Rakesh Kumar - Thanks for the question and using MS Q&A platform.
When exporting a Delta table from ADLS Gen2 to a CSV file using DataFrame.coalesce(1) or DataFrame.repartition(1) in Azure Databricks, Spark automatically creates additional files such as:
-
_SUCCESS – indicates the job completed successfully.
-
_committed_* / _started_* – used internally by Spark’s commit protocol to ensure atomic and fault-tolerant writes.
Note: These files cannot be suppressed or disabled via Spark configuration—they are part of the standard write behavior. The recommended solution is to post-process the output using dbutils.fs to isolate and move the actual CSV file.
To avoid exposing these extra files to downstream systems or users, the best practice is to:
- Write the CSV to a temporary directory
- Identify the actual CSV file (e.g.,
part-00000-*.csv)
- Use
dbutils.fs.cp() or dbutils.fs.mv() to move or copy only the CSV file to the final destination
- Optionally delete the temporary directory
Here is the sample code:
# Step 1: Write to a temporary location
df.coalesce(1).write.mode("overwrite").option("header", "true").csv("/mnt/tmp/export_csv")
# Step 2: Identify the CSV file
files = dbutils.fs.ls("/mnt/tmp/export_csv")
csv_file = [f.path for f in files if f.path.endswith(".csv")][0]
