytes, but IntelliSense treats them as if it were compiling for x86 (4 bytes).
- Sometimes IntelliSense also shows an “E1504: internal error” message.
See screenshots below:
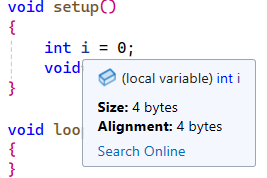
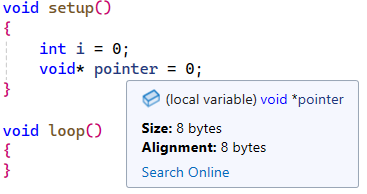
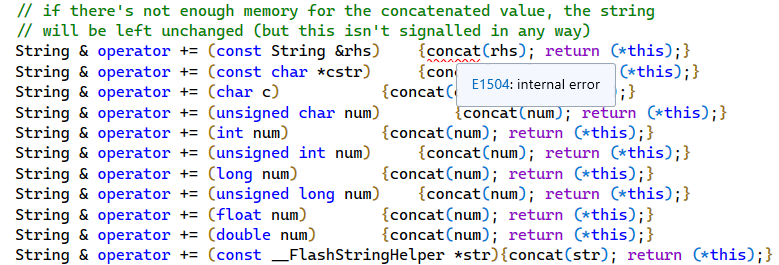
If I remove either C or CXX from this line project(TestProgram LANGUAGES ASM C CXX) then IntelliSense works correctly:
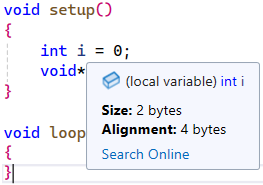
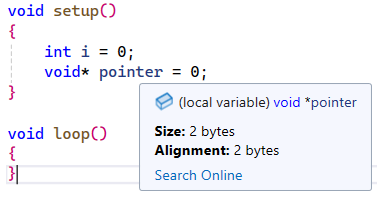
However, in that case, the project fails to build build.log. The “E1504: internal error” still remains.
Expected Behavior
IntelliSense should respect the target platform defined by the CMake toolchain (AVR), so that data type sizes match the actual build target.
Actual Behavior
IntelliSense uses x86 data model and sometimes reports E1504: internal error, even though the project builds successfully for AVR.
Question
How can I make IntelliSense correctly detect and use AVR data model settings (e.g., 2-byte int/pointer) when using a CMake-based Arduino project?