# Step 3: Move the CSV file to final location
dbutils.fs.mv(csv_file, "/mnt/final/export/data.csv")
# Step 4: Clean up temporary directory
dbutils.fs.rm("/mnt/tmp/export_csv", recurse=True)
Here is an example: (aka: Demo for you 😊)
This will indeed write:
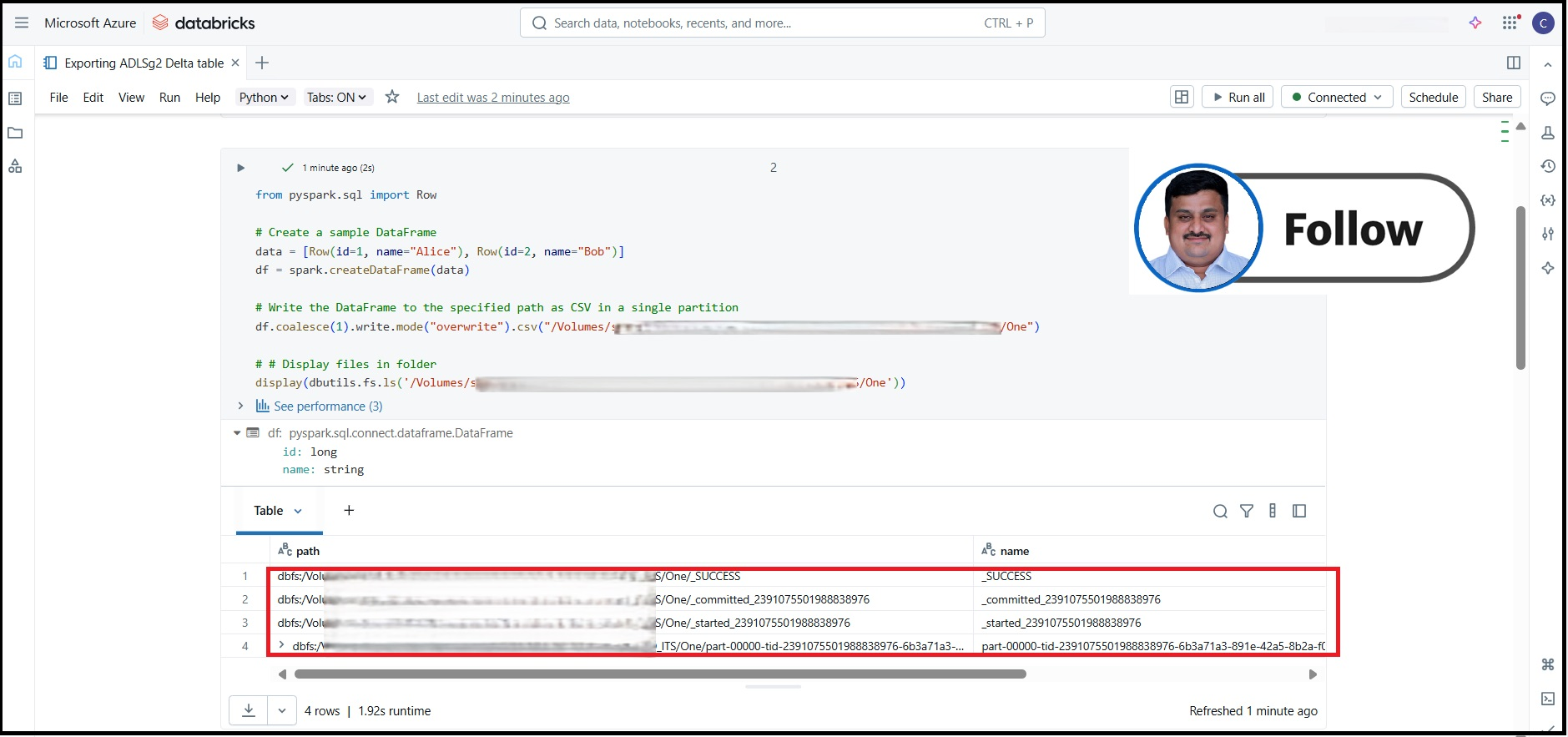
- One CSV file (e.g.,
part-00000-*.csv)
- Along with
_SUCCESS and possibly _committed_* files
from pyspark.sql import Row
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = [Row(id=1, name="Alice"), Row(id=2, name="Bob")]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data)
# Write the DataFrame to the specified path as CSV in a single partition
df.coalesce(1).write.mode("overwrite").csv("/Volumes/XXXXX/XXXX/XXX/XXX/One")
✅ To isolate the CSV file and remove the extras, here’s the complimentary PySpark code:
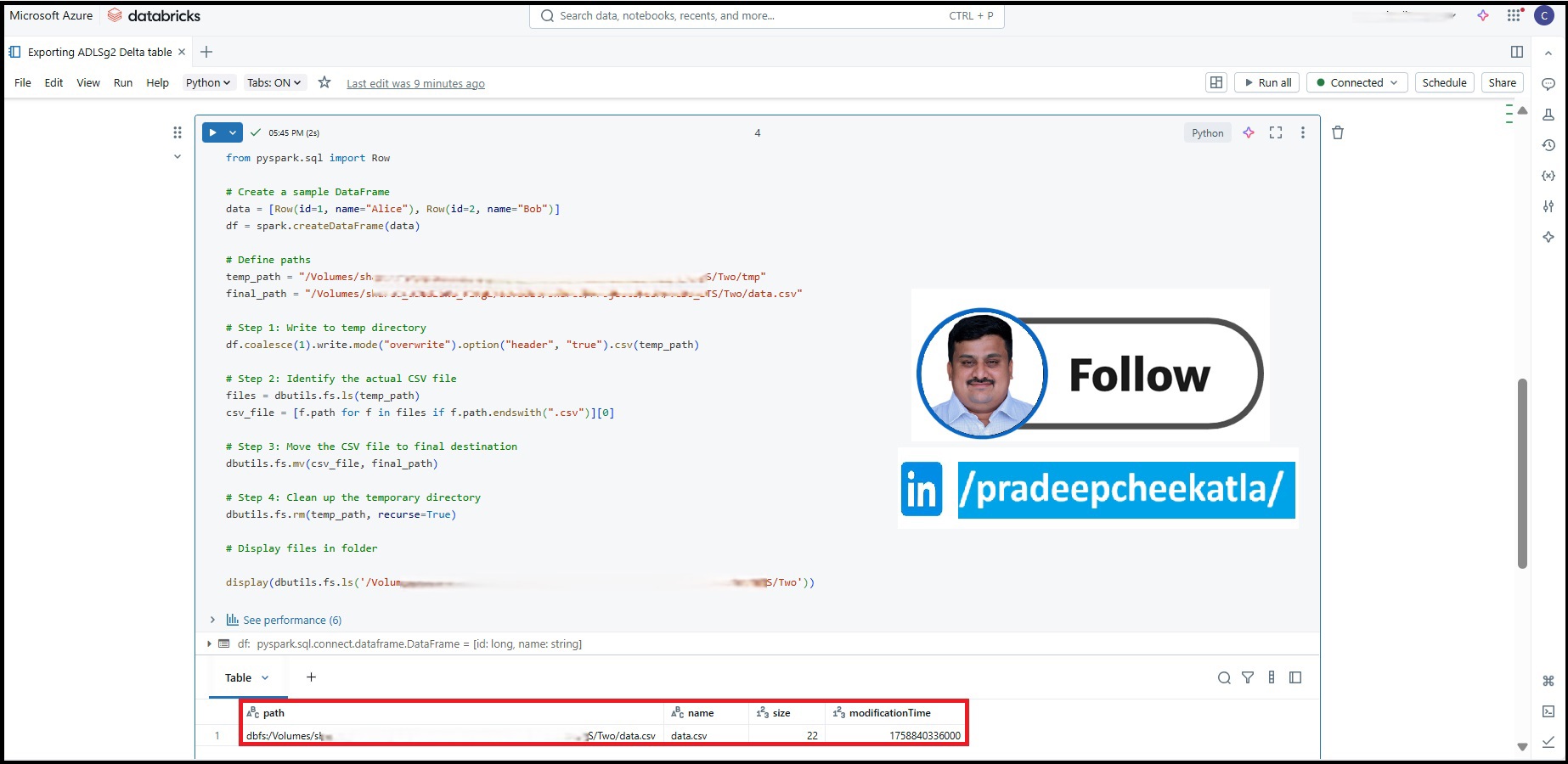
from pyspark.sql import Row
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = [Row(id=1, name="Alice"), Row(id=2, name="Bob")]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data)
# Define paths
temp_path = "/Volumes/XXXXX/XXXX/XXX/XXX/Two/tmp"
final_path = "/Volumes/XXXXX/XXXX/XXX/XXX/Two/data.csv"
# Step 1: Write to temp directory
df.coalesce(1).write.mode("overwrite").option("header", "true").csv(temp_path)
# Step 2: Identify the actual CSV file
files = dbutils.fs.ls(temp_path)
csv_file = [f.path for f in files if f.path.endswith(".csv")][0]
# Step 3: Move the CSV file to final destination
dbutils.fs.mv(csv_file, final_path)
# Step 4: Clean up the temporary directory
dbutils.fs.rm(temp_path, recurse=True)
# Display files in folder
display(dbutils.fs.ls('/Volumes/XXXXX/XXXX/XXX/XXX/Two'))
Hope this information is helpful. Please feel free to reach out if you have any further questions or need additional assistance. If this response addresses your query, kindly consider clicking 'Upvote' and selecting 'Accept Answer'—this may help other community members who come across this thread.
𝘛𝘰 𝘴𝘵𝘢𝘺 𝘪𝘯𝘧𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘦𝘥 𝘢𝘣𝘰𝘶𝘵 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘭𝘢𝘵𝘦𝘴𝘵 𝘶𝘱𝘥𝘢𝘵𝘦𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘪𝘯𝘴𝘪𝘨𝘩𝘵𝘴 𝘰𝘯 𝘈𝘻𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘋𝘢𝘵𝘢𝘣𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘬𝘴, 𝘥𝘢𝘵𝘢 𝘦𝘯𝘨𝘪𝘯𝘦𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘯𝘨, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 Data & AI 𝘪𝘯𝘯𝘰𝘷𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴, 𝘧𝘰𝘭𝘭𝘰𝘸 𝘮𝘦 𝘰𝘯 𝘓𝘪𝘯𝘬𝘦𝘥𝘐𝘯.
